QUESTIONS
SECTION A
(Answer all the questions from this section)
-
- Define the term mineral. (2 marks)
- Give three examples of metamorphic rocks. (3 marks)
-
- Differentiate between rotation and revolution of the earth. (2 marks)
- State three reasons why the interior of the earth is very hot. (3 marks)
-
- Name two areas in Kenya where heath and moorland vegetation is found.(2 marks)
- State threecharacteristics of mangrove forests. (3 marks)
- The diagram below shows a vertical section through the zones of underground water.
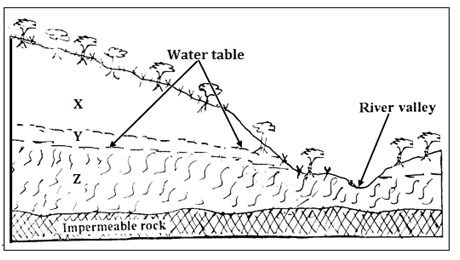
- Name the zones marked X, Y and Z (3 marks)
- State three ideal conditions necessary for the formation of an artesian well. (3 marks)
- Outline four ways through which lakes in Kenya were formed. (4 marks)
SECTION B
(Answer question 6 and any other two questions from this section)
- Study the map of Yimbo provided and use it to answer questions that follow.
-
- Give two methods used to present relief on the map extract. (2 mark)
- What is the latitudinal extent of the area covered by the map? (2mark)
- Determine the six figure grid reference of a waterhole North of Port Southby. (2 marks)
-
- Identify four types of natural vegetation in the area covered by the map. (4 marks)
- Citing evidence from the map, give two social services offered in the area covered by the map. (4 marks)
- (Describe the relief of the area covered by the map (5 marks
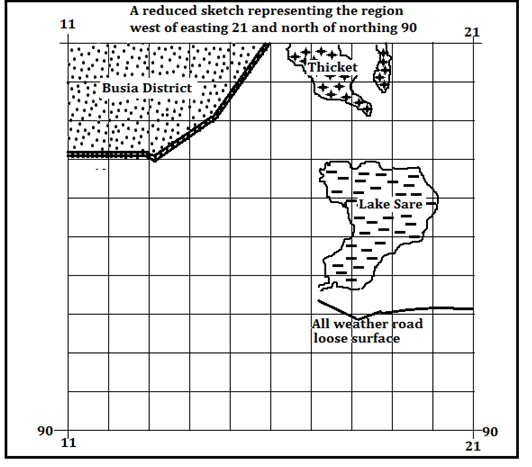
- Draw a square 10 cm by 10 cm to represent the region west of easting 21 and North of Northing 90. On the square, mark and name:
- Lake Sare
- A thicket
- Busia District
- All weather road loose surface. (6 marks)
-
-
-
- Differentiate between weather and weather forecasting. (2 marks)
- Give three examples of low clouds. (3 marks)
- Explain how the following factors affect the temperature of a place:
- Cloud cover. (3 marks)
- Aspect. (3 marks)
- With the aid of a well labelled diagram, describe how convectional rainfall is formed. (8 marks)
- Suppose you were to carry out a field study at a weather station:
- State three objectives that you would set for the study. (3 marks)
- Give three follow up activities for the field study. (3 marks)
-
- The diagram below represents types of faults and some fault features.
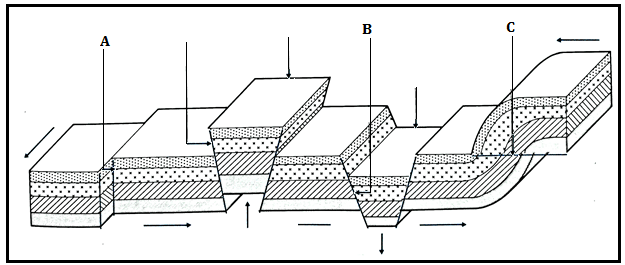
- Name the type of faults marked A, B and C. (3 marks)
- Explain how Isostatic adjustment causes earth movements (3 marks)
-
- Apart from rift valleys and fault blocks, list three other features formed due to faulting. (3 marks)
- Using well labelled diagrams, describe how a rift valley is formed due to compression forces. (8 marks)
- Explain four ways through which features resulting from faulting affects human activities. (8 marks)
-
- Define the term desertification. (2marks)
- Explain three ways in which wind transports its load (6marks)
- With the aid of a well labeled diagram, describe how yardangs are formed (7 marks)
- A group of form four students went out for a field study on action of water in an arid area.
