QUESTIONS;
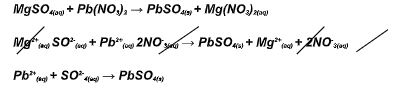
- In an experiment, lead nitrate Pb(NO3 )2(aq) reacted with magnesium sulphate (MgSO) 4(aq)
- Derive an ionic equation for the above reaction. (3mks)
- Given lead (II) oxide, nitric (V) acid, sodium carbonate solution, water, explain into details how you can prepare lead II carbonate.(3mks)
-
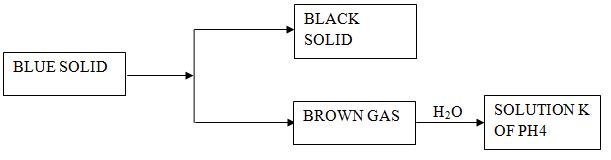
- Identify:
- Black solid –
- Blue solid –
- Brown –
- Write a chemical equation between Brown gas and water to form solution K. (2mks)
- Identify:
- The reactivity of alkali metals increase down the group while that of halogens increase up the group. Explain. (2mks)
- The first and second ionization energies of sodium are 496KJMol - and 4563KJMol - respectively. Explain why the second ionization energy is far much higher than the first ionization energy.(2mks)
- Explain the following observations:
- Solid sodium chloride does not conduct electricity whereas molten sodium chloride and sodium chloride solution are good conductors of electricity. Explain. (2mks)
- Sodium has a melting point of 98ºC while aluminium has a melting point of 660ºC (atomic numbers : Na=11, Al=13) (2mks)
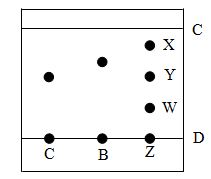
- Spots of pure pigments A and B and a mixture Z were placed on a filter paper and allowed to dry. The paper was then dipped in a solvent. The results obtained were as the paper chromatogram.
- Which is the; (2mks)
- Baseline?
- Solvent front?
- Which of the pure pigments was a component of Z? Explain. (2mks)
- Which is the; (2mks)
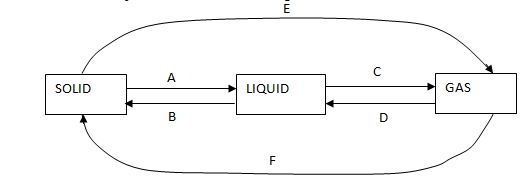
- The diagram below shows the inter-conversions between the various states of matter. Study it and answer the questions that follow:
- Name the processes labeled A to E.(3mks)
- Name any two substances that can be recovered from a solid mixture using the processes labeled E and F.(2mks)
-
- What is rust? (1mk)
- Explain one advantage of rusting. (1mk)
- Name two methods of preventing rust.(2mks)
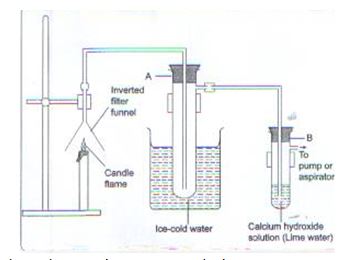
- The set-up below was used to investigate the products formed when candle wax burns in air. Study it and answer the questions that follow.
- What observations are made in:
- Test-tube A? (1mk)
- Test-tube B? Explain. (2mks)
- Explain why test-tube A is dipped in cold water. (1mk)
- What observations are made in:
- The atomic numbers of elements C and D are 19 and 9 respectively. State and explain the electrical conductivity of the compound CD in:
- Solid state. (1½ mks)
- Aqueous state. (1½ mks)
- What type of bond is formed when lithium and fluorine reacts? Explain. (Atomic numbers Li=3 and F=9) (2mks)
- Iron (III) oxide was found to be contaminated with copper (II) sulphate. Describe how a pure sample of iron (III) oxide can be obtained. (3mks)
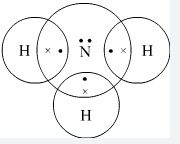
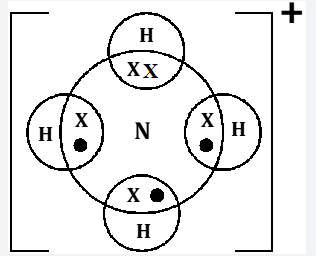
- Using dots (.) and crosses (x) to represent electrons draw diagram to represent the bonding in; (2mks)
- NH3
- ) NH4+
-
- What are isotopes? (1mk)
- Lithium has two isotopes . Determine the number of neutrons in (2mks)
- If the relative atomic mass of lithium is 6.94. Which of the two isotopes is the most abundant? Give a reason. (2mks)
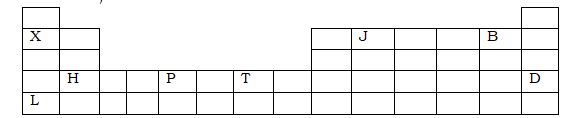
- The grid shown below represents the periodic table. Study it and answer the questions that follow (the letters do not represent actual symbols of the elements)
- What is the atomic number of H? (1mk)
- Which letters represent elements in the same group? (2mks)
- What is the name given to the group of elements in which P and T belong?(1mk)
- Which letters represent non-metal? (3mks)
- Which letter represents the most reactive metal? (1mk)
- If an atom of J has 8 neutrons, state its mass number.
