SECTION A: (25 MARKS)
Answer ALL questions this section in the spaces provided.
- State the laws of refraction (3 mks)
-
- Define local action (1mk)
- A charge of 4.8C flows through a lamp every second. Calculate the number of electrons involved per second. (3mks)
- Give two differences between a primary and a secondary cell (4mks)
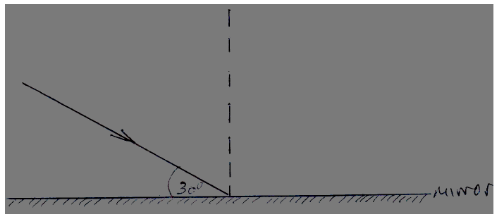
- The figure below shows a ray of light incident on a plane mirror.
- What is the angle of reflection? (1mk)
- The mirror is rotated clockwise through an angle of 10°. Through what angle does the reflected ray rotate? (2mks)
- A hockey player trains on a nylon fiber surface. As he runs around, his shoes rub against the surface and he becomes positively charged.
- Explain in terms of particles involved, how he becomes positively charged. (1mk)
- State what happens to the nylon-fiber surface as it becomes positively charged. (1mk)
- State two defects of a simple cell. (2mks)
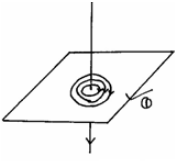
- The diagram below shows a current carrying conductor placed in a magnetic field.
- Sketch the resulting magnetic field pattern. (1mk)
- On the diagram show direction of force.
- What is dispersion of light? (1mk)
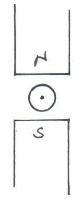
- Draw the magnetic field pattern around the arrangement shown below (2mks)
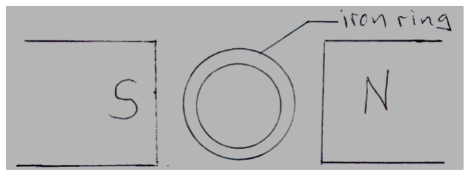
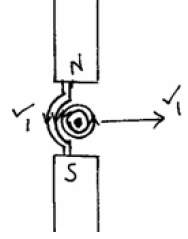
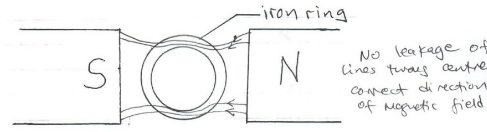
- The diagram in figure 7 below shows one method of making a magnet.
Fig.7
What polarity is at X and Y when the switch is closed.
X = ______________________(1 mark)
Y = ______________________ (1 mark)
SECTION B (55 MKS)
- A parent comes to you seeking your advice whether to use a white shawl or a black one to wrap her child to kept it warm. Which shawl would you advice to use and why? (2 marks)
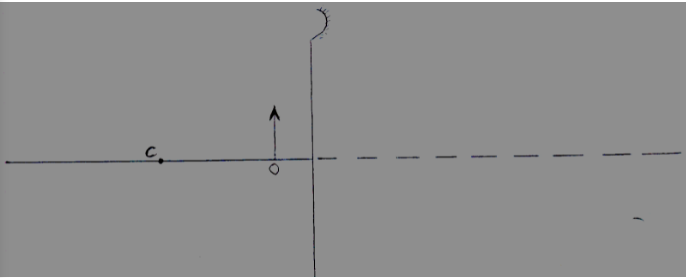
- Complete the figure 10 below to show the position of the image of object A in the mirror M. (2 marks)
Fig.10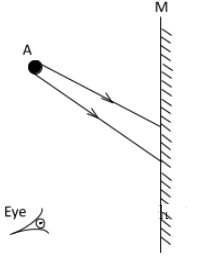
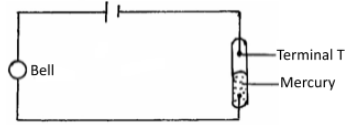
- Figure 11 shows a fire alarm circuit.
