Instructions to Candidates
- This paper consists of two sections A and B.
- Answer all the questions in Sections A in the spaces provided.
- You should check the question paper to ascertain that all the pages are printed as indicated and that no questions are missing.
SECTION A
Answer all the questions in Sections A in the spaces provided.
- Name the three major branches of biology. (3mks)
- Explain why the following processes are important during the preparation of temporary slides:-
- Staining (1mk)
- Use of a sharp cutting blade (1mk
- Distinguish between the following terms :-
- Magnification and resolution of a microscope (2mks)
- Mounting and staining of a specimen (2mks)
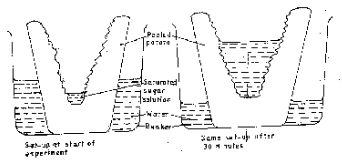
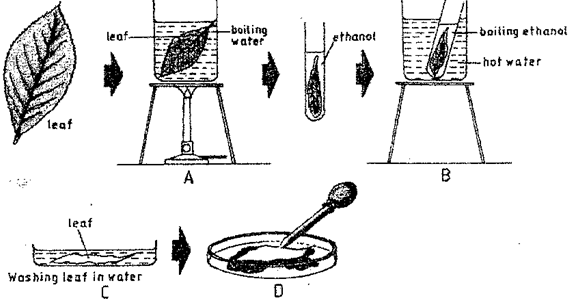
- The diagrams below show an experiment set up to investigate a certain process in a plant tissue.
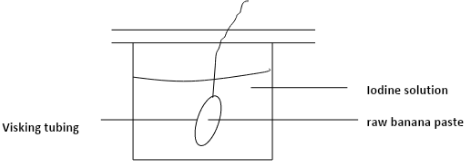
Explain the results obtained after 30 min. (3mks) - A student mashed a piece of raw banana and made it into paste by adding water, placed the paste in a visking tubing and suspended it in a beaker containing iodine solution as shown below. The set- up was left for 40 minutes.
- State the physiological process under investigation. (1 mark)
- Account for the result obtained in the table. (2 marks)
- Arrange the following from the largest to the smallest:
Tissue,cell,organism,organelle,organ system,organ, ( 1mk) - State two factors that affect enzymatic activities (2 marks)
- Name the sites where light and dark reactions of photosynthesis take place. ( 2 mks)
- The diagram represents part of the human digestive system.
- Name the organs labeled L and M. (2mks)
-
- Name the juice secreted by K. (1mk)
- State the function of the juice named in (b) (i) above (3mks)
- Name one enzyme secreted by M (1mks)
-
- Name two salivary glands found in human mouth (2mks)
- state two functions of saliva (2mks)
-
- State two ways in which the guard cells differ from other adjacent epidermal cells 2mks)
- Apart from guard cells name other two cells that carryout photosynthesis in a leaf.(2mk)
- Give the importance of leaf mosaic in the process of photosynthesis. (1mk)
- State the functions of the following cell organelles. (2 mks
- Golgi apparatus
- Ribosomes
- The table below shows the concentration of important plant nutrients
Name the process by which the above ions could have been taken up by the plants.(2mks)ion Concentration in pond water (ppm) Concentration in cell sap (ppm) Potassium 200 50 Chloride 0.5 20 - Potassium
- Chloride
- State two properties of monosaccharide. (2mks)
SECTION B
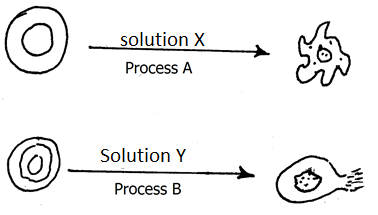
- The diagram below illustrates the behavior of red blood cells when placed into two different solutions X and Y.
- Suggest the nature of solution X and Y (2mks)
- Name the process represented by each of the letters A and B (2mks)
- Explain the observation made at the end of process B above. (3mks)
- A plant cell was placed in solution Y, and it did not burst. State the structure in the plant cell that prevented it from bursting.(1mk)
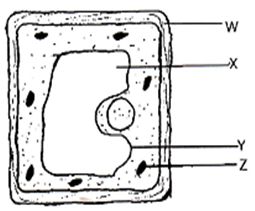
- The figure below shows a diagram of a cell as seen under a light microscope. Study it and answer the questions that follow.
