SECTION A (40 MARKS)
Answer ALL the questions in this section in the spaces provided
-
- Distinguish between natural and acquired immunity (l mark)
- Define the term allergy (l mark)
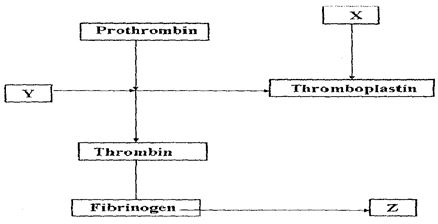
- The chart below shows the blood clotting mechanism
- Name the blood cells represented by X (1mark)
- The end product of the mechanism represented by Z (1 mark)
- Explain how the following environmental factors increase the rate of transpiration.
- Temperature (2 marks)
- Humidity (1 mark)
- Atmospheric pressure (1 mark)
- A student wanted to observe human red blood cells under a light microscope. He put l0ml of solution X,Y and Z in three boiling test tubes. The solutions were of different concentration .In each of the test tubes he put three drops of blood sample. The experiment was left to stand for 30 minutes. He placed one drop of solution X on glass slide and observed under the microscope. The same procedure was repeated for solutions Y and Z.
He made the following observation.
Solution Observation X Normal Cells Y Wrinkled Cells Z No cells observed - What was the physiological process observed. (1mk)
- Explain why red blood cells observed in solution Y were wrinkled. (3mks)
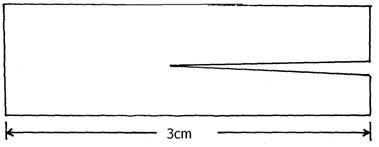
- A 3cm long piece of kale (sukuma wiki) stem was cut halfway along its length as shown below.
- If the piece was placed in solution Z for 30 minutes, its shape changed . Using a pencil draw a diagram in the space provided to show the expected change. (1mk)
- Explain the results obtained in C (i) above. (3mks)
- During an ecological study, students collected and marked 120 ants and released them. After 48 hours, the students captured another 90 ants, 20 of which had been marked previously.
- How many ants were there in the compound? Show your working. (3mks)
- What are the limitations of this method in sampling animal populations. (4mks)
- State two other methods which could be used to determine the population. (1mk)
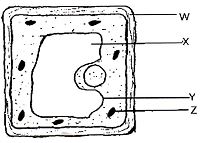
- Examine the diagram below carefully and use it to answer the questions that follow.
- Name the parts labeled X, Y, and Z (3marks)
X:
Y:
Z: - State the substance by which the part labeled W is made up of (1mark)
- Name the process by which mineral salts move into the structure labeled X (1mark)
- Explain what happens to a red blood cell when placed in distilled water. 3marks)
- Name the parts labeled X, Y, and Z (3marks)
-
- Name two sites where gaseous exchange takes place in an aquatic plant. (2marks)
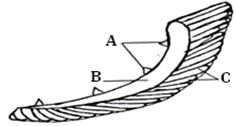
The diagram below represents the gills of a bony fish. Study it and answer the questions that follow.- Name the parts labeled A, B, and C (3marks)
- State the function of the part labeled A (1mark)
- Explain how the part labeled C is adapted to perform its functions (2marks)
- Name two sites where gaseous exchange takes place in an aquatic plant. (2marks)
Answer question 6 (compulsory) and either question 7 or 8 in the spaces provided after question 8
- Two individuals A and B drunk volumes of concentrated solution of glucose. The amount of glucose in their blood was determined at intervals. The results are shown in the table below. Time (minutes) Glucose level in blood mg / 100cm3
Time (minutes) Glucose level in blood mg/100cm3
0
15
30
45
60
90
120
150A B 87
110
135
115
100
95
90
8884
123
170
188
208
202
144
123- On the grid provided, plot graph of glucose level in blood against time on the same axis. (6marks
