INSTRUCTIONS TO CANDIDATES
- Write your name and admission number in the spaces provided above.
- Sign and write the date of examination in the spaces provided.
- ANSWER ALL QUESTIONS IN THE SPACES PROVIDED.
- All working must be clearly shown where necessary.
- Mathematical tables or silent electronic calculators may be used.

QUESTIONS
- Define the following terms (3mks)
- Isotopes
- Mass number
- Isomers
-
- Give a reason why ammonia gas is highly soluble in water. (1mk)
- The structure of ammonium ion is shown below
Name the type of bond represented in the diagram by N H……………………… (1mk)
- Both diamond and graphite have giant atomic structures. Explain why diamond is hard while graphite is soft. (2mks)
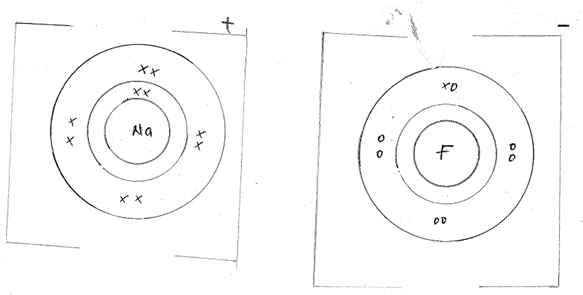
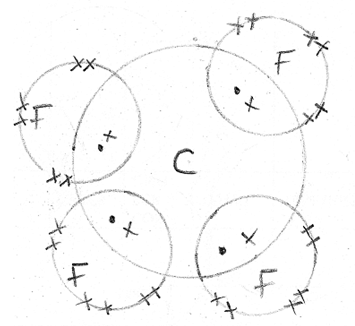
- Using dot (.) and crosses(x) to represent electrons, show bonding in the compounds formed when the following elements reacts. (C-=6, Na=11, F=9)
- Sodium and fluorine (1mk)
- Carbon and fluorine (1mk)
- The table below gives information about the major components of crude oil. Study it and answer the questions that follow.
Components
Boiling point oC
Gases
Below 40
Petrol
40-175
Kerosene
175-250
Diesel oil
250-350
Lubricating oil
350-400
Bitumen
Above 400
- Which of the compounds of crude oil has molecules with the highest number of carbon atoms? Explain (1mk)
- Name the process you would use to separate a mixture of diesel and petrol (1mk)
- What condition could cause a poisonous gas to be formed when Kerosene is burnt (1mk)
- The set up below was used to prepare nitric (V) acid
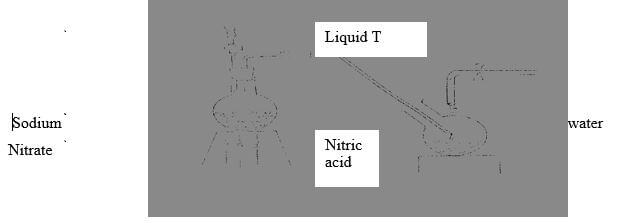
- Give the name of liquid T(1mk)
T……………………………………………………………………………………… ..(1mk) - Write the equation for the reaction which took place in the reaction flask (1mk)
- Explain why nitric acid is stored in a dark bottle (1mk)
- Give the name of liquid T(1mk)
- The table below gives information on four elements represented by K L M & N. Study it and answer the questions that follow. The letters do not represent the actual symbols of the elements.
Elements
Electron arrangement
Atomic radius
Ionic radius
K
2, 8 2
0.136
0.065
L
2, 8, 7
0.099
0.181
M
2, 8, 8, 1
0.203
0.133
N
2, 8, 8, 2
0.174
0.099
- Which two elements have similar chemical properties? Explain (2mks)
- A certain carbonate XCO3 , reacts with dilute hydrochloric acid according to the equation
XCO3(s) +2HCl (aq) → XCl2 (aq) + CO2 (g) + H2O (l)
If 4g of the carbonate reacts completely with 40cm3 of 2M hydrochloric acid, calculate the relative atomic mass of X.
(C=12.0 ,O=16.0, Cl=35.5). (3 Marks) - Give two uses of ethene gas (2 Marks)
-
- What is meant by allotropy? (1 Mark)
- The diagram below shows the structure of one of the allotropes of carbon.