- Name three structures that show that it is a plant cell and not a animal cell 3mks
- Name the photosynthetic pigment that is found in the structure labelled Z and state its function. 2mks
- State the name and function of the fluid found in X 2mks
- On the diagram label the structure that contains the DNA 1mk
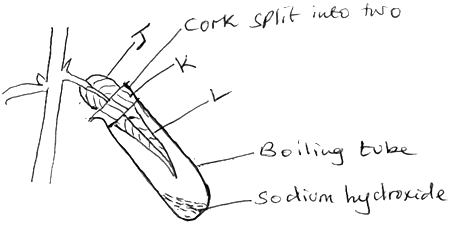
- A potted plant with healthy leaves was kept in the dark for 48 hours. One of the leaf was then partly enclosed in a wide boiling test tube containing sodium hydroxide solution. The whole set up was then kept in sunlight for six hours. The diagram is shown below.
- Suggest the aim of the experiment. (1mk)
- Why was the set up kept in the dark for 48 hours? (1mk)
- Why was the set up kept in the sunlight for six hours? (1mk)
- What is the importance of sodium hydroxide solution in the set up? (1mk)
- State the colours observed on each part when the leaf was tested for starch (3mks)
- State the form in which carbohydrates are stored in the liver. (1mk)
- The organisms below were collected from a certain habitat. Study them and answer the questions that follow.`
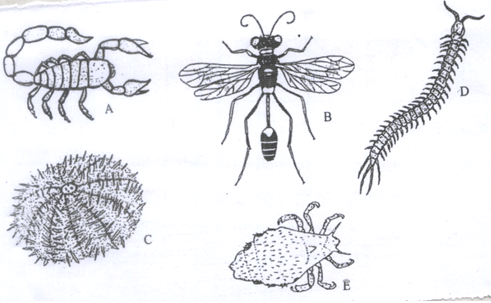
- In which kingdom do the organisms belong (1mk)
- State two external features that are found in organism B. 2mks
- State the method used to collect:
- Organism B 1mk
- Organism D 1mk
- State one precaution that should be taken when collecting organism A 1mk
- Identify two modes of locomotion in specimen B ( 2mks)
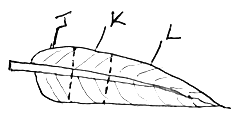
- The set-up below illustrates a procedure that was carried out in the laboratory with a leaf plucked from a green plant that had been growing in sunlight.
- What was the purpose of the above procedure? (1mark)
- Give reasons for carrying out step A,B and C in this procedure. 3marks)
- Name the reagent that was used at the step labeled D . (1mark)
- State the expected result on the leaf after adding the reagent named in (iii) above.(1mark)
- Describe the adaptations of the ileum to its function 20 marks

MARKING SCHEME
- Name the three major branches of biology.(3mks)
- Zoology
- Botany
- Biochemistry
- Explain why the following processes are important during the preparation of temporary slides :-
- Staining (1mk)
- Make cells visible;
- Use of a sharp cutting blade(1mk)
- Prevent distortion of cells;
- Staining (1mk)
- Distinguish between the following terms :-
- Magnification and resolution of a microscope (2mks)
- Magnification – Ability of a microscope to enlarge tiny objects
- Resolution – Ability of a microscope to separate between two tiny structures under magnification to appear distinct
- Magnification – Ability of a microscope to enlarge tiny objects
- Mounting and staining of a specimen (2mks)
- Mounting – The placing of prepared slide on stage of a microscope;
- Staining – Use of chemical stain on specimen for clear observation
- Magnification and resolution of a microscope (2mks)
- The diagrams below show an experiment set up to investigate a certain process in a plant tissue.
Explain the results obtained after 30 min.(3mks)- Water was hypotonic to cell sap of adjacent; and these cell absorb water through osmosis; and their cell sap became less conc. Than those of next cell; the process was repeated until water reached the sugar solution.;
Or - Sugar solution was hypotonic to cell sap of adjacent cells; they lost water by osmosis; cell sap became more conc. than those of next cell; the process was repeated until water was drawn from the beaker.
