INSTRUCTIONS TO CANDIDATES
- This paper consists of two sections: A and B.
- Answer ALL the questions in section A. in section B, answer question 6 and any two other questions.
SECTION A
-
- Define the term ‘photograph’ (2 mks)
- List three limitations of using photographs. (3 mks)
-
- State the three types of fieldwork. (3 mks)
- List three ways through which data may be presented. (3 mks)
-
- What is mining? (2 mks)
- Name three methods of underground mining. (3 mks)
-
- What is forestry? (2 mks)
- Name the three major natural forests of the world. (3 mks)
-
- State the two characteristics of both primary and secondary data. (2 mks)
- Write down two methods that can be used in taking measurements as a method of collecting data. (2 mks)
SECTION B:
Answer question 6 and any other two questions from this section.
- (Compulsory)
You intend to carry out a field study on the weather experienced in the locality of your school.-
- State four ways you would prepare for the study. (4 mks)
- State two hypothesis for the study. (2 mk)
- Describe how you would use the raingauge during the study. (4 mks)
- State how you would record the information while in the field. (2 mks)
- What is the importance of a reconnaissance in field work. (5 mks)
- State two advantages and two disadvantages of observation as a method of data collection. (4 mks)
- State four factors that must be considered when preparing a questionnaire. (4 mks)
-
-
- Explain how the following factors influence the exploitation of minerals.
- Technology (2 mks)
- Quality of the ore (2 mks)
- Accessibility (2 mks)
- Explain four factors which influence the occurrence of minerals. (8 mks)
- Name the minerals found in the following areas in East Africa. (5 mks)
- Kariandusi –
- Kerio valley –
- Mwadui –
- Ruhuhu valley –
- Tororo -
- Explain three ways in which minerals contribute to the economy of Kenya. (6 mks)
- Explain how the following factors influence the exploitation of minerals.
-
- What is ‘dead ground’ in photograph work? (2 mks)
- Give two differences between aerial photographs and ground photographs. (4 mks)
- Below are the nine parts of a photograph, name the parts marked A, B, C and D.
A C B D - Name the three types of ground photographs. (3 mks)
- Describe the clues that may be used to interpret the following in a photograph:-
- Relief of an area. (3 mks)
- Drainage of an area. (3 mks)
- Industrial and mining activities. (3 mks)
- State three advantages of photographs. (3mks)
-
- What is statistical data? (2 mks)
- Name the two types of questionnaires. (2 mks)
- State two disadvantages of interviews as a method of data collection. (2 mks)
- List the three types of sampling. (3 mks)
- Study the data in the table below and answer the questions that follow.
Kenya: Leading export crops by value (Ksh. Million)
CROP TEA HORTICULTURE UNROASTED COFFEE 2000 35150 21210 11700 2001 34480 19840 7460 2002 34370 28330 6540 2003 33000 36480 6280 2004 36000 39540 6940 - Calculate the percentage increase in values of each export commodity between the years 2003 and 2004. (6 mks)
- On a graph paper, draw a comparative line graph to represent the data in the table above. (6 mks)
- What two conclusions about the three commodities can you draw from the graph? (2 mks)
- State two advantages of using comparative line graphs. (2 mks)
-
- Distinguish between indigenous forests and planted forests. (4 mks)
- Explain how the following factors influence the distribution of natural forests.
(6 mks)- Temperature
- Altitude
- Soils
- State four characteristics of temperate hardwood forests. (4 mks)
- Explain three factors that favour the development of softwood forests in Canada. (6 mks)
- State five problems facing forestry in Kenya. (5 mks)

MARKING SCHEME
- Define the term ‘photograph’ (2 mks)
- This is an image of an object recorded by a camera on a film.
- List three limitations of using photographs. (3 mks)
- Photographs are expensive to produce.
- Vertical aerial photographs are difficult to interpret without steveoscopes.
- If the camera is not well focused, images may be blurred.
- Some objectives especially in aerial photographs may not be clear.
- Define the term ‘photograph’ (2 mks)
-
- State the three types of fieldwork. (3 mks)
- Field study or field teaching
- Excursions
- Field work research
- List three ways through which data may be presented. (3 mks)
- Drawing graphs and charts.
- Drawing sketch maps and diagrams.
- Displaying the completed questionnaires
- Playing the tapes
- Writing a report
- Giving a lecture
- Displaying the labeled samples.
- State the three types of fieldwork. (3 mks)
-
- What is mining? (2 mks)
- This is the process of extracting valuable minerals both solid and liquid, from the earth’s crust.
