QUESTIONS
SECTION A (30MARKS)
Instructions: Answer all the questions in the space provided
- State four factors to consider when siting farm structures. (2 marks)
- State four reasons for keeping livestock healthy. (2 marks)
- Name two breeds of goat kept for milk production originating from temperate regions. (1 mark)
- Name four examples of external parasites belonging to class insecta. (2 marks)
- State four safety precautions to be observed when using workshop tools. (2 marks)
- State four duties of a worker bee. (2 marks)
- Distinguish between crutching and ringing as used in livestock production. (1 mark)
- List four methods of preserving fish after harvesting. (2 marks)
- State four factors that determine nutritional requirement of an animal. (2 marks)
- Explain the functional difference between a rip saw and cross-cut saw. (1 mark)
- State four signs of parturition in cattle. (2 marks)
- Name four sources of energy concentrates (2 marks)
- Identify four signs of heat in a rabbit. (2 marks)
- State four predisposing factors of livestock diseases. (2 marks)
- State four structures necessary for handling dairy animals. (2 marks)
- State two ways in which underground water sources can be polluted. (1 mark)
- State two ways that show good feeding help to control livestock diseases. (1 mark)
- What is cropping to fish farming? (1 mark)
SECTION B (20MARKS)
Answer all questions in this section
- A poultry farmer has maize containing 8 % DCP and soya bean containing 43% DCP .If the farmer wants to make 100kg of the feed using Pearsons square method .Calculate the proportions in which the two ingredients would have to be mixed to make a feedstuff containing 15% DCP.(Show your working) (5marks)
-
- Identify the practice demonstrated in the illustration below. (1 mark)
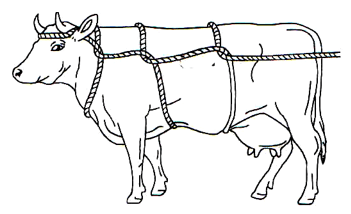
- Give four occasions when it may be necessary to carry out the practice above in livestock. (2 mark)
- Give two animal conditions under which the method cannot be used. (2 marks)
- Identify the practice demonstrated in the illustration below. (1 mark)
- The following is an illustration of the digestive system of a ruminant.
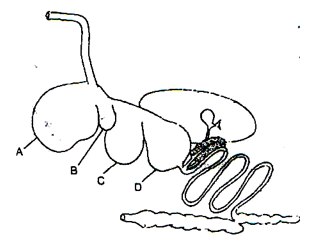
- Name the parts labelled A, B, C and D. (2 marks)
- Name the part of the system where microbial activity takes place. (1 mark)
- State two microbial activities that take place in the part named in (b) above. (2 marks)
-
- Identify the following workshop tools. (2 marks)
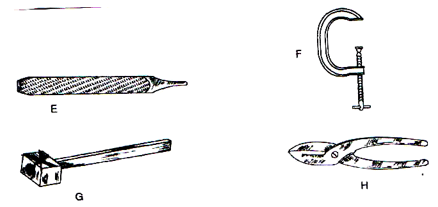
- State the use of each tool in the farm (2 marks)
- How would a farmer maintain tool labelled F. (1 mark)
- Identify the following workshop tools. (2 marks)
SECTION C (40MARKS)
Answer two questions in this section
-
- Explain the importance of fencing in the farm. (8 marks)
- Explain six functional requirements of a calf pen. (6 marks)
- Describe the procedure of harvesting honey. (6 marks)
-
- Explain six general methods of disease control. (12 marks)
- Describe the life cycle of two host tick. (5 marks)
- State three control measures of tapeworm. (3 marks)
-
- Explain eight characteristics of indigenous cattle breeds. (8 marks)
- Give four differences between the large white and land race breeds of pig. (4 marks)
- Describe the management during parturition in cattle. (8 marks)
MARKING SCHEME
- Factors to consider when using farm structures
- Accessibility
- Location of homestead
- Topography
- Proximity to amenities
- Farmer tastes and preferences
- Relationship between structure
- Direction of prevailing wind.
- Drainage. Any 4× ½ =2 mks
- Reasons for keeping livestock healthy.
- Healthy animals produce good quality products
- Healthy animals give maximum production.
- Healthy animals do not spread diseases to animals or human.
- Good health gives animals a longer economic and productive life .
- Healthy animals grow well and fast to reach maturity quickly.
- Healthy animals are economical and easy to keep. Any 4× ½ =2 mks
- Dairy goats include:
- Saanen
- Toggenburg
- British alphine Any 2× ½ =1 mk.
-
- Tse tse flies
- Keds
- Mosquitoes
- Flies
- Lice
- Fleas Any 4× ½ =2 mks
- Precautions when using workshop tools.
- Tools should always be left in safe place after use.
- Use the correct tool for the correct purpose.
- Tools should be maintained and serviced to remain in good working conditions.
