QUESTIONS
Instructions:
Answer all the questions in the spaces provided
-
- Define a soluble base. (1mk)
- Aqueous solutions of 2M ethanoic acid and 2M nitric (v) acid were tested for electrical conductivity. Which solution is a better conductor of electricity? Explain. (2mks)
-
- Explain why it is not advisable to prepare a sample of carbon (IV) oxide using lead (II) carbonate and dilute sulphuric (VI) acid. (2mks)
- State a method that can be used to collect dry carbon (IV) oxide gas. Give a reason. (1mk)
- The following are formulae of organic compounds. Use the formular to answer the questions that follow.
CH3CH2CH2OH;
CH3COOH;
CH3CH2CH2CH3;
CH3CCCH3;
Select;-
- Two compounds which when reacted together produce a pleasant smelling compound. (1mk)
- Name the compound formed in (i) above. (1mk)
- Select an unsaturated hydrocarbon.
- Name the compound selected in a (iii) above. (1mk)
-
-
- State Boyle’s law. (1mk)
- Explain why a balloon filled with helium gas deflates faster than a balloon of the same size filled with argon gas. (2mks)
- 30.0cm3 of aqueous sodium hydroxide containing 8.0g per litre of sodium hydroxide were completely neutralized by 0.294g of a dibasic acid. Determine the relative formula mass of the dibasic acid. (Na=23, O=16, H=1) (3mks)
- Study the flow chart in figure below and answer the questions that follow.
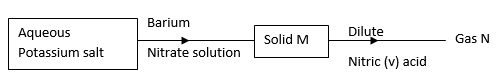
Gas N forms a white suspension with aqueous calcium hydroxide.- Name the anion present in the potassium salt. (1mk)
- Write an ionic equation for the formation of solid M. (1mk)
- Give the uses of gas N. (2mks)
- Element U has atomic number 12 while element V has atomic number 16.
- Using dot (.) and cross(x) diagram show bonding in the two elements. (1mk)
- State the bond type in the compound formed in (a) above. Explain. (2mks)
- When ethane gas is compressed at a high temperature, a solid is formed.
- Give the name of the solid. (1mk)
- Explain why it is not advisable to allow the solid accumulate in the environment. (2mks)
- In the Harber process, nitrogen reacts with hydrogen according to the following equation.
3H2(g) + N2(g) 2NH3(g) ; H= -92KJmol-1- What would be the effect of adding a catalyst on the position of the equilibrium? (1mk)
- What would be the effect of increasing the pressure to the system on the position of the equilibrium? Explain. (2mks)
- Explain why it is not advisable to use temperatures higher that 773K in the haber process. (2mks)
- You are provided with solid potassium hydrogen carbonate. Describe how a solid sample of potassium nitrate can be prepared. (2mks)
-
- Define the term molar heat of displacement. (1mk)
- The following ionic equation represents the reaction between Zinc metal and an aqueous solution of copper ions.
Zn(s) + Cu2+(aq) Zn2+(aq) + Cu(s) H =-ve
Draw an energy level diagrams to represent the reaction. (2mks)
- Study the setup below and answer the questions that follow.
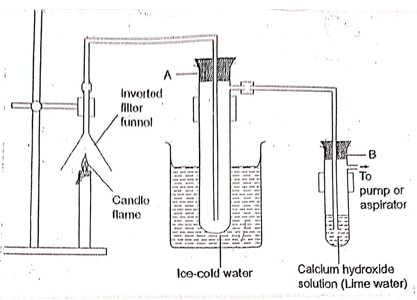
- Name the substance that was collected in test tube A. (1mk)
- Write an equation for the reaction which occurs in tube B: in
- In the first few minutes of the experiment. (1mk)
- After a long time. (1mk)
- Explain the equations in (b) above. (2mks)
- Give a suitable conclusion for the experiment in the set up. (1mk)
- Explain why a solution of sodium chloride conducts electricity while that of sugar does not. (2mks)
- Explain why commercial indicators are preferred to flower extracts as acid-base indicators. (2mks)
- (NH4)2HPO4 is a fertilizer used by farmers to boost their crop production.