- Water was hypotonic to cell sap of adjacent; and these cell absorb water through osmosis; and their cell sap became less conc. Than those of next cell; the process was repeated until water reached the sugar solution.;
- A student mashed a piece of raw banana and made it into paste by adding water, placed the paste in a visking tubing and suspended it in a beaker containing iodine solution as shown below. The set- up was left for 40 minutes.
- State the physiological process under investigation. (1 mark)
- Diffusion
- Account for the result obtained in the table. (2 marks)
- Iodine molecules from the beaker moved into the visking tubing by diffusion since they were small in size; Color of iodine solution outside remained brown as starch molecules were too large to pass through the visking tubing. (2 marks)
- State the physiological process under investigation. (1 mark)
- Arrange the following from the largest to the smallest : Tissue,cell,organism,organelle,organ system,organ, ( 1mk)
- Organism,organ system,organ,tissue,cell,organelle;
- State two factors that affect enzymatic activities (2 marks)
- Temperature pH co- factors, co- enzymes; enzyme product concentration; substance concentration/ metabolic poison
- Name the sites where light and dark reactions of photosynthesis take place ( 2 mks)
- Light reaction - Granum/thylokoid
- Dark reaction - Stroma
- The diagram represents part of the human digestive system.
- Name the organs labeled L and M.(2mks)
- L - Duodenum
- M - Pancrease
-
- Name the juice secreted by K.(1mk)
- bile
- state the function of the juice named in (b) (i) above(3mks)
- emulsification/ emulsification of fat; neutralize acidic chime from stomach; provides alkaline media(for enzyme to work)
- Name the juice secreted by K.(1mk)
- Name one enzyme secreted by M (1mks)
- lipase; pancreatic amylase;trypsin
- Name the organs labeled L and M.(2mks)
-
- Name two salivary glands found in human mouth (2mks)
- Sublingual; submaxillary/ submandibular; parotid
- state two functions of saliva (2mks)
- Lubricating food; digestion of starch; moistens food; provides alkaline medium; soften food; dissolves food. Acc, for correct component of saliva to correct function
- Name two salivary glands found in human mouth (2mks)
-
- State two ways in which the guard cells differ from other adjacent epidermal cells (2mks)
- Guard cells have chloroplast;
- They are bean shaped;
- Apart from guard cells name other two cells that carryout photosynthesis in a leaf.(2mk)
- Spongy mesophyll cell;
- Palisade cells;
- State two ways in which the guard cells differ from other adjacent epidermal cells (2mks)
- Give the importance of leaf mosaic in the process of photosynthesis. (1mk)
- prevents some leaves from obstructing others from receiving sunlight
- State the functions of the following cell organelles.
- Golgi apparatus (2 mks
- Packaging and transport of glycoproteins
- Secretions of synthesised proteins.
- Ribosomes
- Manufacture / synthesis proteins
- Golgi apparatus (2 mks
- The table below shows the concentration of important plant nutrients
Name the process by which the above ions could have been taken up by the plants. 2mks)- Potassium- Diffusion
- Chloride-Active transport
- State two properties of monosaccharides.(2mks)
- Soluble in water;
- Sweet to taste;
- Are crystallisable;
- Are reducing sugars;
SECTION B
- The diagram below illustrates the behaviour of red blood cells when placed into two different solutions X and Y.
- Suggest the nature of solution X and Y (2mks)
- Solution X – hypertonic;
- Solution Y – hypotonic;
- Name the process represented by each of the letters A and B (2mks)
- Process A Crenation;
- Process B – Haemolysis;
- Explain the observation made at the end of process B above. (3mks)
- Red blood cell gains excess water by osmosis; from hypotonic solution; swell and burst ;
- a plant cell was placed in solution Y, and it did not burst. State the structure in the plant cell that prevented it from bursting.(1mk)
- cellulose cellwall/cell wall
- Suggest the nature of solution X and Y (2mks)
- The figure below shows a diagram of a cell as seen under a light microscope. Study it and answer the questions that follow.
