- This paper consists of three sections; A, B and C
- Answer ALL the questions in sections A, B and C
- All answers to be written in English
SECTION A (40 MKS)
ANSWER ALL QUESTIONS IN THE SPACES PROVIDED
- Name three equipments used for large scale over head irrigation. (3mks)
- Name three beef cattle breeds (3mks)
- Distinguish between each of the following pair of terms as used in crop production
- Thinning and rogueing (2mks)
- Seedling bed and nursery bed (2mks)
- State three agricultural practices that pollute surface water sources (3mks)
- State three benefits of using vegetative propagation in orange production (3 mks)
- Name one vegetative material used to propagate each of the following:
- Bananas (1mk)
- Pineapples (1mk)
- Irish potatoes (1mk)
- Pyrethrum (1mk)
- Give two activities carried out during hardening off tomato seedlings (2mks)
- Differentiate between olericulture and pomoculture (2mks)
- State three advantages of shifting cultivation (3mks)
- State three advantages of adding organic matter to sandy soils. (3mks)
-
- Differentiate between macro – nutrients and micro – nutrients (2mks)
- State two functions of calcium in plant growth and development (2mks)
- Name three implements used for primary cultivation (3mks)
- State three factors that influence soil formation. (3 mks)
SECTION B (2OMKS)
ATTEMPT ALL QUESTIONS
- The diagram below shows a bag of Calcium Ammonium Nitrate fertilizer.

- Classify the fertilizer (1mk)
- Explain the effect of applying the above fertilizer on soil pH. (1mk)
- A farmer was advised to apply 50kgs of Nitrogen per hectare. How many bags of the above fertilizer will this farmer require for one hectare? Show your working. (3mks)
- Below is a diagram of a tool used in livestock rearing
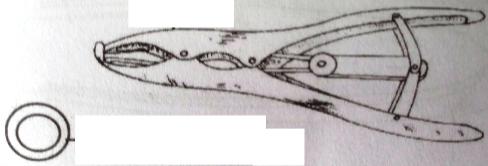
- Identify the tool (1mk)
- State two uses of the tool. (2mks)
- Give two reasons why farmers prefer using the tool (2mks)
- The diagram below illustrates a feature observed after digging the soil several metres deep. Study the diagram and answer the questions that follow.
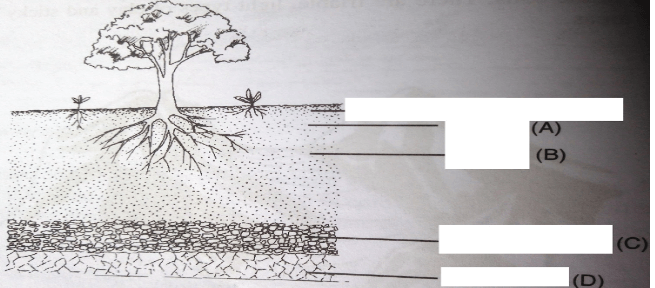
- Identify the feature that the diagram above represents in the study of soil (1mk)
- Name the parts of the diagram labeled A, B, C and D. (4mks)
- State two ways in which the knowledge of the above feature would be of benefit to a farmer. (2mks)
- Sabasaba Secondary School agriculture students visited a dairy cattle farm and found the following record. Study it and answer the question that follow.