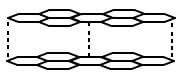
- Identify the allotrope ( 1 Mark)
- State one property of the above allotrope and explain how it is related to its structure. (2 Marks)
- 60cm3 of oxygen gas diffused through a porous hole in 50seconds. How long will it take 80cm3 of sulphur(iv)oxide to diffuse through the same hole under the same conditions (S=32.0 , O=16). (3 Marks)
- The ionisation energies for three elements X,Y, and Z are shown in the table below:
Element
X
Y
Z
Ionisation energy
(KJ/mole)
419
318
394
- What is meant by ionisation energy? (1 Mark)
- Which element is the strongest reducing agent? Give a reason. (2 Marks)
- In the figure below:
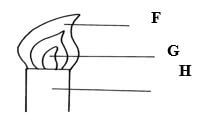
- Name the parts labeled F, G, and H. (1 ½mks)
F……………………………………………………………………………………………....
G……………………………………………………………………………………………....
H…………………………………………………………………………………………….... - Describe an experiment that would confirm that region labeled G is unsuitable for heating (1½mks)
- Name the parts labeled F, G, and H. (1 ½mks)
- The diagram below is a set up used to investigate the effect of heat on hydrated copper(II) sulphate. Study the diagram and answer the questions that follow.
copper (II) sulphate crystals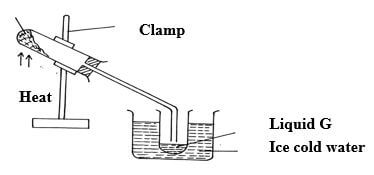
- Why is boiling tube slanted as shown? (1mk)
- What is observed in the boiling tube. (1mk)
- Identify liquid G. (1mk)
- The electronic arrangement of two stable ions Q2+ and P2- are 2.8.8 and 2.8.8 respectively.
- Write the electron arrangement of atoms Q and P. (1mks)
Q………………………………………………………………………………………....…
P………………………………………………………………………………………....… - What is the most likely structure of an oxide element P? (1mk)
- Write the electron arrangement of atoms Q and P. (1mks)
- The set up below was used by a student. Filter paper soaked in purple litmus solution was placed in the middle of the combustion tube.
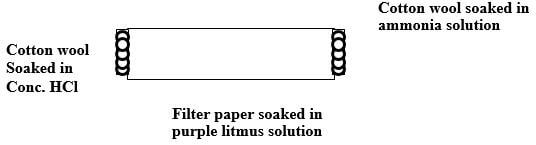
- What is the main aim of the experiment. (1mk)
- State the first observation likely to have been made in the tube. Explain the observation. (2mks)
- The empirical formula of a compound is CH2 and it has a molecular mass of 42.
- What is the molecular formula of this compound? (1mk)
- Write the general formula of the homologous series to which the compound belongs. (1mk)
- Draw the structural formula of the third member of this series and give its IUPAC name. (1mk)
- 3.22g of hydrated sodium sulphate, Na2SO4 X H2O were heated to a constant mass of 1.42 g. determine the value of X in the formula ( Na=23.0, S = 32.0, O = 16, H = 1) (3mks)
- Complete the following reactions. (2mks)
- C2H2 → 1 mole of HCl(s)
1 mole Cl2 - CH3CH3 U.V light
- C2H2 → 1 mole of HCl(s)
- A white solid K was heated. It produced a brown gas A and another gas B which relights a glowing splint. The residue left was yellow even after cooling.
- Identify gases A and B (1mks)
- Write a balanced chemical equation for the decomposition of solid K. (1mk)
- An atom X contains 90% of 168X isotope and 10% of 188Xisotope. Calculate the relative atomic mass of X. (2mks)
- Explain why aluminium articles are not easily corroded. (1mk)
- Dry chlorine gas was passed through two pieces of coloured cotton cloth as shown.
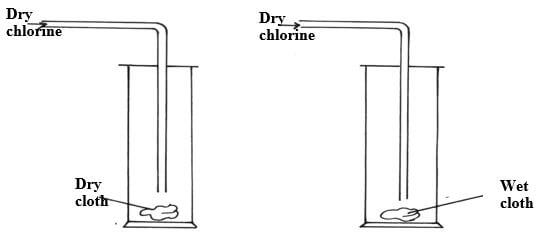
- State what is observed in each experiment. (2mks)
Experiment 1
Experiment 2 - Explain your observation using an equation for experiment 2 (1mk)
- State what is observed in each experiment. (2mks)
- When burning magnesium ribbon is put into a gas jar of carbon (IV) oxide gas, it continues to burn leaving behind white solid powder and black solid specks as residue write chemical equation for the reaction that produces.