-
- What is rust? (1mk)
- Name three methods of rust prevention. (3mks)
- Distinguish between ionization energy and electron affinity of an element. (2mks)
- State one physical property shared by chlorine, neon, argon and fluorine.(1mk)
-
- Explain why Noble gases are generally unreactive. (1mk)
- State two uses of Noble gases. (2mks)
- Give two reasons as to why most laboratory apparatus are made of glass.(2mks)
MARKING SCHEME
- In an experiment, lead nitrate Pb(NO3)2(aq) reacted with magnesium sulphate (MgSO)4(aq)
- Derive an ionic equation for the above reaction. (3mks)
- Given lead (II) oxide, nitric (V) acid, sodium carbonate solution, water, explain into details how you can prepare lead II carbonate. (3mks)
- PbCO3 is an insoluble salt,
1 st procedure;
React lead oxide with nitric acid to convert it into a soluble salt.
PbO(s) + 2HNO3(aq) → Pb(NO3)2(aq) + H2O(l)
Then double decomposition i.e.
Pb(NO3)2(aq) + Na2CO3(aq) → PbCO3(s) + 2NaNO3(aq) - Filter the solution to obtain NaNO3 as filtrate and PbCO3 as solid.
- Filter the solid PbCO3 between filter papers.
- PbCO3 is an insoluble salt,
-
- Identify:
- Black solid – CuO
- Blue solid – Cu(NO3)2
- Brown – NO2
- Write a chemical equation between Brown gas and water to form solution K.(2mks)
- 2NO2(g) + H2O(l) → HNO2(aq) + HNO3(aq)
- Identify:
- Derive an ionic equation for the above reaction. (3mks)
- The reactivity of alkali metals increase down the group while that of halogens increase up the group. Explain. (2mks)
- Alkali metals lower in the group lose the electron more readily hence they are more reactive.
- Halogens lower in the group have less ability to attract and hold the extra electron. Hence reactivity of halogens increases up the group.
- The first and second ionization energies of sodium are 496KJMol - and 4563KJMol - respectively. Explain why the second ionization energy is far much higher than the first ionization energy. (2mks)
- After removal of the first electron, the number of electrons gets fewer than the protons. Thus the electrons are attracted more strongly to the nucleus making it more difficult to remove the second electron.
- Explain the following observations:
- Solid sodium chloride does not conduct electricity whereas molten sodium chloride and sodium chloride solution are good conductors of electricity. Explain. (2mks)
- Solid sodium chloride has no free ions hence cannot conduct electricity while molten sodium chloride and in sodium chloride solution has free ions to move about hence able to carry charge from one point to another.
- Sodium has a melting point of 98ºC while aluminium has a melting point of 660ºC (atomic numbers : Na=11, Al=13)(2mks)
- The outermost energy level in Aluminium has 3 electrons while sodium atom has 1 electron, furthermore, an aluminium atom is smaller than a sodium atom resulting to a stronger metallic bond.
- Solid sodium chloride does not conduct electricity whereas molten sodium chloride and sodium chloride solution are good conductors of electricity. Explain. (2mks)
- Spots of pure pigments A and B and a mixture Z were placed on a filter paper and allowed to dry. The paper was then dipped in a solvent. The results obtained were as the paper chromatogram.
- Which is the; (2mks)
- Baseline? D
- Solvent front? C
- Which of the pure pigments was a component of Z? Explain. (2mks)
- A Because pigment Y from Z has moved same distance as pure pigment A.
- Which is the; (2mks)
- The diagram below shows the inter-conversions between the various states of matter. Study it and answer the questions that follow:
- Name the processes labeled A to E. (3mks)
- A – Melting
- B – Freezing
- C – Vaporization / evaporationD – condensation
- E – Sublimation
- F – Deposition
- Name any two substances that can be recovered from a solid mixture using the processes labeled E and F. (2mks)
- Ammonium chloride, iodine (III) chloride and Aluminium chloride
- Name the processes labeled A to E. (3mks)
-
- What is rust? (1mk)
- Rust is hydrated iron (III) oxide
- Explain one advantage of rusting. (1mk)
- It helps in the breakdown of waste containers made of iron.
