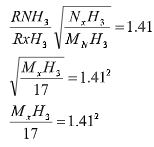-
- Distinguish between ionization energy and electron affinity. (2mks)
- The atomic number of A and B are 9 and 17 respectively. Compare the electron affinity of A and B. Explain . (1mk)
- Use the reaction scheme below to answer the questions that follow.
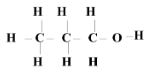
- Draw the structure of alcohol X. (1mk)
- Name process Y. (1mk)
- Write the molecular formula of the 5 th member in which propene belong. (1mk)
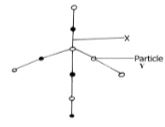
- Silicon (IV) oxide has a structure similar to that of diamond. Part of the structure is shown below.
- What does x represent? (1mk)
- What type of structure is shown by the diagram? (1mk)
- Predict one physical property of silicon (IV) oxide and explain how it is related to its structure. (1mk)
- Describe how a dry solid sample of lead (II) chloride can be prepared using the following reagents dilute nitric (V) acid dilute hydrochloric acid and lead (II) carbonate. (3mks)
-
- State Graham’s law of diffusion. (1mk)
- Ammonia gas diffuses 1.41 times faster than gas XH 3 .Determine the relative atomic mass of element X.( H =1 , N = 14) (2mks)
- An ore of iron was found to contain 7g of iron and 3g. of oxygen.( fe = 56 O =16)
- Workout its emprical formula. (2mks)
- Write a balanced equation for reaction of the oxide in (a) with hot carbon. (1mk)
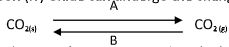
- Carbon (iv) Oxide can undergo the changes below.
- What are process A and B?
- ..................................................( 1mk)
- ..................................................(1mk)
- Suggest one use of carbon (iv) oxide that utilizes process A and B. (1 mk)
- What are process A and B?
- The table sows the PH values of solutions A to E
Solution A B C D E PH 6 13 2 10 7 - What is meant by the term PH? (1mk)
- Which of the solutions contains the largest number for hydroxide ions (1mk)
- What will be the PH value of the mixture of D and E. (1mk)
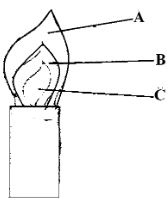
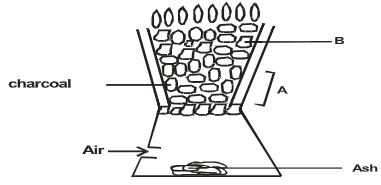
- The diagram below shows a Bunsen Burner when in use.
Which of the labeled parts is used for heating? Give a reason. (2mks) - The table below shows the atomic numbers of elements T, U, V and W. Study it and answer the questions that follow.
The letters are not the actual symbols of the elements.
Element T U V W Atomic number - What type of bond would be formed between:-
- elements U and W (1mk)
- elements V and U (1mk)
- Which of the elements are metals. (1mk)
- What type of bond would be formed between:-
- Oxygen gas can be prepared in the laboratory by catalytic decomposition of hydrogen peroxide.