Fig.11
Explain how the fire alarm functions. (3 marks) - A highly negatively charged rod is gradually brought close to the cap of a positively charged electroscope. It is observed that the leaf collapses initially and then diverges. Explain the observation. (3 marks)
- In figure 12 the arrow indicates the direction of the current in the conductor. Sketch on the diagram the magnetic field pattern due to the current. (1 marks)
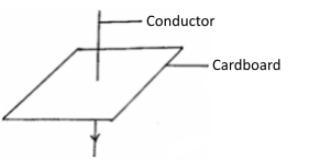
Fig.12 -
- In estimating the height of a tree, the following measurements were recorded:
Height of the rod = 180cm.
Length of the shadow of the rod = 116cm
Length of the shadow of the tree = 420cm
Calculate the height of the tree. (3 marks) - State three methods of making magnets. (3 marks)
- In estimating the height of a tree, the following measurements were recorded:
-
- Define an echo. (1mk)
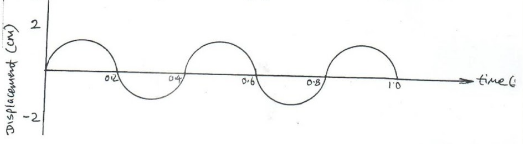
- The figure below shows the displacement-time graph of a wave travelling at 0.4ms−1
- How many complete waves are shown? (1mk)
- Determine the period time of the wave (1mk)
- A person stands between two high walls d metres apart. He stands 400m from the nearer wall. He blows a whistle and hears two echoes, the first one after 2.5 seconds and the second one 2 seconds later. Determine:
- The speed of sound in the air. (3mks)
- The value of d (3mks)
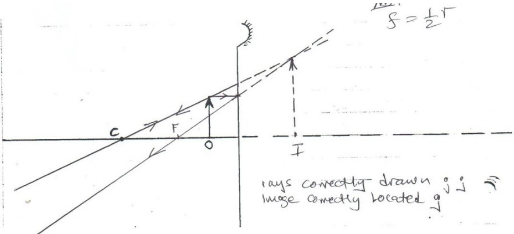
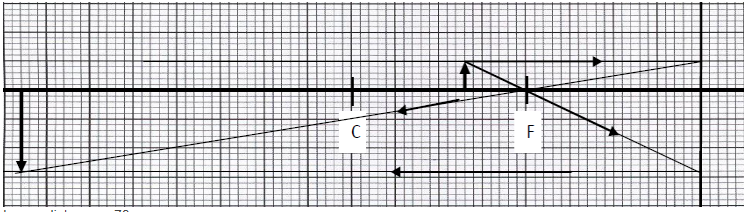
- The figure below shows an object placed in front of a concave mirror
- On the same diagram, locate the position of the image (3mks)
- What is the magnification of the image? (3mks)
-
- State the laws of reflection (2mks)
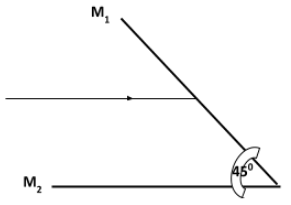
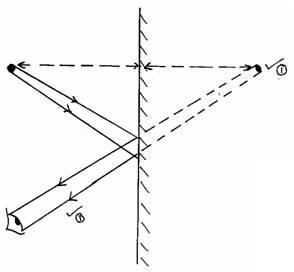
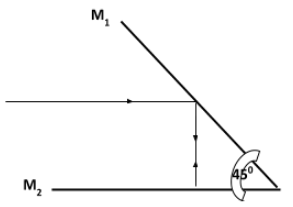
- Two plane mirrors M1 and M2 and inclined to each other and a ray of light shone on M1 as shown:
Show on the diagram the path followed by the ray until it is reflected by M2 (2mks) - Define the following terms as used in refraction (4mks)
- Absolute refractive index
- Total internal reflection
- Critical angle
- Refraction
-
- Given that the refractive index of diamond is 2.42 and the velocity of light in air 3.0 X 108 m/s,calculate the velocity of light in diamond. (3mks)
- A glass block of thickness 12 cm is placed on a mark placed on a plain paper. The mark is viewed normally through the glass. Calculate the apparent depth of the mark and hence the vertical displacement. (refractive index of glass is 1.5) (3mks.)
- State Snell’s law of refraction. (2mks)
-
- Define magnification (1mk)
- State two differences between a concave and a convex reflectors (2mks)
- a concave mirror of focal length 20 cm forms a real image three times the size of the object. If the object height is 4cm; determine, using graphical method, the:
- object distance (3mks)
- The image distance (1mk)

Marking Scheme
-
- Angle of refraction, the normal and Angle of incidence at the point of incidence all lie in the same plane.
