- State the types of change that take place in each of the following situations.
- Burning a piece of charcoal
- Heating copper (ii) carbonate strongly. (1mk)
- Heating Zinc (II) Oxide strongly. (1mk)
- Name another gas which is used with Oxygen in welding. (1mk)
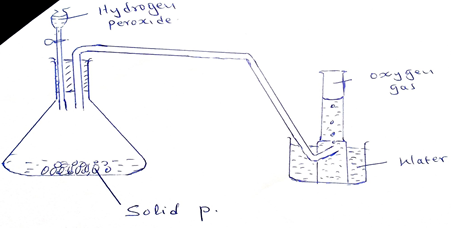
- The diagram below is a set – up for the Laboratory preparation of Oxygen gas.
- Name solid P. (1mk)
- Write an equation for the reaction that takes place in the conical flask. (2mks)
- Give two commercial uses of Oxygen. (2mk)
- State two reasons why hydrogen is not commonly used as fuel. (2mks)
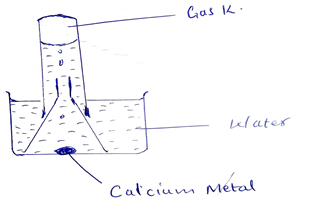
- The figure shows a set – up by a form three student to prepare a certain gas.
- Write an equation for the formation of gas K. (2mks)
- Give one use of gas K in the industries. (1mk)
- Give one use of the resulting solution after the metal has reacted. (1mk)
- Write an equation for the formation of gas K. (2mks)
- Outline the differences between luminous and non-luminous kinds of the flames. (2mk)
-
- What are acid-base indicators? (1mk)
- Outline the advantages of the universal indicator over the other acid – base indicators. (2mks)
-
- State Charles law? (1mk)
- Explain why motor vehicle tyres should not be inflated hard during the dry season if the vehicle is to be driven over a long distance during the day. (2mks)
- A gas occupies 450cm3 at 27°C. What volume would the gas occupy at 177°C; if pressure remains constant?? (3mk)
- Convert the temperature below to the absolute scale.
- 0°C (1mk)
- 50°C (1mk)
- −30°C (1mk)
- State boyle’s law of gases? (2mk)
- Describe how a solid sample of lead (II) Sulphate would be prepared using the following reagents.
- Sodium Sulphate (3mks)
- Nitric (V) acid
- Solid lead (II) Carbonate
- In the manufacture of Sodium Carbonate by Solvay process, ammoniated brine trickles down the carbonator while carbon (VI) oxide rise up the same tower.
- What is ammoniated brine? (1mk)
- What is the main source of carbon (IV) Oxide in the above process? (1mk)
- Write two equation for the reactions in the Carbonator (2mks)
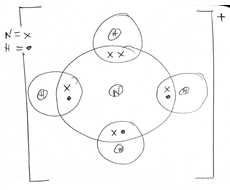
- Using dots (.) and Cross (x) to represent electrons draw diagram to represent.
- NH4+ (2mks)
- Mg2N3 (2mks)
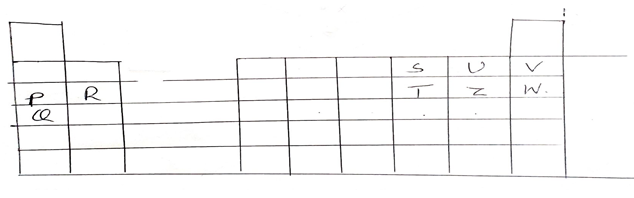
- The grid below shows part of the periodic table, use it to answer the questions follow. The letters do not represent actual symbol of elements.
- Identify the families name to which element shown below. Belongs.
- P and Q . (1mk)
- R (1mk)
- U (1mk)
-
- Which element is highly reactive metal? Explain 2mks)
- Select the element which is highly reactive non-metal. Explain (2mks)
- Which of the elements has the highest atomic radius? Explain (2mks)
- Give electron configuration of
- Element S (1mk)
- Element Q (1mk)
- Compare the atomic radius of P and R. Explain. (2mks)
- Write down the formula of the compounds formed between (2mks)
- Element P and S
- Element R and T
- Identify the families name to which element shown below. Belongs.
- Name the type of bonding and structure found in.