- Write the chemical equation for the reaction. (1mk)
- State the Name of the suitable catalyst used. (1mk)
- Give one industrial use of oxygen (1mk)
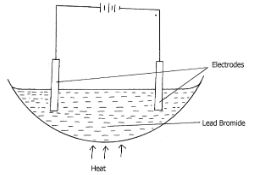
- The diagram below shows electrolysis of lead bromide
- Label the anode. (1mk)
- Write half equations to shows reactions at cathode. (1mk)
- State one application of electrolysis. (1mk)
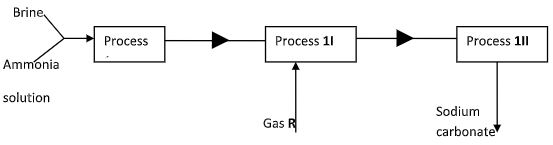
- Below is a simplified scheme of solvary process. Study it and answer the questions that follow:
- Identify gas R… (1mk)
- Write an equation for process III (1mk)
- Give one use of sodium carbonate (1mk)
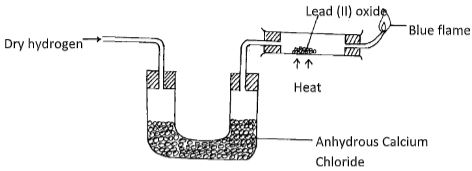
- The set-up below was used to investigate the properties of hydrogen
- State the observations that was made in the combustion tube as the reaction progressed to completion (2mks)
- Write equations for the reactions ;
- In the combustion tube (1mk)
- At the jet of the delivery tube (1mk)
- State the properties of hydrogen that were investigated (2mks)
- Classify the process below as chemical or physical changes (2mks)
Process Physical or chemical change (a) Fractional distillation (b) Displacement reaction (c) Sublimation (d) Neutralization - Iron reacts with oxygen in the presence of moisture to form hydrated iron (III) oxide. Fe2O3.2H2O
- What name is given to the process that produces hydrated iron (III) oxide? (1 mk)
- What does the term ‘hydrated’ mean? (1 mk)
- Name one method used to prevent corrosion of iron. (1 mk)
- The table below gives elements represented by letters which are not the actual symbols.
Element U V W X Y Z Atomic No. 8 12 13 15 17 20 - Select an element that can form divalent anion. (1 mark)
- What is the structure of the oxide of W? (1 mark)
- Compare the atomic radius of W and X. (1 mark)
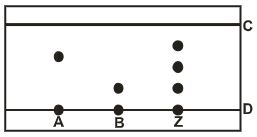
- Spots of three pure pigments A,B and mixture Z were placed on a filter paper and allowed to dry. The paper was then dipped in a solvent. The results obtained were as on the paper chromatogram.
- Identify;
- Baseline. (1mark)
- Solvent front. (1mark)
- Which pure pigment was component of Z.? (1mark)
- Identify;
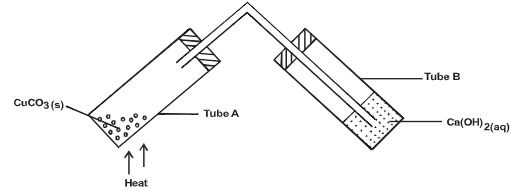
- The following was used to investigate the effect of heat on a sample of Copper(II) Carbonate.
- State the observation made in test tube. (2 marks)
- ………
- ………
- Write equation for the reaction that occurs in tube A. (1mark)
- State the observation made in test tube. (2 marks)
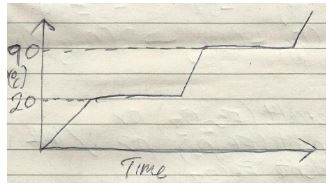
- Sketch a graph of temperature time for a pure substance A with a melting point of 20°C and boiling point of 90°C and it is heated from 0°C to 100°C. (2marks)
- The diagram below shows a burning “jiko” in a room which has sufficient supply of oxygen.
- Using chemical equations, explain what happens at A and B. (2marks)
- State the main danger of emitting excess carbon (IV) oxide into the atmosphere. (1mark)
- 3.22g of hydrated Sodium Sulphate, Na2SO4oXH2O were heated to a constant mass of 1.42g, determine the value of X in the formula. (Na = 23, S = 32, O = 16, H=1). (2 mks)
-
- The atomic number of Sulphur hydrogen and oxygen are 16, 1 and 8 respectively. Write the electron arrangement of Sulphur in the following substances.
- H2S………………………… (1 mk)
- SO32- ………………………..(1 mk)
- State the number of neutrons and electrons in the species of Aluminum shown below:
2713 Al3+
Neutrons ………………………………( 1mk)
Electrons ……………………………( 1 mk)
- The atomic number of Sulphur hydrogen and oxygen are 16, 1 and 8 respectively. Write the electron arrangement of Sulphur in the following substances.
