INSTRUCTIONS TO CANDIDATES:
- Answer ALL the questions
- Answers should be written in the spaces provided
SECTION A: (40 MARKS)
- The chart below represents a food web. Use it to answer the questions that follow.
- Construct two food chains ending with tertiary consumer in each case. (2mks)
- Which organism has the largest variety of predators in the food web? (1mk)
- Name secondary consumers in the food web. (1mk)
- Suggest three ways in which the ecosystem would be affected if there was a prolonged drought. (3mks)
- To estimate the population size of crabs in a certain lagoon, traps were laid at random 400 crabs were caught, marked and released back into the lagoon. Four days later traps were laid again and 374 crabs were caught. Out of the 374 crabs, 80 were found to have been marked.
- Calculate the population size of crabs in the lagoon. (2mks)
- State three assumptions that were made during the investigation. (3mks)
- What is the name given to this method of estimating the population size? (1mk)
- Other than the method named above, state any other two methods that are used to estimate population size. (2mks)
-
- Classify the bean plant in to each of the following taxa. (3mks)
- Kingdom
- Division
- Class
- Name the microscopic living threads that make up the body of a fungus. (1mk)
- State the structural differences between Gymnospermatophyta and Angiospermatophyta. (4mks)
- Classify the bean plant in to each of the following taxa. (3mks)
- The chart below is a summary of blood clotting mechanisms in man.
- Name
- The blood cells represented by X. (1mk)
- Metal ion represented by Y. (1mk)
- Identify product Z and state its significance. (2mks)
- Name the process by which the human body naturally stops bleeding. (1mk)
- How can low blood volume be brought back to normal? (2mks)
- Give a reason why blood doesn’t clot in unwounded blood vessels. (1mk)
- Name
- The diagram below represents the general appearance of a section of the cell membrane under an electron microscope.
- State the possible composition of layers A and B. (2mks)
- What is the significance the structure A in the membrane? (2mks)
- State two properties of the cell membrane that make it efficient in its functions. (2mks)
- Give two reasons why an electron microscope is useful in the study of the cell structure. (2mks)
SECTION B
Answer Question 6 (COMPULSORY) and either Question 7 or 8 in the spaces provided.
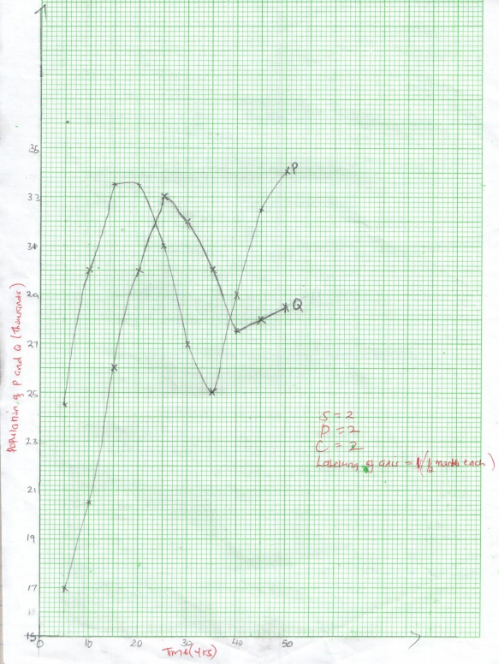
- The data provided represents populations of a predator and its prey over a fifty years periods.
Time in years Population in relative population of P (in thousands) Numbers population of Q (in thousands) 5
10
15
20
25
30
35
40
45
5024.5
30
33.5
33.5
31
27
25
29
32.5
3417
20.5
26
30
33
32
30
27.5
28.0
28.5-
- Using the same axes, draw graphs of the relative populations of P and Q against time. (7mks)
- With a reason identify the curve that represents the prey. (2mks)
- Accounts for the two populations between 25 and 32 years. (2mks)
- Which years were the two populations equal. (2mks)
- Apart from predation, state three biotic factors that may have led to the decline of the prey population. (2mks)
- Describe the hazards of air pollution by sulphur (IV) oxide. (4mks)
-
- Explain how the mammalian heart is structurally adapted to its functions. (20mks)
-
- Give any two functions of leaves in plants. (2mks)
- Explain how leaves of mesophytes are suited to their functions. (18mks)

Marking Scheme
- The chart below represents a food web. Use it to answer the questions that follow.