- Name three erosional features that they are likely to have observed (3 marks)
- State three problems they have encountered during the field study. (3marks)
- What activities would they recommend to the residents in the area as an effort to control desertification? (4 marks)
-
- List three types of glacier. (3marks)
- Explain how glacier erodes through the following processes.
- Plucking (3 marks)
- Abrasion (3 marks)
- The diagram below shows some features formed due to glacial deposition in lowlands.
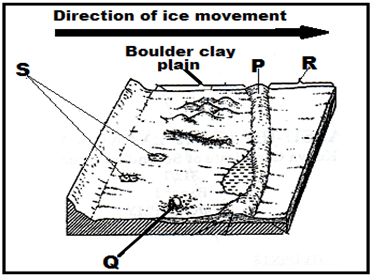
- Name the parts marked P, Q, R and S. (4marks)
- Describe how a glacial troughis formed. (6marks)
- Explain three negative effects of glaciated landscapes. (6 marks)

MARKING SCHEME
SECTION A
-
- Define the term mineral. (2 marks)
A mineral is an inorganic and crystalline substance occurring naturally with a definite chemical composition at / beneath the surface of the earth. - Give three examples of metamorphic rocks. (3 marks)
- Marble
- Quartzite
- Slate
- Schist
- Graphite
- Soapstone
- Gneiss
- Hornblende
- Define the term mineral. (2 marks)
-
- Differentiate between rotation and revolution of the earth. (2 marks)
Rotation refers to the spinning of the earth on its axis whereas revolution refers to the movement of the earth round the sun on its orbit. - State three reasons why the interior of the earth is very hot. (3 marks
- The original heat at formation is still being retained.
- Intense pressure from the weight of overlying materials which generates a lot of heat.
- Due to the breakdown of radioactive elements releasing heat in the interior.
- Differentiate between rotation and revolution of the earth. (2 marks)
-
- Name two areas in Kenya where heath and moorland vegetation is found. (2 marks)
- Mt. Kenya
- Mt. Elgon
- Aberdare Ranges.
- State three characteristics of mangrove forests. (3 marks)
- Trees have aerial roots which grow from the trunk into the sea.
- The trees are hardwoods.
- Trees are medium in size with branches at low levels.
- The leaves are hard and broad.
- The trees are evergreen.
- The tree barks are thin and smooth
- Name two areas in Kenya where heath and moorland vegetation is found. (2 marks)
- The diagram below shows a vertical section through the zones of underground water.
- Name the parts zones marked X, Y and Z (3 marks)
X – Zone of non-saturation
Y – Zone of intermittent/seasonal saturation
Z – Zone of permanent saturation - State three ideal conditions necessary for the formation of an artesian well. (3 marks)
- The aquifer must lie in between two impermeable rocks.
- The aquifer must bend downwards from the intake area to form a broad shallow basin.
- The sides of the aquifer must be exposed in a high rainfall area or a lake.
- The aquifer must be made of the same material to allow water to pass through.
- The mouth of the artesian well must be at a lower level than the intake area.
- Name the parts zones marked X, Y and Z (3 marks)
- Outline four ways through which lakes in Kenya were formed. (4 marks)
- Due to crustal down warping.
- Due to faulting
- Due to vulcanicity.
- Due to erosion.
- Due to deposition.
- Due to human activities such as construction of dams.
SECTION B
- Study the map of Yimbo provided and use it to answer questions that follow.
-
- Give two methods used to present relief on the map extract.(2 mark)
- Use of contours and form lines
- Use of trigonometrical stations
- What is the latitudinal extent of the area covered by the map? (2mark)
From 0000’ to 0015’ South - Determine the six figure grid reference of a waterhole North of Port Southby. (2 marks)
283826
- Give two methods used to present relief on the map extract.(2 mark)
-
- Identify four types of natural vegetation in the area covered by the map. (4 marks)
- Thicket
- Scrub
- Scattered trees
- Woodland
- Papyrus /swamp vegetation
- Citing evidence from the map, give two social services offered in the area covered by the map. (4 marks)
- Education due to the presence of schools such as Maranda School and Orengo School.