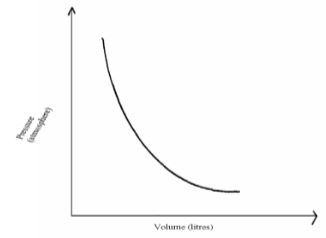
- The graph below shows the behaviour of a fixed mass of a gas at constant temperature.
- What is the relationship between the volume and the pressure of the gas. (1 mk)
- 12 litres of oxygen gas at one atmosphere pressure were compressed to 2.5 atmospheres pressure at constant temperature. Calculate the volume occupied by the oxygen gas. (2 mks)
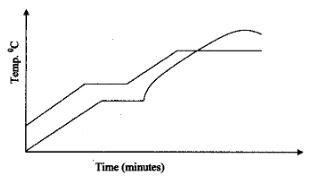
- Two samples of a similar substance from different containers were investigated. The graph below represents the variation of temperature with time when heated.
- Explain the variation in the curves of:
Sample I……………………(1mk)
Sample II……………………(1mk) - Common salt is sprinkled on roads during winter in temperate countries. Explain.(1mk
- Explain the variation in the curves of:
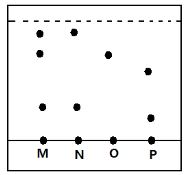
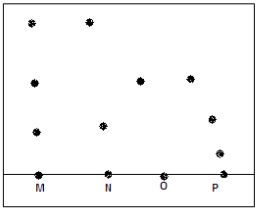
- Study the diagram below and answer the questions.
- On the diagram mark the base line. (1mk)
- Name the dyes which are in M. (1mk)
- Which mixture of dyes has the dye with lowest solubility? Explain. (1mk)
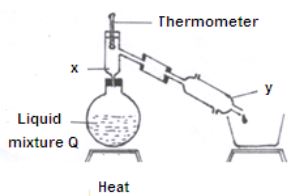
- Study the diagram below and answer the questions that follow. The diagram shows the method used to separate components of mixture Q.
- Name X and Y. (1mk)
X………………………
Y……………………… - What is the purpose of apparatus X? (1mk)
- Show the direction of flow of cold water used for cooling the vapour formed. (1mk)
- Name X and Y. (1mk)
MARKING SCHEME
-
- Ionization energy is the energy required to remove an election from 1mk atom in gaseous state while electron affinity is the energy required by an atom 1mk to require an electron in gaseous state.
- is higher / greater ½mk than A because A is smaller atom therefore its nuclear attract electrons strongly ½mk
-
- Dehydration 1mk
- C6H12 1mk
-
- Covalent bond 1mk
- Giant atomic structure 1mk
- Hard 1mk high density // high melting points Silicon and oxygen 1mk atoms are compactly held by strong covalent bonds throughout its structure
- Add ½mk excess lead (II) carbonate to dilute nitric (V) acid
- Filter ½mk to remove excess ½ unreacted lead (II) carbonate
- Add ½mk dilute hydrochloric acid to the filtrate
- Filtre ½mk and dry ½mk the residue
-
- The rate of diffusion of a gas is inversely 1mk proportional to the square root of its density provide temperature and pressure are kept constant
MXH3 = 17 X 1.142
= 33.7977 - RAM of x = 33.7977 − 3
= 28.7977
- The rate of diffusion of a gas is inversely 1mk proportional to the square root of its density provide temperature and pressure are kept constant
Fe O 7
7/56
0.125
0.1253
3/6
0.1875
0.125
½
1.5
2:3
Fe2O3- 2 Fe2O3(s) + 3C(s) → 4Fe(s) + 3CO2(g)
-
- Sublimation
- Deposition
- Temporary refrigiration
-
- Measure of acidity or basically of an aqueous solution (1mk)
- B (1mk)
- 10 (1mk)
- C - It's he hottest part (2mks)
-
-
- Ionic bond 1mk
- Covalent bond 1mk
- T ½mk and W ½mk
-
-
- 2H2O2(aq) → 2H2O(l) + O2(g) 1mk
- U.B eqn. – zero mk
- Penalise ½ mk for wrong or missing s.s
- Manganese (IV) oxide 1
-
- Used in welding and cutting metals as oxyacetyline/ oxyhydrogen.
