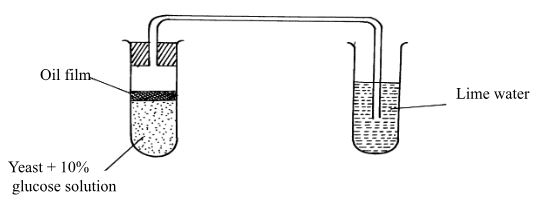
- The apparatus below was used to investigate certain process that occurs in plants:-
- Name the process that was being investigated (1mk)
- How would you remove dissolved oxygen from the glucose before the experiment commencing? (1mk)
- State what happens to the lime water as the experiment proceeds to the end (1mk)
- State the role of oil film the experiment (1mk)
- Explain what would happen if the temperature of glucose solution and yeast was raised beyond 45°C? (1mk)
- State three economic importance of the process named in (a) above in industry? (3mks)
- Two fresh potato cylinders of equal length were placed one in distilled water and the other in concentrated sucrose solution.
- State the expected observations in term of length of the potato cylinders in (2mks)
- distilled water
- sucrose solution
- Account for the change in length of the cylinder in:
- Distilled water (1mk)
- Sucrose solution (1mk)
-
- What would be the result in terms of length if a boiled potato was used? (1mk)
- Explain your answer in (c)(i) Above (1mk)
- State two uses of the physiological process being demonstrated in the experiment(2m)
- State the expected observations in term of length of the potato cylinders in (2mks)
-
- Distinguish between the terms homodont and heterodont. (1mk)
- What is the function of carnasial teeth? (1mk)
- A certain animal has no incisors, no canines, 6 premolars and 6 molars in its upper jaw, in the lower jaw there are 6 incisors, 2 canines,
6 premolars and 6 molars. Write its dental formula (1mk) - Suggest the likely type of food eaten yby the organism (1mk)
- The action of ptyalin stops at the stomach. Explain. (1mk)
- State a factor that denatures enzymes. (1mk)
- Name two features that increase the surface area of small intestines. (2mks)
-
- Describe how insect pollinated flowers are adopted to pollination (5 marks)
- Describe the role of each of the following hormones in the human menstrual cycle. (3 marks)
- Oestrogen
- Progesterone
- Luteinizing hormone
-
- What is meant by the following terms?
- Protandry ( 1 mark)
- Self- sterility ( 1 mark)
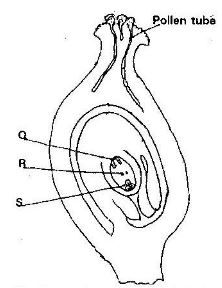
- The diagram below shows a stage during fertilization in plant
- Name the parts labeled Q, R, and S ( 3 marks)
Q
R
S - State two functions of the pollen tube ( 2 marks)
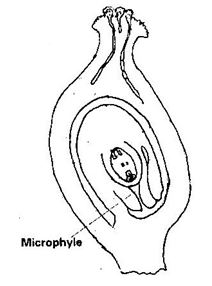
- On the diagram, label the micropyle ( 1 mark)
- Name the parts labeled Q, R, and S ( 3 marks)
- What is meant by the following terms?
SECTION B (40 MARKS)
Answer question 6 (compulsory) in the spaces provided and either question 7 OR 8 in the spaces provided after question 8.
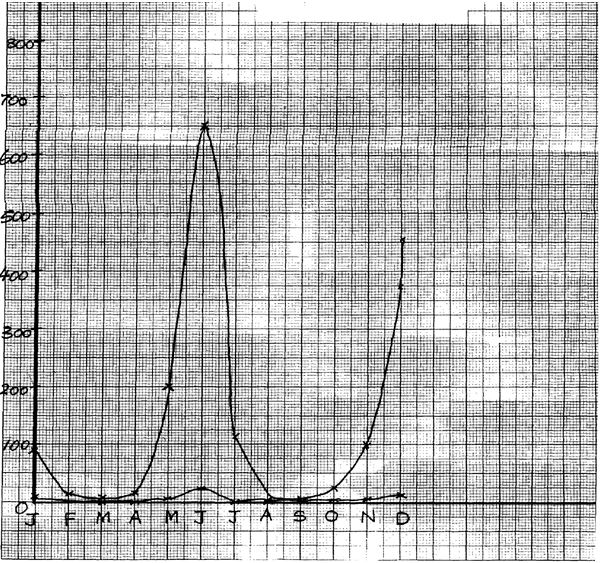
- In an ecological study, a locust population and that of crows was estimated in a grassland area over a period of one year. The results were tabulated as shown below.
Months J F M A M J A S O N D No. of Adult locusts x 102 90 20 11 25 200 625 15 10 35 192 456 Number of crows 4 2 0 1 8 22 2 1 1 5 15 Amount of rainfall 20 0 55 350 520 350 10 25 190 256 350 - Draw a graph of population of locusts and crows against time (7mks)
-
- State the relationship between rainfall and locust population (1mk)
- Account for the relationship you have stated in b (i) above (2mks)
- What happens on the populations of locusts and crows in the months of January to March? (2mks) Give a reason.