- Health due to the presence of a dispensary at grid square 1496.
- Describe the relief of the area covered by the map. (5 marks)
- The highest point is 1318 metres at grid square 1699 while the lowest point is approximately 1137 metres along the shores of Lake Victoria
- There is a basin on the western parts that is occupied by Lake Victoria.
- Several hills such as Ramogi, Usengi, Serawongo Usire and Abiero occur in the area.
- Steep slopes occur at Ramogi and Usengi hills while most parts to the east are gently sloping.
- There are few and wide river valleys in the eastern parts of the area.
- The land generally slopes from east towards west.
- There is a col at Usengi hill.
- Some parts along river Yala in the Northern region are flat as evidenced by absence of contours.
- Identify four types of natural vegetation in the area covered by the map. (4 marks)
- Draw a square 10 cm by 10 cm to represent the region west of easting 21 and North of Northing 90. On the square, mark and name:
- Lake Sare
- A thicket
- Busia District
- All weather road loose surface. (6 marks)
-
-
-
- Differentiate between weather and weather forecasting. (2 marks)
Weather is the state of the atmosphere of a given place for a short period of time whereas weather forecasting is the prediction of the state of the atmosphere of a place for the next 24 hours, two days or week. - Give three examples of low clouds. (3 marks)
- Stratus.
- Nimbostratus.
- Stratocumulus.
- Differentiate between weather and weather forecasting. (2 marks)
- Explain how the following factors affect the temperature of a place:
- Cloud cover. (3 marks)
Dense /thick cloud cover during the day blocks insolation thus lowers the temperature. Absence of clouds ensures maximum insolation thus high day temperature.
Thick clouds at night blocks outgoing terrestrial radiation thus warmer nights than usual. Cloudless skies at night ensure maximum terrestrial radiation thus low temperatures/cold nights. - Aspect. (3 marks)
Slopes exposes to sunshine are warmer while those that are less exposed are colder.
Slopes facing towards the equator in temperate regions are warmer while those facing pole wards are colder.
- Cloud cover. (3 marks)
- With the aid of a well labelled diagram, describe how convectional rainfall is formed. (8 marks)
- Convectional rainfall mainly occurs in hot lowland regions.
- A large water body such as a lake or sea is heated through insolation causing evaporation to occur.
- Maximum heating of both the land and the water body occurs in the afternoon.
- Heated moist air above the water body rises as cooler drier air descends to replace it forming convection currents.
- As the warm moist air rises, pressure decreases causing it to expand leading to rapid cooling.
- The cooled moist air condenses at higher altitude forming dense cumulonimbus clouds.
- When the clouds are heavy, they release the water in large torrential drops as convectional rainfall mainly in the afternoon.
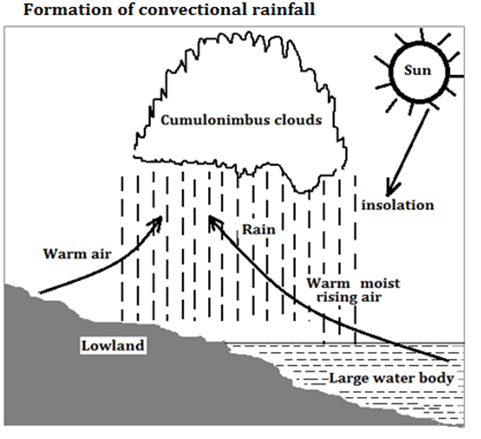
- Suppose you were to carry out a field study at a weather station:
- State three objectives that you would set for the study. (3 marks)
- To find out the highest monthly rainfall ever recorded at the station.
- To find out the hottest year recoded over the last 20 years
- To find out if the weather station receives satellite data.
- To find out how data recorded at the station is analysed.
- To find out the wettest year recorded at the station.
- Give three follow up activities for the field study. (3 marks)
- Writing a report on data collected.
- Drawing of graphs to present numerical data.