- The white solid powder. (1mk)
- Black solid specks. (1mk)
- Describe how you would obtain pure solid samples of each of the following components of a solid mixture containing ; Lead (II) chloride, Sodium carbonate and calcium sulphate. (3mks)
-
- State Boyle’s gas Law. (1mk)
- A fixed mass of a gas has a volume of 250cm3 at 27ºC and 750mmHg pressure. Calculate the gas volume that the gas would occupy at 41ºC and 750mmHg pressure. (0º = 273k) (2mks)
- The diagram below shows a sample of ammonium chloride being heated in a dry boiling tube containing a plug of cotton and dump red litmus paper
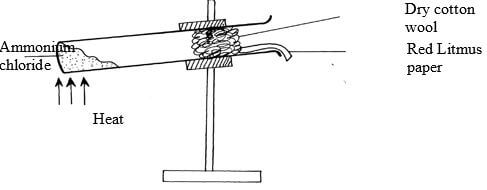
State and explain what would be observed on the red litmus paper. (2mks) -
- The following diagram represents a set-up used to investigate conditions necessary fro rusting of iron.
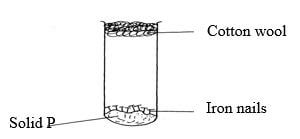
After several days it was found that the nails did not rust. Identify solid P. (1mk)
- The following diagram represents a set-up used to investigate conditions necessary fro rusting of iron.
-
- Write a chemical equation for the combustion of laboratory gas , when the Bunsen burner produces a non-luminous flame. (1mk)
- Describe two observable characteristics of aluminous flame. (1mk)
- Name the following compounds (1 mark)
- CH3CH=CHCH3
- CH3-CH2-CH-CH2CH2CH3 (1 mark)
CH2CH3
- The diagram below represents aset up that can be used to react Lithium with water to produce gas X which is then reacted with copper II oxide.
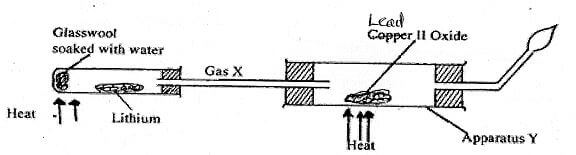
- Write an equation for the reaction between gas X and CuO (1mark)
- Give the observation made in the apparatus (1 mark)
- Why is it necessary to burn excess gas at the end of the jet (1 mark)
- Solution R,S and T have PH values shown in the table below:
Solution
pH value
R
1.0
S
6.5
T
8.0
- What do you deduce about the nature of solution R? (1 mark)
- Which solution would react most vigorously with sodium hydrogen carbonate. (1 mark)
- Which solution is likely to be ammonia solution? (1 mark)

MARKING SCHEME
-
- Atoms of the same element with same atomic number but different mass
no.s/neutrons - Total sum of protons and neutrons
- Compounds with the same molecular formula but different structural formula
- Atoms of the same element with same atomic number but different mass
-
- Both ammonia and water are polar molecules and hydrogen bonds are formed.
- Co-ordinate bond/dative bond.
- In diamond all the bonds are strong covalent bonds while in graphite structure has layers that are held together by weak vander waals forces that are easily broken
-
-
-
- Bitumen, last to be collected has the highest boiling point.
- Fractional distillation
- Limited supply of oxygen
-
- Conc. Sulphuric(VI) acid reject if concentrated missing
- H2SO4 (l) + NaNO3(s) NaHSO4(aq) + HNO3(g)
- Prevent decomposition of nitric acid by light
- K and N; same group/same valence electrons/loose two electrons
- No. Of moles of HCl in 40cm3 of 2M HCl
Moles of HCl in 40cm3 + 2M HCl
=40 x 2= 0.08 moles
1000
XCO3 : HCl
1 : 2
Moles of XCO3 =0.08 x 1= 0.04 moles
2
0.04 moles → 4g
1 mole → ?
1 x 4= 100g
0.04
XCO3 = 100
X = 100 - [12 + (16 x 3)] = 40g -
- Artificial ripening of fruits
- Manufacture of polyethene
-
- allotropy is the existence of an element in more than one form without change of state
-
- graphite
-
- it is a lubricant because layers slide over each other
- a good conductor of both heat and electricity because it has delocalised/mobile electrons
- RO2 = √MMSO2
RO2 MMO2
Rate of O2 = 60/50 = 12cm3/s
1.2 = √64
RO2 32
1.2 = 1.414
RO2
= 0.8486
0.8486 = 80/t
t = 80/0.8486
= 94.27 sec.
-
- It is the minimum energy required to remove an electron from an atom in gaseous state
- Y. It has the lowest ionization energy hence requires the least amount of energy to give out its electron
-
- F – pale blue zone
G – almost colourless zone
H – chimney ( ½mk each) - Slip a piece of manila paper /wooden splint into region and quickly remove before it catches fire. The inner part remains unburnt// not charred ( 1½mks)
- Hold a match stick on a pin and let the head rest on the chimney when the chimney is lit the head of the match stick in the zone does not light.