- Construct two food chains ending with tertiary consumer in each case. (2mks)
- Green plants →grasshoppers→Lizards→Snakes
- Green plants → grasshoppers → Lizards → Cats
- Green plants → Mice → Snake → Hawk
- Green plants →Mice → Snakes → Cats
- Which organism has the largest variety of predators in the food web?(1mk)
- Mice
- Name secondary consumers in the food web. (1mk)
- Lizard
- Cat
- Hawk
- Snakes
- Suggest three ways in which the ecosystem would be affected if there was a prolonged drought. (3mks)
- Most plants will die/dry
- Some organisms may starve to death
- Some organisms may migrate.
- Construct two food chains ending with tertiary consumer in each case. (2mks)
- To estimate the population size of crabs in a certain lagoon, traps were laid at random 400 crabs were caught, marked and released back into the lagoon. Four days later traps were laid again and 374 crabs were caught. Out of the 374 crabs, 80 were found to have been marked.
- Calculate the population size of crabs in the lagoon. (2mks)
Population = First Number marked × Second capture
Marked recarptured
= 400×374 = 1870
80 - State three assumptions that were made during the investigation.(3mks)
- There was even distribution of crabs.
- No movement in and out of lagoon/no migration
- Released crabs mixed freely with remaining population.
- Marked crabs had enough time to mix with the rest.
- What is the name given to this method of estimating the population size? (1mk)
- Capture recapture method
- Other than the method named above, state any other two methods that are used to estimate population size. (2mks)
- Body counts
- Quadrat
- Transect (belt and line)
- Calculate the population size of crabs in the lagoon. (2mks)
-
- Classify the bean plant in to each of the following taxa. (3mks)
- Kingdom – Plantae
- Division – Spermatophyta
- Class – Dicotyledonae
- Name the microscopic living threads that make up the body of a fungus. (1mk)
- Hyphae (Accept mycelium)
- State the structural differences between Gymnospermatophyta and Angiospermatophyta. (4mks)
Gymnospermatophyta Angiospermatophyta Produce naked seeds
Xylem composed mainly of tracheids
Phloem lacks companion cell
Are cone bearingSeeds enclosed in a fruit wall
Xylem has tracheids and vessels
Phloem has companion cells
Are flower bearing.
- Classify the bean plant in to each of the following taxa. (3mks)
- The chart below is a summary of blood clotting mechanisms in man.
- Name
- The blood cells represented by X. (1mk)
- Platelets
- Metal ion represented by Y. (1mk)
- Calcium ions / Ca+2
- The blood cells represented by X. (1mk)
- Identify product Z and state its significance.
- Fibrin; it forms an insoluble meshwork that seals the broken surface.
- Name the process by which the human body naturally stops bleeding. (1mk)
- Clotting
- How can low blood volume be brought back to normal? (2mks)
- Transfusion
- Taking fluids
- Eating ion in food stuff
- Taking iron tablets.
(any 4 x ½ )
- Give a reason why blood doesn’t clot in unwounded blood vessels.(1mk)
- Presence of heparin.
- Name
- The diagram below represents the general appearance of a section of the cell membrane under an electron microscope.
- State the possible composition of layers A and B. (2mks)
- A – proteins
- B – Lipids / Phospholipids
- What is the significance the structure A in the membrane? (2mks)
- Protein is sensitive to changes in temperature / pH; which makes it efficient in allowing substances to move across cell membrane.
- Proteins give the membrane structural support.
- State two properties of the cell membrane that make it efficient in its functions. (2mks)
- Semipermiability, it selects what enters and what leaves the cell.
- It has electric charges so that it can detect changes in the environment.
- Give two reasons why an electron microscope is useful in the study of the cell structure. (2mks)
- The electron microscope has a high resolution and high magnifying power thus give fine details of the cell.
- State the possible composition of layers A and B. (2mks)
- The data provided represents populations of a predator and its prey over a fifty years periods.
-
- Using the same axes, draw graphs of the relative populations of P and Q against time. (7mks)
- With a reason identify the curve that represents the prey. (2mks)
- Curve P – increase in population of P leads to increase in population of Q. They provide plenty of food.
- Accounts for the two populations between 25 and 32 years. (2mks)
- Both organisms are declining with time. Population of P is declining sharply due to a higher rate of predation, since number of predators is high. Q is declining due to stiff competition for food.
- Which years were the two populations equal. (2mks)
- 23rd and 39th.