- Analysing and classifying the data collected
- Displaying processed photographs taken during the study.
- Conducting group discussions based on data collected.
- Giving a lecture to other students.
- State three objectives that you would set for the study. (3 marks)
-
- The diagram below represents types of faults and some fault features.
- Name the type of faults marked A, B and C. (3 marks)
- Shear fault
- Reversed fault
- Normal fault
- Thrust fault
- Explain how Isostatic adjustment causes earth movements (3 marks)
Processes such as erosion, deposition and melting of large masses of ice may interfere with the balance existing between the sial and the sima.(Isostacy)
Massive erosion or melting of ice on the continental crust makes it thinner/lighter while thick deposits on the oceanic crust adds a lot of weight leading to sinking inwards.
As the oceanic crust sinks, the lighter continental crust uplifts to maintain the former balance.
Sinking of the oceanic crust and uplifting of the continental crust results in vertical earth movements -
- Apart from rift valleys and fault blocks, list three other features formed due to faulting. (3 marks)
- Fault steps
- Escarpments
- Tilt blocks
- Using well labelled diagrams, describe how a rift valley is formed due to compression forces. (8 marks)
- Layers of rocks are subjected to compression forces.
- A strain occurs on the rocks leading to the formation of two adjacent and parallel reversed faults.
- Continued compression pushes the two blocks on either side of the faults (side blocks) to a higher level.
- The centre blocks is left at its position.
- The protruding sides are worn out through denudation processes such as weathering, erosion and mass wasting forming escarpments.
- The centre block at a lower level surrounded by steep escarpments is called a rift valley.
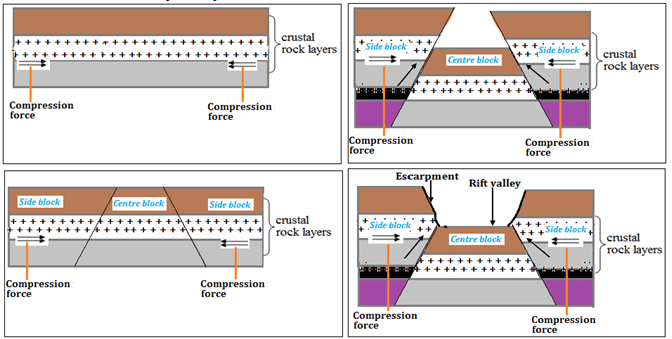
- Apart from rift valleys and fault blocks, list three other features formed due to faulting. (3 marks)
- Explain four ways in which features resulting from faulting influences human activities. (8 marks)
- Block Mountains and horsts formed through faulting are water catchment areas thus sources of rivers which provide water for agriculture domestic/ industrial use.
- Uneven sinking during the formation of a Rift Valley forms depressions that are filled with water to form of lakes that are important fishing grounds.
- Subsidence of land during formation of Rift valleys has led to exposure of minerals that are mined to generate income.
- Windward slopes of fault blocks influence formation of relief rainfall which favour agricultural activities/ forestry/ settlement.
- Faulting has resulted to formation of deep faults which are passage of steam jets that are harnessed to generate electricity.
- Faulting results in the formation of Rift Valleys, escarpments and fault blocks that form attractive sites for tourism activity thus generating income.
- Fault features such as fault blocks and escarpments create difficulties in the construction of roads, railways and pipelines thus increasing the cost of construction.
- Name the type of faults marked A, B and C. (3 marks)
-
- Define the term desertification. (2 marks)
Desertification is the process through which marginal lands are degraded due to climate change and human activities - Explain three ways in which wind transports its load (6 marks)
Saltation process occurs where coarse grained sand particles are transported through a series of shorts jumps / bouncing along the earth surface.
Suspension process is where very fine materials are picked by which raised high and blown for long distances.
Surface creep occurs where heavy materials are rolled /pushed for short distances along the earth surface over short distances. - With the aid of a well labeled diagram, describe how yardangs are formed. (7 marks)
- Initially, there existed a band of outcrop rock with alternating hard and soft rocks which did lie vertical to each other on a desert surface.
- The vertical rock layers did lie parallel to direction of the prevailing wind
- Soft rocks were eroded directly by wind through abrasion.