- What is the concentration of glucose in the blood of A and B at the 20 th minute? (1mark)
- Explain why the glucose level in person A stopped rising after 30minutes while it continued to rise in person B. (2marks)
- Account for the decrease in the glucose level in person A after 30minutes and person B after 60minutes. (4marks)
- Name the compound that stores energy released during oxidation of glucose. (1mark)
- State five factors that determine energy requirements in human (5marks)
- Name the organ in which control of blood sugar level mainly takes place. (1mark)
-
- State four characteristics of gaseous exchange surfaces. (4mks)
- Describe the mechanism of gaseous exchange in a mammal. (l6mks)
-
- What is meant by the term digestion? (2mks)
- Explain the role of bile in the digestion of food. (4mks)
- Describe the digestion of protein in the human body. (l4mks)
MARKING SCHEME
-
-
Natural Acquired Inherited/transmitted from the parent to the offspring; Developed after suffering from a disease/through vaccination - Allergy-Drastic reaction of the body seen in a few individuals towards foreign substances that are normally harmless to the rest population/hypersensitive reaction of the body to the harmless substances;
-
- Platelets/Thrombocytes;
- Fibrin clot; reject clot alone
-
- High temperature in the atmosphere causes temperature of the leaf to rise; thus increasing the vapour pressure in the intercellular air spaces this causes increase in transpiration rate;
- Low humidity in the atmosphere/dry air results to high vapour in the intercellular air space than the air surrounding the leaf; hence increase diffusion gradient hence higher transpiration rate
- Low atmospheric pressure causes an increase in evaporation from a wet surface/less opposing to evaporating molecules thus higher rate of transpiration;
-
-
- Osmosis; (1 mark)
- Solution Y is hypertonic/ high concentrations; water moved from cell to solution (2marks)
(Y);
Cell became flaccid/ shrinks; (1mark) -
- Cortex cells/ cortical cells absorbs water; expanding /curving away to the epidermis; epidermal cells are water proof; (3 marks)
-
- Approximate population = No. of organisms in first catch x No. of oragnisms in second catch
No. of marked organisms recaptured
P = FM x SC
MR ;
i.e
120 x 90
= 20 ; 540 ants; - Does not consider migration of organisms into and out of study area.
- Does not consider the effect of paint used in marking on the animals behaviour
- Released animals may not mix freely with the remaining population.
- Marked organism may not have adequate time to mix with the rest.
- Does not consider the effect of weather on the organisms behaviour (any 4)
-
- Quardrat method
- Belt transect method
- Line transect method X
- Approximate population = No. of organisms in first catch x No. of oragnisms in second catch
-
-
- X – Vacuole / Sap vacuole
- Y – Tonoplast;
- Z – Chloroplast; (3marks)
- Cellulose (1mark)
- Active transport (1mark)
- The cell sap is hypertonic to the solution / distilled water; hence water molecules move into the cell; by osmosis; making it to swell and eventually burst; (3marks)
-
-
- Pneumatophores / Aerial breathing roots;
Stomata; (2marks)-
- – Gill rakers;
- – Gill bar / arch;
- – Gill filaments; (3marks)
- Trap food / solid particles hence prevent them from clogging the gill filaments; (1marks)
-
- Highly vascularised to transport away oxygen that has diffused in;
- Thin epithelium to reduce the distance gases diffuse across;
- Numerous to increase surface area for maximum absorption of oxygen.