- Name two methods of preventing rust. (2mks)
- Oiling and greasing.
- Alloying
- Plating
- Galvanizing
- What is rust? (1mk)
- The set-up below was used to investigate the products formed when candle wax burns in air. Study it and answer the questions that follow.
- What observations are made in:
- Test-tube A? (1mk)
- Colourless liquid
- Test-tube B? Explain. (2mks)
- A white precipitate is formed because burning candle produce CO2 that react with lime water to form a white precipitate.
- Test-tube A? (1mk)
- Explain why test-tube A is dipped in cold water. (1mk)
- To condense water vapour.
- What observations are made in:
- The atomic numbers of elements C and D are 19 and 9 respectively. State and explain the electrical conductivity of the compound CD in:
- Solid state. (1½ mks)
- In solid state – does not conduct because ions are not free.
- Aqueous state. (1½ mks)
- Conducts because ions are free.
- Solid state. (1½ mks)
- What type of bond is formed when lithium and fluorine reacts? Explain. (Atomic numbers Li=3 and F=9) (2mks)
- Ionic bond: lithium loses electron to form positive ion. Fluorine gains electron to form negative ion. Hence the two ions are held by ionic bond.
- Iron (III) oxide was found to be contaminated with copper (II) sulphate. Describe how a pure sample of iron (III) oxide can be obtained. (3mks)
- Add water to the mixture, copper (II) sulphate dissolves while iron (III) oxide does not. Filter the mixture to obtain iron (III) oxide as residue.
- Using dots (.) and crosses (x) to represent electrons draw diagram to represent the bonding in; (2mks)
- NH3
- NH+4
- NH3
- What are isotopes? (1mk)
- Atoms of the same element but with different mass number.
- Lithium has two isotopes . Determine the number of neutrons in Li (2mks)
- Lithium has two stable isotopes: ^6Li and ^7Li.
- ^6Li has 3 protons and 3 neutrons
- ^7Li has 3 protons and 4 neutrons
- Lithium has two stable isotopes: ^6Li and ^7Li.
- If the relative atomic mass of lithium is 6.94. Which of the two isotopes is the most abundant? Give a reason. (2mks)
- the relative atomic mass is closer to the mass number of the more abundant isotope.
- What are isotopes? (1mk)
- The grid shown below represents the periodic table. Study it and answer the questions that follow (the letters do not represent actual symbols of the elements)
- What is the atomic number of H?(1mk)
- 20
- Which letters represent elements in the same group?(2mks)
- X and L
- What is the name given to the group of elements in which P and T belong?(1mk)
- Transition element
- Which letters represent non-metal?(3mks)
- J, B and D
- Which letter represents the most reactive metal?(1mk)
- L
- If an atom of J has 8 neutrons, state its mass number.
- 14
- What is the atomic number of H?(1mk)
- What is rust? (1mk)
- Rust is hydrated iron (III) oxide
- Name three methods of rust prevention.(3mks)
- Painting
- Alloying
- Oiling and greasing
- Galvanizing
- What is rust? (1mk)
- Distinguish between ionization energy and electron affinity of an element.(2mks)
- Ionization energy is the energy required to remove an electron from an atom in gaseous state while electron affinity is the energy released when an atom in gaseous state gains an electron.
- State one physical property shared by chlorine, neon, argon and fluorine. (1mk)
- They are gases at room temperature.
-
- Explain why Noble gases are generally unreactive.(1mk)
- They are unreactive because they have a stable electron arrangement.
- State two uses of Noble gases.(2mks)
- Argon is used as an insulator in arch-welding.
- Neon gas is used in street and advertisement lights.
- Helium can be used instead of hydrogen in balloons for meteorological research.
- Explain why Noble gases are generally unreactive.(1mk)
- Give two reasons as to why most laboratory apparatus are made of glass.(2mks)
- Does not react with most chemicals.
- Are relatively cheap
- Are transparent thus enabling reactions to be observed easily as they are taking place.
Join our whatsapp group for latest updates
Tap Here to Download for 50/-
Get on WhatsApp for 50/-
Download Chemistry Questions and Answers - Form 2 End Term 1 Exams 2023.
Tap Here to Download for 50/-
Get on WhatsApp for 50/-
Why download?
- ✔ To read offline at any time.
- ✔ To Print at your convenience
- ✔ Share Easily with Friends / Students