- F – pale blue zone
-
- Prevent water formed to run back to hot part which could crack
- Blue solid turns white //crystals form powder //colourless drops of liquid on cooler parts
- G is water
-
- Q – 2.8.82 (1mk) P – 2. 8.6 (1mk)
- oxide of P has simple molecular structure (1mk)
-
- Compare rate of diffusion of gases
- Litmus turns blue NH3 diffuses faster since it is lighter ( 2mks)
-
- (CH2)n = 42
(12 + 2)n = 42
14n = 42
n = 3 √ ½
Mf = 3(CH2) C3H6 √ ½ - CnH2n √ 1
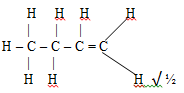
But-2-ene
- (CH2)n = 42
- Cpd - 3.22g mass of NaSO4 = 1.42g
Mass of H2O = 3.22 – 1.42 = 1.8g √ ½
Na2SO4 H2O
Mass 1.42 1.8
Moles 1.42 = 0.01 √ ½ 1.8 √ ½ = 0.1
142 18
Mole ratio 0.01√ ½ 0.1
0.01 0.1
1:10
X = 10 √ ½ -
- CH3CH2OH Conc. H2SO4 170ºC CH2CHC1
- CH3CH3 1 mole Cl2(g) U.V light CH3CH2Cl(g) + HCl(g)
-
- A – Nitrogen (IV) oxide √ 1/ NO2(g)
B – Oxygen/ O2(g) √ 1 - 2Pb(NO3)2(s) 2PbO(s) + 4NO2(g) + O2(g) √ 1
- A – Nitrogen (IV) oxide √ 1/ NO2(g)
- (90/100 x 16) + (10/100 x 18) √ 1
= 14.4 + 1.8 = 16.2 √ 1 - Aluminium reacts with oxygen to from aluminium oxide which coats the surface of he article and prevents further reaction with air and water. √ 1
-
- Exp. 1 – No change on the dry cloth because no formation of hypoochlorous acid responsible for bleaching.
Exp. 2- The wet cloth turned white due to bleaching as chlorine dissolves in water in the wet cloth to form hypochlorous - Cl2(g) + H2O(l) HCl(aq) + HOCl(aq)
- Dye + HOCl(aq) {Dye +[O] } + HCl √1
- Exp. 1 – No change on the dry cloth because no formation of hypoochlorous acid responsible for bleaching.
-
- O2(g) + 2Mg(s) 2MgO(s) √ (1mk)
- 2Mg + CO2(g) 2MgO(s)+ C(S) √ (1mk)
-
- Mix With Cold Water, Sodium Carbonate Dissolves√ (½mk)
- Filter off Lead (II) Chloride And Calcium sulphate as residue √ (½mk)
- Evaporate the filtrate to obtain sodium chloride
- Mix the residue with hot water to dissolve Lead (II) chloride√ (½mk)
- Filter off Calcium sulphate as a residue dry over dessicator
- Cool the filtrate to precipitate Lead (II) chloride √ (½mk)
Filter off residue as Lead (II chloride and dry √ (½mk)
- The volume of a given mass of a gas at constant temeprature is inversely proportional to its pressure√ (1mk)
- Red litmus paper turns blue since ammonium chloride decomposes to form ammonia and hydrogen chloride gas ammonia diffuses faster
- Anhydrous Calcium Chloride
-
- Either
CH4(g) + O2(g) CO2(s) + 2H2O(g)
2C2H6(g) + 7O2(g) 4CO2(g) + 6H2O(l)
C3H8(g) + 5O2(g) 3CO2(g) + 4H2O(l)
2C4H10(g) + 13O2(g) 8CO2(g) + 10H2O(l) - Yellow √(½mk) // sooty
Large, unsteady, √(½mk)
- Either
-
- But-2-ene✔1
- 3 –ethylhexane✔1
-
- H2(g) + CuO(s) Cu(s) + H2O(l)
- lead(ii)oxide Changes colour from orange to grey lead
- to prevent an explosion when it mixes with air. ✔1
-
- it is strongly acidic✔1
- R✔1
- T✔1
Download Chemistry P1 Questions and Answers - Form 3 Term 3 Opener Exams 2022.
Tap Here to Download for 50/-
Get on WhatsApp for 50/-
Why download?
- ✔ To read offline at any time.
- ✔ To Print at your convenience
- ✔ Share Easily with Friends / Students