- Used to remove Iron impurities during steel making (Any 1 x 1mk)
- 2H2O2(aq) → 2H2O(l) + O2(g) 1mk
-
- On the diagram ( left hand electrode)
- Pb(s) → Pb2+(aq) +2e 2e- → Pb2+ (l) + 2e- → Pb(s)
- Extraction of metals
-
- CO2
- 2NaHCO3(s) → Na2CO3(s) + CO2(g) + H2O(g)
- making glass, softening hard water
-
- Yellow lead (II) oxide turned to red then grey.
- H2(g) + PbO(s) → H2O(l) + Pb(s)
- 2H2(g) + O2(g) → 2H2O(l)
- Reducing properties of hydrogen
Combustion nature of hydrogen
-
- Physical change ½ mk
- Chemical change
- physical change
- chemical change
-
- Rusting
- has water of crytalization
- painting,electroplating,anodizing,Gavaization
-
- U
- Molecular
- X is smaller than W
-
-
- D 1mark
- C 1mark
- B 1mark
-
-
-
- – fumes of colourless gas observed. Green solid turns black
- – White precipitate is observed 1mark
- CuCO3 (g) CUO(s) + CO2(g) 1mk
-
-
- A: carbon reacts with excess air to form carbon(iv) oxide ½ mark
C(s) + O2(g) → CO2(g) ½ mark
B: Carbon (iv) oxide is reduced to Carbon (ii) oxide by hot carbon ½ mark
C(s) + CO2(g) → 2CO(g) ½ mark - Carbon (iv) oxide causes global warming 1mark
- A: carbon reacts with excess air to form carbon(iv) oxide ½ mark
NA2SO4 H20 Mass
RFMMoles
Divide by smallest No.
1.42
1421.42
1420.01
0.01
11.8
18
1.8
180.1
0.1
10
X = 10 ½mk-
-
- S16 = 2.8.6 (1 mk)
- S12 = 2.8.2 (1 mk)
-
- Neutron – 14 ( 1 mk)
- Electron – 10 ( 1 mk)
-
-
- At constant temperature the volume is inversely proportional to the pressure Formula
1
Vd d (1mk) - P1V1 = P2V2 ½mk
12 X1 = 2.5 X V2 ½mk
12 x 1
V2 = 2.5 ½mk = 4.8 litres ½mk (2 mks)
- At constant temperature the volume is inversely proportional to the pressure Formula
-
- Sample I is a pure substance since pure substance have a sharp melting and boiling points. (1mk)
Sample II is impure since the melting point is lower than that of a pure substance and its boiling point is higher than that of pure substance which is characteristic phenomena of an impure substance. (1mk) - Since ice causes skidding, common salt becomes an impurity to water (ice) causing it to melt at a lower temperature. (1mk)
- Sample I is a pure substance since pure substance have a sharp melting and boiling points. (1mk)
-
- M has N and O (1)
- P
-
- X- fractionating column (1mk)
Y- Liebig condenser - to condense back the component of higher boiling point. (1mk)
- shown on the diagram (1mk)
- X- fractionating column (1mk)
Download Chemistry Paper 1 Questions and Answers - Form 3 End Term 2 Exams 2023.
Tap Here to Download for 50/-
Get on WhatsApp for 50/-
Why download?
- ✔ To read offline at any time.
- ✔ To Print at your convenience
- ✔ Share Easily with Friends / Students