- Tools should be handled correctly in use.
- Use safety devices to reduce accidents.
- All tools should be stored properly in a tool cabinet or tool racks. Any 4× ½ =2 mks
- Duties of a worker bee:
- Clean the hive.
- Collect nectar, pollen and tree resins.
- Collect water.
- Guard the hive.
- Feed the queen.
- Feed the brood and drones.
- Built combs and seal cracks
- Make honey and bee wax. Any 4× ½ =2 mks
- Crutching is the practice of cutting wool around the external reproduction organ of a female sheep while ringing is the practice of trimming wool around the sheath of the penis of rams to facilitate mating.1×1=1m (mark as a whole)
- Methods of preserving fish.
- Sun drying
- Salting
- Freezing
- Smoking Any 4× ½ =2 mks
- Factors determining nutritional requirement of an animal.
- Age
- Body weight
- Physiological condition
- Exercise /Activity.
- Level of production.
- Weather condition. Any 4× ½ =2 mks
- Rip saw are used for cutting along grains of wood while cross cut saw is used for cutting across the grains. 1×1=1 mks
- Signs of parturition in cattle
- Restleness
- Swollen vulva
- Clear mucus discharge from the vulva.
- Pelvis muscles slacken.
- Full and distended udder.
- Thick milk from the teats.
- Water bag appears and burst before calving. Any 4× ½ =2 mks
- Sources of energy concentrates.
- By products of flour mills.
- By product of breweries.
- By products of sugar industries
- Whole grain 4× ½ =2 mks
- Signs of heat in a rabbit.
- Restlessness
- Frequent urination
- Swollen vulva
- Doe throws itself on its side.
- Doe rubs against the ball.
- Doe try to attract other rabbit’s in the next hutch. Any 4× ½ =2 mks
- Predisposing factors of livestock diseases.
- Age
- Sex
- Colour
- Species
- Breed
- Physiological condition
- Environment
- Overcrowding. Any 4× ½ =2 mks
- Structures necessary for handling dairy animals.
- Milking shed/parlour
- Crush
- Spray race/plunge dip.
- Calf pen 4× ½ =2 mks
- Ways in which underground water sources can be polluted.
- Run –off water
- Contamination with sewage /human waste.
- Oils and acids from washing of machinery.
- Mixing with chemicals from the farm.
- Ways that show good feeding help to control livestock diseases.
- Control deficiency diseases
- Impart resistance to diseases.
- Enhance good physical appearance /good coat cover. Any 2× ½ =1 mks
- Cropping is remove of marketable size fish from the pond. 1×1=1 mk
-
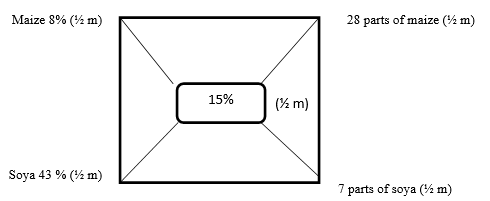
Total parts = 28 + 7 = 35 parts ( ½ m)
Kg of maize = 28/35 x 100=80kg (1m)- kg of soya = 7/35 x 100=20 kg (1m)
-
- Casting an animal
-
- When inspecting an animal
- When castrating an animal.
- When dehorning /disbudding.
- When branding
- When trimming hooves. Any 4× ½ =2 mks
-
- When the animal is pregnant.
- When the animal has physical injuries. 2×1=2mks
-
-
- A-Rumen
- B-Reticulum
- C-Omasum
- D-Abomasum 4× ½ =2 mks
- Rumen (part A) 1×1=1mk
-
- Fermentation of food.
- Synthesis of vitamin B complex and K.
- Breakdown of proteins to peptides, amino acid and ammonia.
- Breakdown of carbohydrates /cellulose in to volatile fatty acids. Any 2×1=2 mks
-
-
-
- E-wood rasp
- F-G-clamp
- G-Mallet
- H-Tin -snip. 4× ½ =2 mks
-
- E - smoothing wood surface /curved surfaces.
- F - Holding objects securely while carrying out various operations.
- G - Driving wood chisels.
- H - Cutting thin sheet of metal. 4× ½ =2 mks
-
- Lubricant moving parts
- Oil to prevent rusting.
- Clean after use. Any 1×1=1m
-
-
- Importance of fencing.
- Perimeter fence demarcates the farm land from that of neighbours.
- Fence keeps off wild animals and other intruders.
- Fences are used to separate crop fields from pastures facilitating mixed farming.
- They provide security to the homestead and farm animals.
- They enable farmer to control breeding.
- They help to isolate sick animals from the rest thus preventing diseases.
- They are used to divide pasture in to paddocks facilitating controlled grazing system.
- Controls the movement of animals and people preventing formation of unnecessary paths in the farm.
- Fences help to control the spread of parasites and diseases by keeping off wild animals.