- Name three structures that show that it is a plant cell and not a animal cell 3mks
- sap vacuole;cell wall;chloroplast;tonoplast
- Name photosynthetic pigment that is found in the structure labelled Z and state its function. 2mks
- Name: Chlorophyll
- Function: Traps light energy for photosynthesis
- state the name and function of the fluid found in X 2mks
- Name: Cell sap;
- Function: storage of salts and sugars
- On the diagram label the structure that contains the DNA 1mk
- Label the nucleus
- Name three structures that show that it is a plant cell and not a animal cell 3mks
- A potted plant with healthy leaves was kept in the dark for 48 hours. One of the leaf was then partly enclosed in a wide boiling tube containing sodium hydroxide solution. The whole set up was then kept in sunlight for six hours. The diagram is shown below.
- Suggest the aim of the experiment. (1mk)
- To show that carbon (IV) oxide is necessary for photosynthesis Or To show that light is necessary for photosynthesis
- Why was the set up kept in the dark for 48 hours? (1mk)
- to destarch the leaf
- Why was the set up kept in the sunlight for six hours? (1mk)
- to allow photosynthesis to take place
- What is the importance of sodium hydroxide solution in the set up? (1mk)
- to absorb carbon (IV) oxide
- State the colours observed on each part when the leaf was tested for starch (3mks)
- J Blue black
- K Brown
- L Brown
- State the form in which carbohydrates are stored in the liver. (1mk)
- glycogen;
- Suggest the aim of the experiment. (1mk)
- The organisms below were collected from a certain habitat. Study them and answer the questions that follow.`
- In which kingdom do the organisms belong 1mk
- Animalia;
- State two external features that are found in organism B. 2mks
- legs;wings;antennae;body segments;
- State the method used to collect:
- Organism B 1mk
- sweep net;
- Orgarnism D 1mk
- pitfall trap;
- Organism B 1mk
- State one precaution that should be taken when collecting orgarnism A 1mk
- should be handled with a pair of forceps
- Identify two modes of locomotion in specimen B ( 2mks)
- flying;walking;
- In which kingdom do the organisms belong 1mk
- The set-up below illustrates a procedure that was carried out in the laboratory with a leaf plucked from a green plant that had been growing in sunlight.
- What was the purpose of the above procedure ? (1mark)
- Testing (a leaf) the presence of starch
- Give reasons for carrying out step A,B and C in this procedure. (3marks)
- A. kill the leaf /cells/ protoplasm/ breakdown starch granules/ stop enzymatic activity
- B. Removal of chlorophyll/ dissolve chlorophyll /decolourise the leaf
- C. Soften leaf / makes less brittle.
- Name the reagent that was used at the step labeled D . (1mark)
- Iodine solution
- State the expected result on the leaf after adding the reagent named in (iii) above. (1mark)
- Stain dark blue/ Blue black
- What was the purpose of the above procedure ? (1mark)
- Describe the adaptations of the ileum to its function 20 marks
- Has secretory glands / crypts of lieberkuhn; which secretes enzymes; (maltase / sucrose / peptidase / lipase to complete digestion; of lipids / sugar / proteins.
- Goblet cells secrete mucus ;allows for smooth movement of food ; protect wall of ileum from action of digestive enzymes;
- Very long ;to provide large surface area for absorption;
- Highly folded / coiled; to slow movement of food to allow more time for digestion / absorption / increase surface area for absorption.;
- Has numerous villi ;which increase surface area for absorption / microvillus which further increase surface area for absorption.;
- Ileum wall / villi have thin epithelium; which is only one cell thick to reduce distance over which digested food has to diffuse;.
- Villi are highly vascularised / have a rich network of blood capillaries; for rapid transport of digested food from small intestines / maintain a steep concentration gradient.;
- Villi have lacteals ;for absorption of fatty acids and glycerol;
- Cells of ileum wall have a large count of mitochondria; to release energy that aid in active transport across the epithelium.; Max 20mks
Join our whatsapp group for latest updates
Tap Here to Download for 50/-
Get on WhatsApp for 50/-
Download Biology Questions and Answers - Form 2 Term 1 Opener Exams 2023.
Tap Here to Download for 50/-
Get on WhatsApp for 50/-
Why download?
- ✔ To read offline at any time.
- ✔ To Print at your convenience
- ✔ Share Easily with Friends / Students