- Deflation process removed the worn out materials.
- With time, large furrows developed on the soft rock layers.
- The hard layers of rocks formed ridges standing in between the furrows.
- The ridges of hard rocks are called/formed yardangs
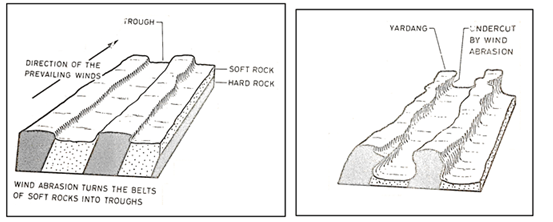
- A group of form four students went out for a field study on action of water in an arid area.
- Name three erosional features that they are likely to have observed. (3 marks)
- Wadi
- Mesas
- Buttes
- Pediment
- Pediplain
- Inselbergs
- State three problems they have encountered during the field study. (3 marks)
- Attack by snakes/insect bites
- High temperatures/Hot weather
- Poor visibility due to dust.
- Difficulty in movement due to gulleys/sand
- Shortage of water/thirst.
- Name three erosional features that they are likely to have observed. (3 marks)
- What activities would they recommend to the residents in the area as an effort to control desertification? (4 marks)
- Erecting barriers to stabilize the spread of sand dunes.
- Controlled grazing through ranching and paddocking.
- Matching the number of herds with the land carrying capacity.
- Planting of trees to protect the soil.
- Introducing drought resistant crops for food.
- Irrigating dry lands to grow food crops and trees.
- Define the term desertification. (2 marks)
-
- List three types of glacier.(3 marks)
- Cirque glacier.
- Valley glacier.
- Piedmont glacier
- Explain how glacier erodes through the following processes.
- Plucking (3 marks)
- Pressure from the overlying mass of ice cause freeze – thaw action
- Melting water fills the cracks/ joints in the bed rock
- As the water freezes, it increases in volume, exerting pressure on the cracks, thus enlarging them
- The enlarged cracks lead to disintegration of the rock
- The disintegrated rock eventually gets embedded within the ice
- As the ice moves, it pulls / gorges out the embedded rock from the parent rock
- Abrasion (3 marks)
- As the ice moves, it collects rocks and bounders on the way
- The stones and boulders are frozen into the moving ice
- Such load is dragged over the underlying rocks polishing / scrubbing/ scratching the surface
- The boulders and angular debris wear away the rocks on the surface smoothening it
- This process is called abrasion.
- Plucking (3 marks)
- The diagram below shows some features formed due to glacial deposition in lowlands.
- Name the parts marked P, Q, R and S. (4 marks)
- P-Terminal moraine.
- Q-Erratic.
- R-Outwash plain.
- S-Kettle lakes
- Describe how a glacial trough is formed.(6 marks)
- Initially, there existed a river valley in a mountainous region.
- The river valley had well developed interlocking spurs.
- The entire river valley was covered with ice during the period of glaciation.
- The river valley was eroded through plucking and abrasion.
- The former interlocking spurs were trimmed through plucking and abrasion forming truncated spurs.
- Plucking process straightened and widened the river valley while abrasion greatly deepened it.
- The eroded materials were deposited in lowlands.
- When ice melted, a wide, flat bottomed valley with steep sides called a glacial trough was formed.
- Name the parts marked P, Q, R and S. (4 marks)
- Explain three negative effects of glaciated landscapes. (6 marks)
- Some boulder clay deposits create a marshy landscape due to poor drainage which hinders agriculture.
- Moraine deposits result in the formations of numerous lakes which reduce arable land e.g within the Canadian shields.
- Infertile sands may be deposited within some outwash plains which make the land unsuitable for agriculture.
- Glaciation results in a rugged landscape which causes difficulties in settlement and construction of transport lines such as roads and railways.
- List three types of glacier.(3 marks)
Download Geography Paper 1 Questions and Answers - Form 3 End Term 2 Exams 2022.
Tap Here to Download for 50/-
Get on WhatsApp for 50/-
Why download?
- ✔ To read offline at any time.
- ✔ To Print at your convenience
- ✔ Share Easily with Friends / Students