- The ration sine of angle of incidence : sine of refraction angle is a constant for a given pair of media.
-
- Internal loss of battery due to local currents that flow between different parts of a plate.
- Q=4.8c
Number of electrons = 4.8
1.6 × 10−19
= 3.0 × 1020 electrons -
Primary cells Secondary cells Are irreversible i.e once they get discharged they cannot be charged again Are reversible and can be easily charged by electrical supply Their internal resistance is very high They possess low internal resistance
-
- 90–30 = 60°
- 2×10 = 20°
-
- On rubbing the surface, electrons are transferred from the shoe to the nylon fibre.This leaves the rubber shoes with a net positive charge.
- The fibre become negatively charged in the process.
- Defects
- Local action
- Polarisation
-
From N-S; around conductor
Direction of force; (NB: lines should not cross) - Dispersion of light.
- Splitting of light into the constituents.
-
- X – South ✓1
Y – North ✓1 - White. ✓1
- To retain the babies temperature, since white shawl is a poor emitter and also poor absorber. ✓1
-
-
- Heat from the fire heats the mercury.
- Mercury expands and touches terminal T, ✓1 thereby completing the circuit and hence the bell rings. ✓
- Initially the rod repels the negative charges that neutralizes ✓1 the positive charges. But since it highly changed more negative charges are repelled downward ✓1making it become negatively charged down there and hence the deflection. ✓1
-
-
- Height of tree = Length of the shadow of tree
Height of rod length of the shadow of rod
Height of tree = 420
180 116
Height of tree = 420 × 180
116
= 420 × 180
116 ✓1
= 651.72cm or 6.517m ✓1 - Electrical
Stroking (double/single)
Hammering
Induction Any 3 correct ✓3
- Height of tree = Length of the shadow of tree
-
- An echo is a reflected sound on meeting a reflector or an obstacle.
-
- 2
- Time=0.45
-
- v = 2d = 2×400
t 2.5
=320ms−1 - v = 2d
t
d = vt = 320(2.5+4.5)
2 2
=1120m
OR
d − 400 = 320 × 4.5
2
d = 720+400
=1120m
- v = 2d = 2×400
-
- M = v/u = 1.8/1 = 1.8
V = 1.8 ± 0.1
HF = 2.4 ± 0.1
M = HF = 2.4
Ho 1.3
=1.85
-
-
- The angle of incidence is equal to the angle of reflection (1MK)
- The incident ray, the reflected ray and the normal at the point of incidence lie on the same plane (2MKs)
-
- This is the refractive index when a ray of light is travelling from vacuum to a given medium.
- Phenomena that occurs when angle of incidence exceeds the critical angle thus light gets reflected internally within the denser medium.
- Critical angle is the angle of incidence in the denser medium for which the angle of refraction in the less dense medium is 90°.
- Refraction is the bending of light when it travels from a medium to another at an angle.
-
- n=speed of light in vacuum /speed of light in medium
n=c/v
2.42=3x10^8/speed of light
Speed of light =3x108/2.42
=1.25x108 m/s - ang = real depth
apparent depth
apparent depth = real depth = (12 × 2) = 8 cm
ang 3
vertical displacement= 12 - 8 = 4 cm - Snell’s law states that the ratio of the sine of angle of incidence to that of sine of angle of refraction is a constant called refractive index.
- n=speed of light in vacuum /speed of light in medium
-
-
- This is the change in the size of an image relative to that of the object
-
Concave reflector Convex reflector Concave or bent-in surface
the reflecting surfaceOuter bulging surface is the
reflecting surfaceIt is a converging mirror It is a diverging mirror It has a real focus It has a virtual focus Image may be real or virtual Image is always virtual
Image distance= 78cm
Object distance = 27cm
Download Physics Paper 2 Questions and Answers - Form 3 End Term 1 Exams.
Tap Here to Download for 50/-
Get on WhatsApp for 50/-
Why download?
- ✔ To read offline at any time.
- ✔ To Print at your convenience
- ✔ Share Easily with Friends / Students