- Ice (2mks)
- Magnesium Chloride. (2mks)
- Explain the following observations.
- Nacl allow electric current to pass through it in a molten state. (1mk)
- Graphite is a non-metal yet it is a conductor of electricity. (1mk)
- A form 2 students electrolyzed lead (II) bromide in a fume cupboard using the apparatus shown below.
- Why is heat needed for this electrolysis? (2mks)
- Suggest the name of a substance that could be used for the electrodes. (1mk)
- State the name of the products of electrolysis at (2mks)
- The anode –
- The cathode-
- Why is heat needed for this electrolysis? (2mks)
- Element A, B, C and D are not actual symbols, have atomic number 19, 9, 12 and 10 respectively.
- Which two elements represent non- metals (1mk)
- Write down the formula of the compound formed between elements B and C and identify the bond present in the compound. 2mks)

MARKING SCHEME
- State the types of change that take place in each of the following situations.
- Burning a piece of charcoal
- Chemical change
- Heating copper (ii) carbonate strongly. (1mk)
- Chemical change
- Heating Zinc (II) Oxide strongly. (1mk)
- Physical change
- Burning a piece of charcoal
- Name another gas which is used with Oxygen in welding.
- Acetylene/ Hydrogen/Ethyne
- The diagram below is a set – up for the Laboratory preparation of Oxygen gas.
- Name solid P. (1mk)
- MnO2
- Write an equation for the reaction that takes place in the conical flask. (2mks)
MnO2
2H2O22H2O(l) + O2 (g)
- Give two commercial uses of Oxygen.
- Used in hospital for breathing difficulties
- Used by mountain climbers and sea divers.
- Name solid P. (1mk)
- State two reasons why hydrogen is not commonly used as fuel. (2mks)
- Not easily available
- Expensive
- A mixture of H2 and our explodes when ignited.
- The figure shows a set – up by a form three student to prepare a certain gas.
- Write an equation for the formation of gas K. (2mks)
Ca(s) + 2H2O(l)Ca(OH)2(aq) + H2(g)
- Give one use of gas K in the industries. (1mk)
- Used in large scale production of ammonia during Habler process.
- Give one use of the resulting solution after the metal has reacted. (1mk)
- Used in good processing
- Sewage treatment
- In paper production.
- Write an equation for the formation of gas K. (2mks)
- Outline the differences between luminous and non-luminous kinds of the flames.
- Luminous flame is long and wavy while non-luminous is short and straight.
- Luminous has four zones while non-luminous has 3 zones.
-
- What are acid-base indicators? (1mk)
- A substance that gives a definite colour in acidic and different definite colour in basic
- Outline the advantages of the universal indicator over the other acid – base indicators. (2mks)
- Universal indicators shows strengths of acids or bases while others doesn’t
- Universal indicators can be kept for long/future use unlike flower extract.
- What are acid-base indicators? (1mk)
-
- State Charles law? (1mk)
- At a constant pressure, the volume of a fixed mass of a gas is directly proportional to its absolute temperature.
- Explain why motor vehicle tyres should not be inflated hard during the dry season if the vehicle is to be driven over a long distance during the day. (2mks)
- The fixed mass of a gas is heated due to friction thus the air will increase in volume.
- A gas occupies 450cm3 at 27°C. What volume would the gas occupy at 177°C; if pressure remains constant.
V1 = V2
T1 T2
V2 = V1T2
T1
450 x 450
300
V2 = 675cm3
- State Charles law? (1mk)
- Convert the temperature below to the absolute scale.
- 0°C (1mk)
0 + 273 = 273K - 50°C (1mk)
50 + 273 = 323K - -30°C
-30°C + 273 = 243K (1mk)
- 0°C (1mk)
- State boyle’s law of gases? (1mk)
- The volume a fixed mass of a gas in inversely proportional to it’s pressure at constant temperature.
- Describe how a solid sample of lead (II) Sulphate would be prepared using the following reagents.
- Na2SO4 (3mks)
- Nitric (V) acid
- Solid lead (II) Carbonate
- Excel lead (II) Carbonate in dilute nitric acid until effervescence stops.
- Filter out the unreacted lead (II) Carbonate
- To the filtrate add Na2SO4 to precipitate out lead (II) sulphate.
