-
- Define the following terms. 3mk
- Indicator
- Neutralization
- Alkali
- The table below shows the pH values of some solutions. Study it and answer the questions that follow.
Which solution is likely;solution PH M 9 R 7 K 3 D 13 G 6 - To produce bubbles/ effervescence with sodium carbonate solution. 1mk
- To be sodium chloride solutions 1mk
- Choose two solutions that can react to form a salt and water only. 1mk
- Which color would solution M show when added methyl orange indicator. (1mk)
- Give a reason why the flower extract indicator is not preferred. 1mk
- What is the advantage of the universal indicator over the other indicators. 1mk
- Define the following terms. 3mk
-
- Indicate whether each of the following is a mixture or a compound. (6mk)
- Black ink-----------------
- Sodium chloride------
- Tea----------------------
- Crude oil--------------
- sea water-------------
- Air--------------------
- State any four differences between a permanent and a temporary change. (4mk.)
Permanent Temporary - A blue compound was heated in the lab in a boiling tube, droplets of a colorless liquid were seen on the cooler parts of the tube and the solid turned to white.
- Name the type of change undergone by the substance above (1mk)
- Identify; _ the white solid (2mks)
_the colorless liquid
- Indicate whether each of the following is a mixture or a compound. (6mk)
-
- Name the following apparatus (2mks)
- Draw the shapes of the following lab apparatus; (4mks)
- Deflagrating spoon
- Pipette
- Teat pipette
- Filter funnel
- State the function of the following lab apparatus; (2mks)
- Dropping funnel
- Desiccator
- List two apparatus used to measure accurate but specific volumes of liquid. (2mks)
- Name the following apparatus (2mks)
-
- What is a flame? (1mk)
- List any four differences between a luminous and a non-luminous flame. (4mks)
- Explain why the luminous flame of the Bunsen burner produces a lot of light (1mk)
- State the functions of the following parts of the Bunsen burner (2mks)
- The collar---
- The base ------
- Which type of flame is most preferred for heating and why? Give two reasons it’s preferred. (3mk)
-
- Choose the most suitable method to get the first substance from the following mixtures; (3MK)
- Water and salt----------------
- Sand and water ---------------------
- Oil and milk-------------------
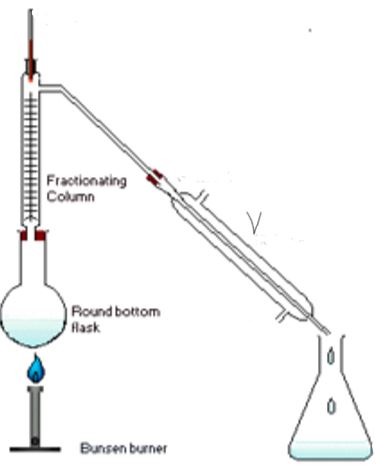
- A student was given a mixture of solution x and solution y which were miscible with boiling points of 84°C and 75°C. The student’s setup the set of apparatus as shown below to separate the two liquids. Study it carefully and answer the questions that follow.
- Name the method above that the student used (1mk)
- What name is given to apparatus V (1mk)
- Indicate on the diagram the direction of flow of water (1mk)
- State the function of each of the following; (2mks)
- Fractionating column-
- Thermometer –
- Which of the two liquids was collected as the first distillate and why? (2mk)
- Choose the most suitable method to get the first substance from the following mixtures; (3MK)
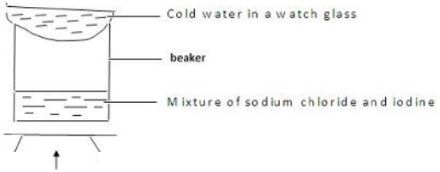
- Draw a well labelled diagram to show how a mixture of sodium chloride and iodine can be separated to acquire a pure sample of each. (3MK)
- DESCRIBE how an oil sample can be extracted from ground nuts. (3mks)
-
- FILL in the table below. (8MK)
ELEMENT SYMBOL Calcium Cu K Sodium F Helium Silver Mg - Identify the elements present in each of the following compounds;
- Lead chloride (1mk)
- Zinc carbonate (1 ½ Mk)
- Aluminum sulphate (1 ½ Mk)
- FILL in the table below. (8MK)
- STATE and EXPLAIN the changes in mass that occurs when each of the following substances are strongly heated in a boiling tube in the lab. (2mk)
- Copper Nitrate
- Zinc oxide
- Define the following terms; (6mks0
- Chemistry
- Drug
- Drug abuse
- Molecule
- Atom
- Element
- Fill in the gaps in the chemical equations below.
- Zinc + hydrochloric acid → ------------------------------------- + Hydrogen (1mk)
- Copper ii oxide + Sulphuric (vi) acid → -------------------------- + ------------------- (2mk)
MARKING SCHEME
-
- Define the following terms. 3mk
- Indicator
- A substance that has a definite colour in an acid and a definite colour in a base
- Neutralization
- A reaction btn an acid and a base to form a salt and water only
- Alkali
- A soluble base
- Indicator
- The table below shows the pH values of some solutions. Study it and answer the questions that follow.
solution PH M 9 R 7 K 3 D 13 G 6
Which solution is likely;- To produce bubbles/ effervescence with sodium carbonate solution. 1mk
- K/G
- To be sodium chloride solutions 1mk
- R
- To produce bubbles/ effervescence with sodium carbonate solution. 1mk
- Choose two solutions that can react to form a salt and water only. 1mk
- M&K, or M&G,or D&K,or D&G
- Which color would solution M show when added methyl orange indicator. (1mk)
- yellow
- Define the following terms. 3mk
-
- Indicate whether each of the following is a mixture or a compound. (3mk)
- Black ink----------------- mixture
- Sodium chloride------ compound
- Tea----------------------compound
- crude oil-------------- mixture
- sea water------------- mixture
- Air-------------------- mixture
- State any four differences between a permanent and a temporary change. (4mk.)