Date Disease Symptom Animal(s) Affected Drugs used Cost of Treatment Given Remarks - Name the record shown above (1mk)
- State two importance of the above record to the farmer (2mks)
SECTION C (40MKS)
ATTEMPT ALL QUESTIONS
-
- Explain seven factors that determine the spacing of a crop. (7mks)
- Explain three advantages of timely planting (3mks)
-
- Give reasons why some seeds are established in a nursery before being transported to the seed bed. (6mks)
- Giving an example, name four types of vegetables that can be grown in Kenya. (8mks)
-
- State and explain seven ways through which soil fertility can be lost. (14 mks)
- State and explain six biotic factors that influence crop production. (6mks)
MARKING SCHEME
SECTION A (40 MKS)
- Name three equipments used for large scale over head irrigation. (3mks)
- Sprinklers
- Water pumps
- Pipes
- Filters (3X1=3mks)
- Name three beef cattle breeds (3mks)
- Hereford
- Galloway
- Aberdeen Angus
- Beef short horns
- Charolais (3X1=3mks)
- Distinguish between each of the following pair of terms as used in crop production
- Thinning and rogueing (2mks)
- Thinning is the removal of excess seedlings from the seed bed while rogueing is removal and destruction of diseased or infected plants. (2mks)
- Seedling bed and nursery bed (2mks)
- Nursery bed is a small piece of land where small seeds are raised into seedlings before transplanting while a seedling bed is a special type of nursery which receives excess seedlings from the nursery bed after pricking out. (2mks)
- Thinning and rogueing (2mks)
- State three agricultural practices that pollute surface water sources (3mks)
- Use of inorganic fertilizers
- Use of excess pesticides
- Over cultivation
- Overgrazing
- Cultivation along river banks (3X1=3mks)
- State three benefits of using vegetative propagation in orange production (3 mks)
- Early maturity of the crop
- Plants assumes desired shape and size
- Possible to obtain two or more varieties of oranges on the same root stock
- Highly yielding
- Maintains parental genetic characteristics / resembles the mother plant
- Possible to propagate seedless varieties (3X1=3mks)
- Name one vegetative material used to propagate each of the following:
- Bananas – suckers (1mk)
- Pineapples – slips / crowns / suckers (1mk)
- Irish potatoes – stem tubers (1mk)
- Pyrethrum – splits (1mk)
- Give two activities carried out during hardening off tomato seedlings (2mks)
- Removal of the shade
- Reduce the frequency of watering (2X1=2mks)
- Differentiate between olericulture and pomoculture (2mks)
- Olericulture is the growing of vegetables such as French beans, cabbages, tomatoes onions under both small scale or large scale while pomoculture is growing of fruits such as citrus, mangoes, passion fruits and pineapples. (2mks)
- State three advantages of shifting cultivation (3mks)
- Land is allowed to rest and regain fertility
- Low incidences of pests and diseases
- Economizes on use of the fertilizers (3X1=3mks)
- State three advantages of adding organic matter to sandy soils. (3mks)
- Improves soil structure
- Reduces leaching of nutrients
- Improves water holding capacity
- Improves nutrients status upon decomposition
- Moderates soil temperature / buffers soil pH (3X1=3mks)
-
- Differentiate between macro – nutrients and micro – nutrients (2mks)
- Macro – nutrients are required by the plants in relatively large quantities while micro – nutrients are required in small quantities (2mks)
- State two functions of calcium in plant growth and development (2mks)
- Elongation of roots and the stem
- Strengthening of plant cell wall
- Helps in protein formation
- Helps in formation of the middle lamella
- Useful in cell division (2X1=2mks)
- Differentiate between macro – nutrients and micro – nutrients (2mks)
- Name three implements used for primary cultivation (3mks)
- Jembe
- Ox – plough
- Disc plough
- Mould board plough (3X1=3mks)
- State three factors that influence soil formation. (3 mks)
- Parent rock / bedrock
- Climatic
- Topography / slope
- Time
- Living organisms / biotic factors (3X1=3mks)
SECTION B (2OMKS)
- The diagram below shows a bag of Calcium Ammonium Nitrate fertilizer.
- Classify the fertilizer (1mk)
- Nitrogenous fertilizer / straight fertilizer (1X1=1mk)
- Explain the effect of applying the above fertilizer on soil pH. (1mk)
- It neutralizes soil acidity
- It raises / increases soil pH
- It has a liming effect (1X1=1mk)
- A farmer was advised to apply 50kgs of Nitrogen per hectare. How many bags of the above fertilizer will this farmer require for one hectare? Show your working. (3mks)
If 20kgN is contained in 100kg CAN
50kg is contained 100kg of CAN X 50kgN
20kg N
= 250kg of CAN
But in the market the fertilizer is packed in 50kg bags
250kg = 5 bags of the fertilizer (3mks)
50kg
- Classify the fertilizer (1mk)
- Below is a diagram of a tool used in livestock rearing
- Identify the tool (1mk)
- Elastrator and rubber ring (1X1=1mk)
- State two uses of the tool. (2mks)
- Docking
- Castration
- Dehorning (2X1=2mks)
- Give two reasons why farmers prefer using the tool (2mks)
- Bloodless
- Less painful
- Less stressful
- Less skills required (2X1=2mks)
- Identify the tool (1mk)
- The diagram below illustrates a feature observed after digging the soil several metres deep. Study the diagram and answer the questions that follow.
- Identify the feature that the diagram above represents in the study of soil (1mk)
- Soil profile
- Name the parts of the diagram labeled A, B, C and D. (4mks)
- A – Top soil
- B – Sub soil
- C – Weathered rocks
- D – Bed rock
- State two ways in which the knowledge of the above feature would be of benefit to a farmer. (2mks)
- Helps the farmer to choose appropriate crop to grow
- Helps to determine the depth of ploughing
- Helps the farmer to determine the kind of foundation or farm structures to construct (2X1=2mks)
- Identify the feature that the diagram above represents in the study of soil (1mk)
- Sabasaba Secondary School agriculture students visited a dairy cattle farm and found the following record. Study it and answer the questions that follow.