- Name three methods of underground mining. (3 mks)
- Slope mining/shaft method
- Solution mining
- Adit mining/Adit method
- Drilling method
- What is mining? (2 mks)
-
- What is forestry? (2 mks)
- This is the science of developing and managing forests, including cultivating them.
- Name the three major natural forests of the world. (3 mks)
- Tropical Hardwood forests
- Temperature Hardwood forests
- Coniferous forests
- What is forestry? (2 mks)
-
- State the two characteristics of both primary and secondary data. (2 mks)
- Discrete
- Continous
- Write down two methods that can be used in taking measurements as a method of collecting data. (2 mks)
- Pacing
- Estimating
- Counting
- Using instruments e.g tape measure, thermometer, meter rule etc.
- State the two characteristics of both primary and secondary data. (2 mks)
- (Compulsory)
You intend to carry out a field study on the weather experienced in the locality of your school.-
- State four ways you would prepare for the study. (4 mks)
- Seek permission from relevant authorities
- Conduct a reconnaissance
- Formulate objectives and hypothesis for the study.
- Choose appropriates methods of data collection.
- Assemble the necessary tools.
- Prepare a working schedule.
- Divide he students into groups.
- State two hypothesis for the study. (2 mk)
- The area experiences abrupt changes of weather in most of the days.
- Most of the days, the area experiences long sunny periods.
(Any other appropriate hypothesis).
- Describe how you would use the raingauge during the study. (4 mks)
- I would take the rainwater which has collected in the collecting bottle(jar) over the past 24 hours.
- I would pour the water in a measuring cylinder specially designed for this purpose.
- I would take the reading.
- I would record the reading in the field book or table.
- The readings would be taken on a daily basis.
(The correct procedure must be followed to score)
- State how you would record the information while in the field. (2 mks)
- I would enter data into the field book in the respective columns.
Or - I would prepare a table and enter the data in the table against the appropriate data.
- I would enter data into the field book in the respective columns.
- State four ways you would prepare for the study. (4 mks)
- What is the importance of a reconnaissance in field work. (5 mks)
- To help in identifying methods of data collection.
- To help in formulating the hypothesis and objectives of the study.
- To assist in estimating the cost of the study.
- To seek permission from the relevant authorities.
- To contact the resources persons and guides.
- To determine the appropriate routes to be used in the field.
- To help in preparing a work schedule.
- To identify problems that are likely to be encountered.
- State two advantages and two disadvantages of observation as a method of data collection. (4mks)
- Advantages
- The data is reliable because it is first-hand information.
- One collects only what is relevant to the study.
- It saves time since one does not have to look for data also where but records exactly what is observed.
- Disadvantages
- Its expensive because one has to travel distance to get to the source of the information.
- It is tedious.
- It is time consuming because one has to look everywhere for the information.
- It limits one to only direct sources of information.
- It’s only suitable for sighted people.
- Old data my not be available to the observer.
- Wrong conclusions can be made when information has change with time.
- Advantages
- State four factors that must be considered when preparing a questionnaire.
(4 mks)- The questions asked should be simple and clear and not ambiguous.
- The questions should not be too many as this discourages the respondents.
- The questions should be arranged in a logical order from the simplest to the most difficult.
- The questions should be strictly related to the topic under study.
- The questions should not annoy the respondent or touch on their privacy or personal life.
- The questions should not be bias.
-
-
- Explain how the following factors influence the exploitation of minerals.
- Technology (2 mks)
- Availability of technical skills and relevant modern machines encourage more mining and lack of the same discourages mining because it becomes too expensive when they have to be imported.
- Quality of the ore (2 mks)
- High quality ores are economical to extract as they yield a large amount of minerals while low,quality ores are rarely extracted since their mineral content is low thus uneconomical.
- Accessibility (2 mks)
- Minerals deposits in remote areas with poorly developed transport systems are less likely to be exploited since it becomes too expensive, while those mineral deposits near ports, and railway lines are likely to be exploited more.
- Technology (2 mks)
- Explain four factors which influence the occurrence of minerals. (8 mks)
- Vulcanicity – As a result of igneous activity the minerals in molten form may solidity in cracks, clerical faults and joints. (veins and lodes)
- Metamorphism – Sometimes heat, great pressure and gases force certain mineral particles within the rocks to change into new minerals.
- Weathering – under hot and humid tropical conditions, rocks are deeply weathered. The process of leaching results in the concentration of minerals in the earth’s crust.
- Erosion – Erosion loosens small minerals particles which are then transported by running water in streams and rivers to the lowlands, hence deposited as alluvial deposits.
- Sedimentation – Deposition, accumulation and concentration of minerals in specific areas over a long period of time may make them occur in layers, beds or seams.