Any 8×1=1=8 mks
- Structural requirements of a calf pen.
- Leak proof roof-The roof should not leak to avoid wetness.
- Draught free-The calf pen should be constructed in such a way that the windward side wall is completely solid to prevent cold wind.
- Proper drainage-The area should be well drained .Poor drainage cause dampness which predisposes the calf to infections.
- Proper lighting –Calf pen should be properly lit to enhance synthesis of vitamin D.
- Single housing-Only one calf should be allowed in a pen to prevent calves from licking each other.
- Adequate space –calf pen should be allowed in a pen to prevent calves from licking each other.
- Adequate space-calf pen should be large enough to allow room for exercise, feeding and watering.
- Concrete floors –This makes cleaning easy. Any 6×1=6mks
- Procedure of harvesting honey
- Honey is harvested early in the morning or late in the evening.
- Approach the hive quietly and blow smoke around the hive and later through the entrance holes using a smoker.
- Lower the hive to the ground.
- Remove the lid.
- Cut the combs from each top bar three centimeters from the surface and place them in a clean container rubbing off the bees using a twig.
- Place back the bars care not to disturb the brood.
- Return the hive to its position. 6×1=6 mks
- Importance of fencing.
-
- General methods of disease control.
- Proper feeding and nutrition –proper feeding not any, avoid deficiency diseases but alo make animal strong hence able to resist disease attack.
- Proper breeding and selection –Healthy animals should be selected for breeding .Such animals should be resistant to prevalent diseases.
- Proper housing and hygiene –Animal houses should meet the necessary requirements for particular animals.
- Isolation of sick animals-This is done to prevent further spread of the disease.
- Imposition of quarantine –Incase of an outbreak of a notifiable disease in a given area effective quarantine measures should be taken.
- Slaughtering affected animals-Incase of attack by highly infectious and contagious disease, it’s advisable to isolate and slaughter the infected animal.
- Use of anti-septic and disinfectants-This ensures cleanliness in the animal houses and surroundings.
- Use of prophylactic drugs-include coccidiostats, drenching animals, use of long lasting drugs and addition of antibiotics in livestock feed.
- Carrying regular vaccination –it’s an artificial way of giving an ani8mal some immunity against particular disease.
- Control of vectors-This help to control transmission of particular diseases such as trypanosomiasis and East Coast Fever.
Any 6×2=12 mks
Stating 6×1=6 mks
Explanation 6×1=6 mks
- Life cycle of two host tick.
- Eggs on the ground hatch in to larvae which climb onto the first host.
- Larvae attach themselves to the host, feed on blood, become engorged and moult in nymph.
- Nymph feeds on the same host, become engorged and then drops on the ground to moult to adults.
- Adults seek a second host on which they feed.
- Adults mate before females fall off to lay eggs. 5×1=5 mks
- Control measures of tapeworm
- Proper meat inspection
- Proper cooking of meat
- Use of latrines by farm workers
- Keep feeding and watering equipment clean.
- Practice rotational grazing.
- Keep animal houses clean.
- Use of prophylactic drugs. Any 3×1=3mks
- General methods of disease control.
-
- Characteristics of indigenous cattle breeds.
- Have humps that store fat which is broken down to energy and water during starvation.
- They are fairly tolerant to high temperatures due to presence of dewlap.
- They have high tolerance to tropical diseases e.g. trypanosomiasis.
- They have4 slow growth rate leading to slow maturity.
- They have low production of both meat and milk.
- They can walk for long period without food and water.
- They have long calving internal for more than a year. 8×1=8 mks
- Differences between large white and land race.
Large white
Land race
Has bread and slightly dished snout.
Has straight snout.
Has got upright ears
Has long ears which drop over the face.
Skin may have few blue spot s.
Completely white in colour.
Large body
Lean body.
- 4×1=4 mks (Mark as a whole)
- Management of cattle during parturition.
- Separate cow from the rest and put in a separate paddock /stall.
- Watch the animal closely.
- Assist animal in case of difficulties
- Allow the cow to clean the calf to facilitate quick and efficient breathing.
- Assist the calf to breath in case of problems.
- Tie and cut the navel cord with a sterilized razor or knife.
- Disinfect the navel cord using iodine
- Ensure placentas are expelled within 24hrs after calving.
- Contact a veterinarian to remove the placenta incase its refrained.
- Assist the calf to suckle colostrum.
- Give the cow plenty of clean water and feed. Any 8×1=8 mks
- Characteristics of indigenous cattle breeds.
Download Agriculture Paper 2 Questions and Answers - Form 3 End Term 3 2022 Exams.
Tap Here to Download for 50/-
Get on WhatsApp for 50/-
Why download?
- ✔ To read offline at any time.
- ✔ To Print at your convenience
- ✔ Share Easily with Friends / Students