- Apart from predation, state three biotic factors that may have led to the decline of the prey population. (2mks)
- Parasitism
- pest and diseases
- competition
- human activities
- Using the same axes, draw graphs of the relative populations of P and Q against time. (7mks)
- Describe the hazards of air pollution by sulphur (IV) oxide. (4mks)
- Sulphur (IV) oxide dissolves in rain water forming acid rain which lowers soil pH leading in poor crop yield and also causing leaching of mineral.
- Causes respiratory diseases e.g bronchitis and pneumonia since it slows down cilia activities causing irritation.
- Corrodes metals e.g. iron, alluminium, and also contaminating drinking water as it contains toxic materials.
- Affect gaseous exchange structures
-
- Explain how the mammalian heart is structurally adapted to its functions. (20 mks)
Adaptation of the mammalian heart to its functions;- It has cardiac muscles which are myogenic, (does not need nervous stimulation) for pumping of blood.
- It connected to vagus and sympathetic nerves; which controls the rate of heart beat depending on the body’s physiological requirements.
- It has tricuspid and bicuspid valves between articles and ventricles which prevents back flow of blood into the right and left ventricles respectively.
- The heart is connected to the coronary artery; which supplies food and oxygen to the cardiac muscles for the pumping action.
- The coronary vein in the heart; is used to remove metabolic wastes.
- The heart is divided into two by atrio-ventricular septum; which prevents mixing of oxygenated blood and deoxygenated blood.
- The heart is enclosed by the pericardial membrane that secretes pericardial fluid which prevents friction in the walls during pumping.
- The outer pericardium layer surrounded by a layer of fat; to act as shock absorbers thus protecting it from mechanical damage.
- It has sino atrial node (S.A.N) to act as a pace maker by regulating the rate of beating and excitation of the heart.
- The walls of the left ventricle are thicker than those of the right ventricles, to generate more pressure to pump blood over longer distance to the rest of the body.
- The tricuspid and bicuspid valves are held by tendrons; which prevents the valves from turning inside out during ventricular contractions.
- The heart is joined by blood vessels aorta distributes blood to all body tissues except the lungs.
- Pulmonary artery which leaves the heart/left ventricle carries deoxygenated blood to the lungs.
- Pulmonary vein entering the heart /left atrium convey oxygenated blood form the lungs to the heart.
- Vena cava entering the right atrium brings in de-oxygenated blood from body tissues.
- Semi lunar valve at the base of the aorta and pulmonary artery; prevents back flow of blood to the ventricles once it has been pumped out.
- The cardiac muscles of the heart never get fatigued hence the rhythmic contractions goes on throughout life.
-
- Give any two functions of leaves in plants. (2mks)
- Carry out gaseous exchange
- Carry out photosynthesis
- Provide surface area for loss of water by transpiration
- Explain how leaves of mesophytes are suited to their functions. (8mks)
- Have broad and flat lamina to increase SA to trap maximum sunlight and take up more CO2 for photosynthesis.
- Are thin to reduce the distance for diffusing gases i.e. CO2 and O2 and also for maximum penetration of light to photosynthetic cells.
- Have palisade cells which contain numerous chloroplast, especially on upper epidermis for maximum light absorption directly from the sun; palisades are also closely packed together with long axis and located beneath the upper epidermis to receive maximum sunlight.
- Have veins that contain vascular tissue i.e. xylem and phloem xylem conduct water and minerals salts from the soil to the leaves/ photosynthetic tissue/cells while phloem translocates soluble products of photosynthesis from the leaves to growing regions.
- Have stomata which allow diffusion of gases CO2 and O2 and also allow transpiration to take place.
- Have guard cells that control opening and closing of stomata hence regulates exchange of gases and water loss.
- Cuticle and epidermis are transparent to allow easier penetration of light to palisade cells.
- The spongy mesophyll contains cells that are loosely packed or have large air spaces to allow easier circulation of gases and diffusion of gases in and out of palisade cells.
- Epidermis is thin i.e. one cell thick to reduce the distance for diffusing gases and ensure penetration of light to photosynthetic cells.
- Give any two functions of leaves in plants. (2mks)
Download Biology Paper 2 Questions and Answers - Form 3 End Term 1 Exams.
Tap Here to Download for 50/-
Get on WhatsApp for 50/-
Why download?
- ✔ To read offline at any time.
- ✔ To Print at your convenience
- ✔ Share Easily with Friends / Students