- Ability to spread singly when in water, further increasing the surface area. mark any 2; (2 marks)
-
- Pneumatophores / Aerial breathing roots;
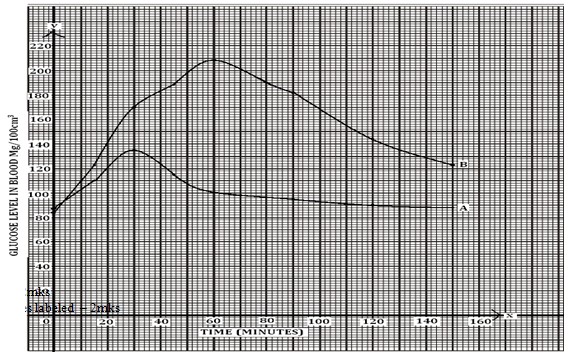
- Label axis – 2mks
- Smooth curves labeled – 2mks
- scale – 1mk
- plots – 1mk
-
- A – 120 ± 1
- B- 140 ± 1
- Person A is capable of regulating sugar while person B is likely to be diabetic
-
- In person A; insulin is released which stimulates the liver to convert excess glucose to glycogen in the liver.
- In person B; insulin is not released; thus the decline is due to glucose being released in urine.
- ATP (Adonosine triphosphate)
-
- Body size
- Occupation
- Age
- Sex gender
- Environmental condition e.g temperature
- BMR
- State of the body viz ill; expectant mother;
- Liver
-
-
- Highly vascularised/network of blood capillaries;
- Large surface area for gaseous exchange;
- Thin membrane/ epithelium/ one cell thick wall/ thin lining;
- Moist (lining); (4mks)
- Breathing in:
- External intercoastal muscles contract; internal intercoastal muscles relax; lifting/raising the ribcage upwards and outwards; muscles of diaphragm contract; hence it flattens; the volume of the thoracic cavity/lungs increases; while the pressure decreases; higher air pressure in the atmosphere forces air into the lungs( through nose);
Breathing Out: - External intercoastal muscles relax; while internal intercoastal muscles contract; moving the rib cage downwards and inwards; the muscles of diaphragm assumes dome shape; the volume of thoracic cavity decreases; while pressure increases; High pressure forcing air out of the lungs(through nose); (16mks)
(20mks)
- External intercoastal muscles contract; internal intercoastal muscles relax; lifting/raising the ribcage upwards and outwards; muscles of diaphragm contract; hence it flattens; the volume of the thoracic cavity/lungs increases; while the pressure decreases; higher air pressure in the atmosphere forces air into the lungs( through nose);
-
-
- Digestion is the enzymatic breakdown of food; into products that can be absorbed; (2mks)
-
- Bile contains bile salts (sodium taulocholate and sodium glycocholate); which emulsify fats thus increasing the surface area for the action of lipase;
- Bile also contains sodium bicarbonate; which neutralizes acid from the stomach;
- The sodium bicarbonate creates alkaline conditions necessary for the action of digestive enzymes in the duodenum and the small intestines; (5mks max4)
-
- In the mouth, the protein is chewed by the action of the teeth and mixed with the saliva for easy swallowing; (No digestion of protein occurs in the mouth)
- In the stomach, the gastric glands in the stomach wall secrete gastric juice;
- Gastric juice contains hydrochloric acid; pepsinogen and rennin;
- Hydrochloric acid activates pepsinogen into pepsin;
- HCL creates the acidic conditions necessary for pepsin to digest protein into polypeptides;
- Rennin hydrolyses the soluble milk protein/ Casein; into an insoluble curd; which is then digested by pepsin;
- in the duodenum, the acidic PH created by the HCL is neutralized by the sodium bicarbonate; present in the pancreatic juice;
- This creates alkaline conditions required by the trypsin; to digest proteins into polypeptides;
- Trypsin is also secreted here in its inactive precursor trypsinogen;
- Trypsinogen is converted into trypsin by the enzyme enterokinase;
- In the small intestine / ileum alkaline conditions prevails;
- The wall of ileum secretes intestinal juice; which contains peptides;
- Peptides complete the digestion of protein breaking polypeptides into amino acids;
(l9mks max 14)
Download Biology Paper 2 Questions and Answers - Form 3 End Term 2 Exams 2023.
Tap Here to Download for 50/-
Get on WhatsApp for 50/-
Why download?
- ✔ To read offline at any time.
- ✔ To Print at your convenience
- ✔ Share Easily with Friends / Students