Permanent Temporary irreversible
new substance formed
change in mass
heat is evolved or absorbed during its formationreversible
no new substance formed
change in mass is negligible
no heat evolved or absorbed during it's formation - A blue compound was heated in the lab in a boiling tube, droplets of a colorless liquid were seen on the cooler parts of the tube and the solid turned to white.
- Name the type of change undergone by the substance above (1mk)
- Temporary chemical change
- Identify; _ the white solid – anhydrous copper ii sulphate (2mk)
_the colorless liquid---- water
- Name the type of change undergone by the substance above (1mk)
- Indicate whether each of the following is a mixture or a compound. (3mk)
-
- Name the following apparatus (2mks)
conical flask round bottomed flask - Draw the shapes of the following lab apparatus; (4mks)
- Deflagrating spoon
- Pipette
- Teat pipette
- Filter funnel
- Deflagrating spoon
- State the function of the following lab apparatus; (2mks)
- Dropping funnel
- To deliver controlled amount of liquids into reaction vessels
- Desiccator
- To keep substances dry/ free of moisture
- Dropping funnel
- List two apparatus used to measure specific volume of liquids accurately (2mks)
- Pipette and volumetric flask
- Name the following apparatus (2mks)
-
- What is a flame? (1MK)
- A mass of burning gases
- List any four differences between a luminous and a non-luminous flame.(4mks)
luminous non luminous long and weavy short and steady yellow blue four zones Three zones less hot fairly hot sooty non sooty produces a lot of light produces less light - Explain why the luminous flame of the Bunsen burner produces a lot of light (1mk)
- The unburnt carbon particles when strongly heated glow white hot
- State the functions of the following parts of the Bunsen burner (2mks)
- The collar--- regulates the amount of air entering the chimney
- The base ---- supports the BB
- Which type of flame is most preferred for heating and why? Give two reasons it’s preferred. (3mk)
- non-luminous flame
- produces more heat 1mk does not produce soot 1mk
- What is a flame? (1MK)
-
- Choose the most suitable method to get the first substance from the following mixtures; (3MK)
- Water and salt---------------- simple distillation
- Sand and water --------------------- filtration
- Oil and milk-------------------use of a separating funnel
- A student was given a mixture of solution x and solution y which were miscible with boiling points of 84°C and 75°C .the students setup the set of apparatus as shown below to separate the two liquids. Study it carefully and answer the questions that follow
- Name the method above that the student used (1mk)
- fractional distillation
- What name is given to apparatus V (1mk)
- liebig condenser
- Indicate on the diagram the direction of flow of water (1mk)
- on the diagram
- State the function of each of the following; (2mks)
- Fractionating column – to enable liquid with a higher bp to condense and flow back to the flask
- Thermometer – to record the bp values of the fraction distilling out.
- Which of the two liquids was collected as the first distillate and why? (2mk)
- liquid Y 1mk because it has a lower bp and will boil earlier 1mk
- Name the method above that the student used (1mk)
- Choose the most suitable method to get the first substance from the following mixtures; (3MK)
- Draw a well labelled diagram to show how a mixture of sodium chloride and iodine can be separated to acquire a pure sample of each. (3MK)
HEAT - DESCRIBE how an oil sample can be extracted from ground nuts. (3mks)
- Place the nuts in a mortar ,Crush them using a pestle 1mk as you crush add a little propanone at a time , ½ mk decant, ½ mk place the solution in the sun for propanone to evaporate 1mk
-
- FILL in the table below. (8MK)
ELEMENT SYMBOL Calcium Ca Copper Cu Potassium K Sodium Na Fluorine F Helium He Silver Ag Magnesium Mg - Identify the elements present in each of the following compounds;
- Lead chloride (1mk)
Lead ½ chlorine ½ - Zinc carbonate (1 ½ Mk)
zinc ½ , carborn ½ , oxygen ½ - Aluminium sulphate (1 ½ Mk)
aluminium ½ , sulphur ½ , oxygen ½
- Lead chloride (1mk)
- FILL in the table below. (8MK)
- STATE and EXPLAIN the changes in mass that occurs when each of the following substances are strongly heated in a boiling tube in the lab. (2mk)
- Copper Nitrate
- the mass decreases, the gas released escaped to the air
- Zinc oxide
- the mass,does not change, only the colour changes
- Copper Nitrate
- Define the following terms; (6mks)
- Chemistry
- the study of the structure, properties and composition of matter and the changes that matter undergoes.
- Drug
- a chemical substance which when taken alters the normal body functions
- Drug abuse
- use of a drug for a purpose not intended for.
- Molecule
- two or more atoms connected by chemical bonds, which form the smallest unit of a substance that retains the composition and properties of that substance.
- Atom
- the smallest particle of an element that can take part in a chemical change
- Element
- a pure substance that can not be broken into simpler substances by any chemical means
- Chemistry
- Fill in the gaps in the chemical equations below.
- Zinc + hydrochloric acid → Zinc Chloride + Hydrogen (1mk)
- Copper ii oxide + Sulphuric (vi) acid → Water + Copper (ii) Sulphate (2mk)
Join our whatsapp group for latest updates
Tap Here to Download for 50/-
Get on WhatsApp for 50/-
Download Chemistry Questions and Answers - Form 1 Term 3 Opener Exams 2023.
Tap Here to Download for 50/-
Get on WhatsApp for 50/-
Why download?
- ✔ To read offline at any time.
- ✔ To Print at your convenience
- ✔ Share Easily with Friends / Students