- Name the record shown above (1mk)
- Health record (1X1=1mk)
- State two importance of the above record to the farmer (2mks)
- Helps in selection
- Helps culling of the animals on health grounds
- Helps the farmer to calculate profits /loss in the farm
- Gives the farmer knowledge on the disease out breaks so that they are controlled on time (2X1=2mks)
- Name the record shown above (1mk)
SECTION C (40MKS)
-
- Explain seven factors that determine the spacing of a crop. (7mks)
- Soil fertility – fertile soils closer spacing is used
- Varieties of the crop – spreading varieties require wider spacing
- Moisture availability – high rainfall require closer spacing
- Use of the crop – crops grown for grain production require wider spacing than grown for fodder
- Pests & diseases control – wider spacing control pest and disease spread.
- Number of seeds per hole – more seeds per hole require wider spacing
- Type of machinery to be used – use of machine require wider spacing (7X1=7mks)
- Explain three advantages of timely planting (3mks)
- Crops make maximum use of rainfall and suitable soil temperature leading to vigorous growth
- Crops establish earlier than weeds, hence smothering them
- Crops escape serious pest and disease attack
- Crops benefit from Nitrogen flush which is available at the beginning of the rains
- For horticultural crops, proper timing ensures that the produce is marketed when prices are high. (3X1=3mks)
- Explain seven factors that determine the spacing of a crop. (7mks)
-
- Give reasons why some seeds are established in a nursery before being transported to the seed bed. (6mks)
- Facilitates production of many seedlings in a small area
- Routine management practices are easily and timely carried out in a nursery than in the main field
- Makes it possible to provide the best conditions for growth such as fine tilth, leveled field and shade
- Facilitates the planting of small seeds which develop into strong seedlings that are easily planted
- It ensures transplanting of only those seedlings that are healthy and vigorously growing
- Excess seedlings from the nursery may be sold, thus become a source of income to the farmer
- Reduce the time the crops take in the field to mature (6X1=6mks)
- Giving an example, name four types of vegetables that can be grown in Kenya. (8mks)
- Leaf vegetables e.g. cabbages, kales, spinach, cowpeas etc
- Root vegetables e.g. carrots, radishes, beet roots, tulips etc
- Fruit vegetables e.g. cucumbers, tomatoes, melons, pumpkins, squashes, pepper etc.
- Pod vegetables e.g. French beans
- Stem vegetables e.g. leeks, asparagus, spring onions etc
- Bulb vegetables e.g. bulbed onions
Stating 4X1=4mks
Examples 4X1=4mks
- Give reasons why some seeds are established in a nursery before being transported to the seed bed. (6mks)
-
- State and explain seven ways through which soil fertility can be lost. (14 mks)
- Soil erosion – when the soil is carried away by water, wind and animals
- Leaching – dissolved minerals in water are carried to lower horizons beyond the reach of many plant roots
- Continuous cropping – harvested crops remove a lot of nutrients from the soil leading to loss of fertility
- Mono cropping – when one type of crop is grown for a long time, the soil becomes infertile for growing the same crop
- Change in soil pH – application of basic or acidic fertilizers affect the availability of crop nutrients thus making the soil infertile
- Burning of the vegetation cover – when the vegetation cover is burned, it destroys the organic matter leading to accumulation of ash that causes nutrient imbalance.
- Accumulation of salts – the accumulation of salts in the soil affects the soil pH and leads to loss of soil fertility.
Stating 7X1=7mks
Explanation 7X1=7mks
- State and explain six biotic factors that influence crop production. (6mks)
- Nitrogen fixing bacteria – convert atmospheric nitrogen to nitrates for plant uptake
- Pollinators – transfer pollen grains from the anther of a flower to the stigma of the same flower or different flower
- Decomposers – organisms which breakdown organic plant and animal remains to release nutrients for the plant.
- Pests – attack crops by eating plant parts, piercing and sucking sap and introduce / spread disease causing micro – organisms
- Pathogens – they cause crop diseases
- Predators – reduce pests population
- Weeds – compete for nutrients, space, light, moisture and spread pests and diseases
Stating 3X1=3mks
Explanation 3X1=3mks
- State and explain seven ways through which soil fertility can be lost. (14 mks)
Download Agriculture Questions and Answers - Form 2 Term 3 Opener Exams 2023.
Tap Here to Download for 50/-
Get on WhatsApp for 50/-
Why download?
- ✔ To read offline at any time.
- ✔ To Print at your convenience
- ✔ Share Easily with Friends / Students