- Filter the mixture to obtain residue
- Wash with distilled water and dry between the filter paper
- In the manufacture of Sodium Carbonate by Solvay process, ammoniated brine trickles down the carbonator while carbon (VI) oxide rise up the same tower.
- What is ammoniated brine? (1mk)
- It is the sodium Chloride saturated with Ammonia.
- What is the main source of carbon (IV) Oxide in the above process? (1mk)
- Heating limestone/calcium carbonate. (CaCO3)
- Write two equation for the reactions in the Carbonator (2mks)
NH3(g( + CO2(g) + H2O(l)NH4HCO3 (aq)
NH4HCO3 (aq) + NaCl(aq)NaHCO3(s) + NH4Cl(aq)
- What is ammoniated brine? (1mk)
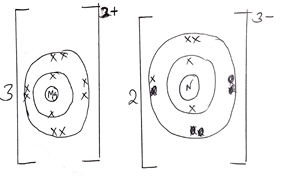
- Using dots (.) and Cross (x) to represent electrons draw diagram to represent. (2mks)
- NH4+ (2mks)
- MgN2 (2mks)
- NH4+ (2mks)
- The grid below shows part of the periodic table, use it to answer the questions follow. The letters do not represent actual symbol of elements.
- Identify the families name to which element shown below. Belongs.
- P and Q. (1mk)
- Alkali metal
- R (1mk)
- Alkaline earth metal
- U (1mk)
- Halogen
- P and Q. (1mk)
-
- Which element is highly reactive metal? Explain (2mks)
- The outermost election is loosely held to the nucleus.
- Select the element which is highly reactive non-metal. Explain (2mks)
- U
- It has high electron affinity compared to Z
- Which element is highly reactive metal? Explain (2mks)
- Which of the elements has the highest atomic radius? Explain (2mks)
- Q- it has 4 energy levels.
- Give electron configuration of
- Element S (1mk)
- 2.6
- Element Q (1mk)
- 2.8.8.1
- Element S (1mk)
- Compare the atomic radius of P and R. Explain. (2mks)
- P has larger atomic radius than R.
- R has many protons than P leading to an increase in nuclear charge thus increasing the force of attraction that holding the outer most electrons of R strongly to the nucleus thus decreasing the atomic radii.
- Write down the formula of the compounds formed between (2mks)
- Element P and S
- P2S
- Element R and T
- RT
- Element P and S
- Identify the families name to which element shown below. Belongs.
- Name the type of bonding and structure found in.
- Ice (2mks)
- Bond- weak van der weals forces
- Structure – Simple muscular structure
- Magnesium Chloride. (2mks)
- Bonding – Ionic
- Structure – giant ionic structure
- Ice (2mks)
- Explain the following observations.
- NaCl allow electric current to pass through it in a molten state. (1mk)
- NaCl has mobile ions and in aqueous solutions
- Graphite is a non-metal yet it is a conductor of electricity. (1mk)
- It has delocalized electrons in their structure which carry electric current.
- NaCl allow electric current to pass through it in a molten state. (1mk)
- A form 2 students electrolyzed lead (II) bromide in a fume cupboard using the apparatus shown below.
- Why is heat needed for this electrolysis? (2mks)
- To change lead (II) bromide into molten state so that ions become free and mobile
- Suggest the name of a substance that could be used for the electrodes. (1mk)
- Plantinum or graphite
- State the name of the products of electrolysis at (2mks)
- The anode – Bromine vapour (brown)
- The cathode- lead (grey)
- Why is heat needed for this electrolysis? (2mks)
- Element A, B, C and D are not actual symbols, have atomic number 19, 9, 12 and 10 respectively.
- Which two elements represent non- metals (1mk)
- B and D
- Write down the formula of the compound formed between elements B and C and identify the bond present in the compound . (2mks)
- CB2
- Is an ionic bond
- Which two elements represent non- metals (1mk)
Join our whatsapp group for latest updates
Tap Here to Download for 50/-
Get on WhatsApp for 50/-
Download Chemistry Questions and Answers - Form 3 Term 1 Opener Exams 2023.
Tap Here to Download for 50/-
Get on WhatsApp for 50/-
Why download?
- ✔ To read offline at any time.
- ✔ To Print at your convenience
- ✔ Share Easily with Friends / Students