- Evaporation – Evaporation of water from lakes and ponds found in arid and semi-arid regions may enhance crystallization of salts, leading to the formation of common salt and gypsum. These salts may later be covered by other deposits making them occur as underground seams.
- Name the minerals found in the following areas in East Africa. (5 mks)
- Kariandusi – Diatomite
- Kerio valley – Flourspar
- Mwadui – Diamonds
- Ruhuhu valley – Coal
- Tororo – Limestone or phosphate
- Explain three ways in which minerals contribute to the economy of Kenya. (6 mks)
- Kenya earns foreign exchange from the exportation of minerals which is used to improve other sectors of the economy.
- Minerals provide raw materials for manufacturing industries. Eg. Trona is used in manufacture of glass, soap, paper etc.
- Mining encourages development of transport and communication facilities.
- Mining activities provide job opportunities for many Kenyans hence raising their standard of living.
- Mining has facilitated provision of infrastructure and social amenities eg. Proper housing, schools and hospitals eg. Magadi Soda Company provides these.
- Explain how the following factors influence the exploitation of minerals.
-
- What is ‘dead ground’ in photograph work? (2 mks)
- This refers to the areas hidden from view of the camera.
- Give two differences between aerial photographs and ground photographs. (4 mks)
- Aerial photos cover relatively large areas compared to ground photographs that can only capture a much smaller area.
- Aerial photographs are taken from the air while ground photographs are taken from the ground.
- Aerial photographs show all the ground features in ground photographs, features near the camera block those further away.
(2 x 2 = 4 mks)
- Below are the nine parts of a photograph, name the parts marked A, B, C and D.
(4 mks)
A – Left backgroundA C B D
B – Right middle ground
C – Middle middle ground
D – Left foreground - Name the three types of ground photographs. (3 mks)
- Ground general view photograph
- Ground close-up photograph
- Ground oblique photograph
- Describe the clues that may be used to interpret the following in a photograph:-
- Relief of an area. (3 mks)
- Presence of hills indicate a highland area.
- Gullies indicate a steep and heavily eroded area.
- Terraced landscapes indicate a steep area.
- Growth of crops e.g tea and coffee show highland areas while rice indicates a plain.
(Any other relevant clue)
- Drainage of an area. (3 mks)
- Lapids and waterfalls indicate that the river is flowing on a steep or hilly area.
- Meanders indicate that the river is flowing on a gentle slope or almost flat land.
- Flood plain indicates that the river is in its old stage.
- Presence of swamp indicate a depression or flat land.
- Long narrow lakes indicate a place affected by faulting.
(Any other relevant clue)
- Industrial and mining activities. (3 mks)
- Factory buildings with large chimneys emitting more.
- Large open pits, large excavators and lorries carrying loads of rocks, show that mining is taking place.
- Nucleated settlement for workers indicate the presence of industries and mines.
- Relief of an area. (3 mks)
- State three advantages of photographs. (3mks)
- Photographs are easy to take. One does not need specific skills to a photograph.
- Taking photographs is not time consuming.
- Photographs are more realistic in showing physical features.
- Photographs record different stages of particular activities or changes that occur in a place over time.
- What is ‘dead ground’ in photograph work? (2 mks)
-
- What is statistical data? (2 mks)
- This refers to the actual facts and figures collected from various areas and arranged in an organized manner.
- Name the two types of questionnaires. (2 mks)
- Personal interview questionnaire
- Rigid questionnaire
- State two disadvantages of interviews as a method of data collection. (2 mks)
- Language barrier may arise where the respondent can only use mother tongue.
- Interviews can be expensive especially where they are conducted directly hence the researcher moves from place to place.
- Interviews are time consuming as the researcher can only talk to one respondent at a time.
- List the three types of sampling. (3 mks)
- Random sampling
- Systematic sampling
- Stratified sampling
- Study the data in the table below and answer the questions that follow.