- If the area of study was one square kilometer, state one method used to estimate the population of :- (2mks)
- Locusts
- Crows
-
- State the trophic levels of the (2mks)
- Locusts
- Crows
- Construct a simple complete food chain involving these organisms (1mk)
- State the trophic levels of the (2mks)
- If the locust were removed from the food chain, what would be its effect? (2mks)
- Define biomass (1mk)
- Describe the
- Process of inhalation in mammals. (10 mks)
- Mechanism of opening and closing of stomata (10 mks)
- Describe how fruits and seeds are suited to their mode of dispersal (20mks)
MARKING SCHEME.
SECTION A (40MARKS)
- The apparatus below was used to investigate certain process that occurs in plants:-
- Name the process that was being investigated
Anaerobi respiration /fermentation; - How would you remove dissolved oxygen from the glucose before the experiment commencing? (1mk)
Boiling the glucose to expel oxygen - State what happens to the lime water as the experiment proceeds to the end (1mk)
Turns white/ becomes milky/cloody /precipitate - State the role of oil film the experiment (1mk)
prevent entry of air/oxygen thus preventing aerobic respiration - Explain what would happen if the temperature of glucose solution and yeast was raised beyond 45°C? (1mk)
High temperature denatures enzymes, reduces/stops respiration/stops the reaction.
High temperature also kills the yeast cells hence stops respiration. - State three economic importance of the process named in (a) above in industry? (3mks)
- Making of beer/Brewing/Ethanol/alcohol;
- Baking industry/Raising of the dough:
- Biogas making
- Manufacture of organic acids
- Dairy industry cheese/yoghurt making
- Name the process that was being investigated
- Two fresh potato cylinders of equal length were placed one in distilled water and the other in concentrated sucrose solution:
- State the expected observations in term of length of the potato cylinders in (2mks)
- distilled water
Increased in length - sucrose solution
Decreased in length
- distilled water
- Account for the change in length of the cylinder in:
- Distilled water (1mk)
Increased in length, absorbed water through osmosis, (since cylinder cells were hypertonic/ at higher concentration) and become turgid - Sucrose solution (1mk)
Reduced in length, cylinder lost water to the hypertonic sucrose solution/become flaccid.
- Distilled water (1mk)
-
- What would be the result in terms of length if a boiled potato was used? (1mk)
No change in length - Explain your answer in (c)(i) Above (1mk)
Cells are dead and cannot carry out osmosis
- What would be the result in terms of length if a boiled potato was used? (1mk)
- State two uses of the physiological process being demonstrated in the experiment (2mks)
- opening and closing of stomata
- Support in plants
- Movement of water from cell to cell
- Feeding in insectivorous plants
- Absorption of water by root hairs
- Absorption of water in the intestines
- State the expected observations in term of length of the potato cylinders in (2mks)
-
- Distinguish between the terms homodont and heterodont. (1mk)
Homodont-Organism has same shape,type and size of teeth
Heterodont-Organism have different number,type,size and shapes of teeth - What is the function of carnasial teeth? (1mk)
Slice flesh and crush bones - A certain animal has no incisors, no canines, 6 premolars and 6 molars in its upper jaw, in the lower jaw there are 6 incisors, 2 canines, 6 premolars and 6 molars. Write its dental formula (1mk)
I=0, C =0, PM = 3, M 3=32
3 1 3 - Suggest the likely type of food eaten by the organism (1mk)
Vegetations/grass - The action of ptyalin stops at the stomach. Explain. (1mk)
Hydrochloric acid in the stomach denatures ptyalin stopping its activity - State a factor that denatures enzymes. (1mk)
High temperatures above 400C.
Extreme pH - Name two features that increase the surface area of small intestines. (2mks)
- Villi
- Microvilli
- Highly coiling
- Long
- Distinguish between the terms homodont and heterodont. (1mk)
-
- Describe how insect pollinated flowers are adopted to pollination ( 5 marks)
- Large brightly coloured corolla / inflorescence / forests / tracts to attract insects.
- Scented to attract insects
- Have secreted nectar to attract that direct flowers secrete nectar to attract insects.
- Pollen grains rough/spiky sticky surface to stick on insect’s body.
- Special shaped corolla tube to enable the insect land.
- Describe the role of each of the following hormones in the human menstrual cycle. (3 marks)
- Oestrogen
- Repair / heal endometrium / wall of uterus, which is destroyed in menstruation.
- Stimulates pituitary gland to produce the luteinising hormone
- Progesterone
- Stimulates the thickening of the uterus,
- increases the blood supply to the endometrium.
- Inhibits the production of follicle stimulating hormone
- Luteinizing hormone
- Responsible for maturation of the graafian follicle
- Causes ovulation.