- Calculate the percentage increase in values of each export commodity between the years 2003 and 2004. (6 mks)
Tea = 36000 − 33000 × 100 = 3000 × 100 = 9.09%
33000 33000
Horticulture = 39540 − 36480 × 100 = 3060 × 100 = 8.39%
36480 36480
Unroasted coffee = 6940 − 6280 × 100 = 660 × 100 = 10.51%
6280 6280 - On a graph paper, draw a comparative line graph to represent the data in the table above. (6 mks)
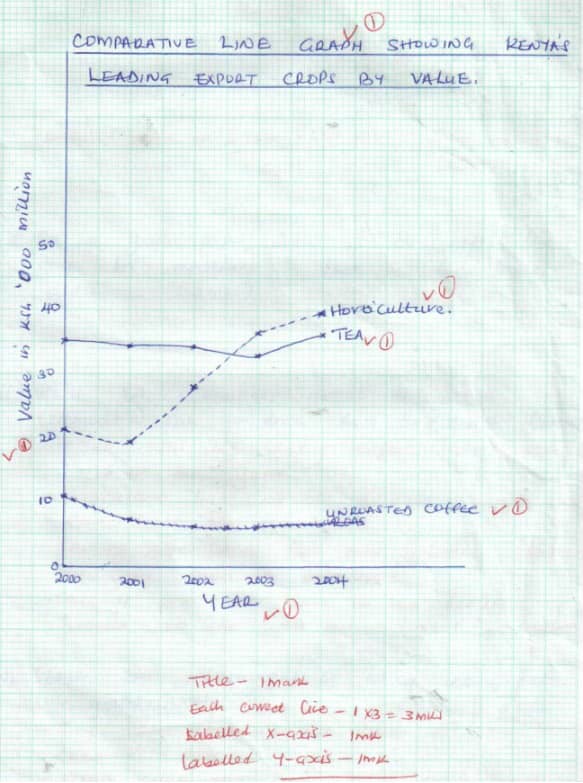
- What two conclusions about the three commodities can you draw from the graph? (2 mks)
- Tea was the leading export crop earlier up to the year 2002.
- Horticulture has been the leading export crop earlier since the year 2003.
- Earnings from coffee have been declining between the years 2000 and 2003.
- Earnings from tea were on the decline between 2000 and 2003 but increased in 2004.
- State two advantages of using comparative line graphs. (2 mks)
- They make comparison of trends for the various commodities easy.
- Exact values can easily be read for each graph since all graphs are plotted from a common base.
- They are simple to construct.
- Comparison of items is easy as all the graphs are drawn on the same chart using common axis.
- Can be used to present more than one set of items unlike many other graphs.
- Calculate the percentage increase in values of each export commodity between the years 2003 and 2004. (6 mks)
- What is statistical data? (2 mks)
-
- Distinguish between indigenous forests and planted forests. (4 mks)
- Indigenous forests are forests that are composed of natural trees that are native to a country while exotic forests are composed of trees that are introduced to a country from other parts of the world.
- Explain how the following factors influence the distribution of natural forests. (6 mks)
- Temperature
- Proper forest growth takes place in areas that receive heavy precipitation. Areas that are very cold or temperatures are very high discourage growth of forests.
- Altitude
- Altitude affects temperature and rainfall very high altitude areas experience very low temperatures which inhibit tree growth. High altitude areas receive high rainfall which supports forest growth.
- Soils
- Forests do well in areas with deep fertile and well drained soils. Thin infertile soils cannot support forest growth.
- Temperature
- State four characteristics of temperate hardwood forests. (4 mks)
- Trees have broad leaves.
- There is a variety of tree species but less than those in the tropical hard wood forests.
- Trees are deciduous. They shed leaves during autumn and remain without leaves in winter.
- Trees are hardwoods but not very bulky.
- The main tree species include silver oak, beach oak, olive and blackwood.
- The forests are fairly open. This makes them easier to exploit.
- Explain three factors that favour the development of softwood forests in Canada. (6 mks)
- The ruggedness of the landscape and thin soils discourage agriculture, hence most of the mts are covered by forests.
- There’s high precipitation throughout the year which encourages forest growth.
- The very low temperatures experienced in Canada discourage settlements and other forms of land use leaving forestry the only economic activity.
- Canada has a low population density. This means that there is a lot of available land for forests.
- State five problems facing forestry in Kenya. (5 mks)
- Cleaning of forests for competition for land for settlement and agriculture hence reducing forest cover.
- There is pest and disease attack. Eg. Cypress trees are attacked by aphids.
- There is degazettement of state forests where large forest area have been cleared reducing the total area under forests.
- Fire outbreaks caused by honey harvesters and hunters have destroyed large areas of forest cover.
- There is illegal logging to get timber and other forest products.
- Wild animals also cause damage to forests, when their population becomes too high causing overgrazing.
- Poor management of forests by government by failing to implement forest conservation policies leading to destruction of large areas of forest land.
- Distinguish between indigenous forests and planted forests. (4 mks)
Download Geography Paper 2 Questions and Answers - Form 3 Mid Term 2 Exams 2021.
Tap Here to Download for 50/-
Get on WhatsApp for 50/-
Why download?
- ✔ To read offline at any time.
- ✔ To Print at your convenience
- ✔ Share Easily with Friends / Students