- Stimulates corpus luteum to secrete progesterone
- Oestrogen
- Describe how insect pollinated flowers are adopted to pollination ( 5 marks)
-
- What is meant by the following terms?
- Protandry ( 1 mark)
Stamens mature and pollen grains are shed off before the stigma matures. - Self- sterility ( 1 mark)
Pollen grains from the anthers cannot grow/germinate on the stigma of the same flower or plant.
- Protandry ( 1 mark)
- The diagram below shows a stage during fertilization in plant.
- Name the parts labeled Q, R, and S ( 3 marks)
Q Antipodal cells
R Polar body / polar nucleus
S Egg cell - State two functions of the pollen tube ( 2 marks)
- Path through which the male gametes reach the embryo sac to enhance fertilization.
- Prevent other pollen grains from developing into pollen tubes hence no multiple fertilization of embryo sac.
- Name the parts labeled Q, R, and S ( 3 marks)
- On the diagram, label the micropyle (1 mark)
- What is meant by the following terms?
SECTION B (40 MARKS)
Answer question 6 (compulsory) in the spaces provided and either question 7 OR 8 in the spaces provided after question 8.
- In an ecological study, a locust population and that of crows was estimated in a grassland area over a period of one year. The results were tabulated as shown below.
Months J F M A M J A S O N D No. of Adult locusts x 102 90 20 11 25 200 625 15 10 35 192 456 Number of crows 4 2 0 1 8 22 2 1 1 5 15 Amount of rainfall 20 0 55 350 520 350 10 25 190 256 350 - Draw a graph of population of locusts and crows against time (7mks)
- Labelling axes ……2mks
- Scale……………....1mk
- Plotting……………2mks
- Joining (smooth)….1mk
- Identifying the graph..1mk
-
- State the relationship between rainfall and locust population (1mk)
The population of locusts increase with increase in that the amount of rainfall; - Account for the relationship you have stated in b (i) above (2mks)
- Increased amount of food;
- Improve breeding conditions
- State the relationship between rainfall and locust population (1mk)
- What happens on the populations of locusts and crows in the months of January to March? (2mks)
Give a reason.- The population of both decreases
- Less food availability for locusts and hence crows
- If the area of study was one square kilometer, state one method used to estimate the population of :- (2mks)
- Locusts …………….capture recapture;
- Crows…………………… total counts
-
- State the trophic levels of the (2mks)
- Locusts………………. primary consumers;
- crows………………..secondaryy consumers;
- Construct a simple complete food chain involving these organisms (1mk)
Grass → Locusts → crows
- State the trophic levels of the (2mks)
- If the locust were removed from the food chain, what would be its effect? (2mks)
- Grass would increase;
- Crows would reduce
- Define biomass (1mk)
Is the total dry weight of organisms at a particular trophic level;
- Draw a graph of population of locusts and crows against time (7mks)
-
- Describe the process of inhalation in mammals. (10 mks)
- External intercostals muscle contract
- Internal intercostals muscles relax.
- Ribs moves upward and outwards-
- Diaphragm muscle contract flattening the diaphragm
- Volume in thoracic cavity
- Pressure decreases in the thoracic cavity than atmospheric pressure
- Air rushes into the lungs.
- Mechanism of opening and closing of stomata (10 mks)
- OPENING
- During the day photosynthesis takes place and sugar is formed in guard cells
- Osmotic pressure increases and water is drawn from neighbouring cells by Osmosis.
- The guard cells become turgid, bulge outward causing opening of stomata
- CLOSING
- During the night there is no photosynthesis and sugar is converted to starch.
- Osmotic pressure decrease and water is lost to the neighbouring cell osmosis.
- Guard cells become flaccid, closing the stomata.
- OPENING
- Describe the process of inhalation in mammals. (10 mks)
- Describe how fruits and seeds are suited to their mode of dispersal (20mks)
- Water dispersal
- Such seeds and fruits enclose air in them to lower their density for buoyancy;
- They are fibrous/ spongy to lower the density for buoyancy;
- Have impermeable seed coat or epicarp to prevent water from entering during flotation so as to avoid rotting;\
- The seeds can remain viable while in water and only germinate while on a suitable medium;
- Wind dispersal
- They are light; and small; to be easily carried by wind currents due to lower density;
- Have developed extension which create a larger surface area; so as to be kept afloat in wind currents e.g. * Parachute like structures; * Wing like structures;
- Animal dispersal
- Brightly colored to attract animals
- Fleshy to attract animals;
- Some have hook like structures to attach on animals fur
- Self dispersal
- They have weak lines on the fruit wall along which they burst open to release seeds, which get scattered. This occurs when temperature changes suddenly
- Water dispersal
Download Biology Paper 2 Questions and Answers - Form 3 Term 3 Opener Exams 2023.
Tap Here to Download for 50/-
Get on WhatsApp for 50/-
Why download?
- ✔ To read offline at any time.
- ✔ To Print at your convenience
- ✔ Share Easily with Friends / Students