- Calculate the mass of phosphorous in a 20kg packet of (NH4)2HPO4 (N=14, H=1, P=31, O=16) (2mks)
- State one advantage of this fertilizer, (NH4)2HPO4 over urea CO(NH2)2 (1mk)
- Name the technique used to separate coloured substances in green leaves. (1mk)
MARKING SCHEME
-
- Define a soluble base. (1mk)
- A substance that dissociates in water to produce hydrocide ions as the only negative ions.
- Aqueous solutions of 2M ethanoic acid and 2M nitric (v) acid were tested for electrical conductivity. Which solution is a better conductor of electricity? Explain. (2mks)
- Nitric acid
It is a strong acid hence dissociates completely to produce many hydrogen ions.
- Nitric acid
- Define a soluble base. (1mk)
-
- Explain why it is not advisable to prepare a sample of carbon (IV) oxide using lead (II) carbonate and dilute sulphuric (VI) acid. (2mks)
- The reaction starts but soon stops.
- It is the insoluble calcium sulphate produced which form a coating on the surface of the calcium carbonate.
- State a method that can be used to collect dry carbon (IV) oxide gas. Give a reason. (1mk)
- Downwards delivery/upward displacement of air
- Co2 is denser that air
Or - Using a gas syringe the gas produced exerts pressure on the piston then pushes it.
- Explain why it is not advisable to prepare a sample of carbon (IV) oxide using lead (II) carbonate and dilute sulphuric (VI) acid. (2mks)
- The following are formulae of organic compounds. Use the formular to answer the questions that follow.
CH3CH2CH2OH;
CH3COOH;
CH3CH2CH2CH3;
CH3CCCH3;
Select;-
- Two compounds which when reacted together produce a pleasant smelling compound. (1mk)
- CH3CH2CH2OH and CH3COOH
- Name the compound formed in (i) above. (1mk)
- propylethanoate
- Select an unsaturated hydrocarbon.
- CH3CCCH3
- Two compounds which when reacted together produce a pleasant smelling compound. (1mk)
- Name the compound selected in a (iii) above. (1mk)
- But-2-yne
NB; don’t mark if not selected in a (ii) above
- But-2-yne
-
-
- State Boyle’s law. (1mk)
- The volume of fixed mass of gas is inversely proportional to its pressure at a constant temperature.
- Explain why a balloon filled with helium gas deflates faster than a balloon of the same size filled with argon gas. (2mks)
- helium is less dense that argon; hence it diffuses out faster than argon.
Rej; deflates for diffusion
- helium is less dense that argon; hence it diffuses out faster than argon.
- State Boyle’s law. (1mk)
- 30.0cm3 of aqueous sodium hydroxide containing 8.0g per litre of sodium hydroxide were completely neutralized by 0.294g of a dibasic acid. Determine the relative formula mass of the dibasic acid. (Na=23, O=16, H=1) (3mks)
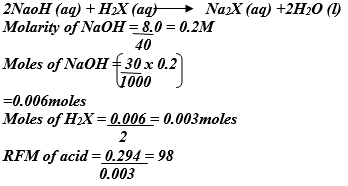
- Study the flow chart in figure below and answer the questions that follow.

Gas N forms a white suspension with aqueous calcium hydroxide.- Name the anion present in the potassium salt. (1mk)
- Carbonate/CO32- or sulphite ion, SO32-
- Write an ionic equation for the formation of solid M. (1mk)
- Ba2++CO32- → BaCO3(s)
Or - Ba2+(aq)+ SO32-(aq) BaSO3(s)
- Ba2++CO32- → BaCO3(s)
- Give the uses of gas N. (2mks)
- If CO2
- Making soft drinks/aerated drinks
- Cloud seeding
- In refrigeration
- In extinguishing fires
- Making baking powder
- If SO2
- As a fumigant
- Manufacture of H2SO4
- Bleaching agent
- A preservative
- Name the anion present in the potassium salt. (1mk)
- Element U has atomic number 12 while element V has atomic number 16.
- Using dot (.) and cross(x) diagram show bonding in the two elements. (1mk)
- State the bond type in the compound formed in (a) above. Explain. (2mks)
- Ionic/electrovalent bond
- There is complete transfer of electrons from the metal V to the non-metal V.
- When ethane gas is compressed at a high temperature, a solid is formed.
- Give the name of the solid. (1mk)
- Polythene/polyethene
- Explain why it is not advisable to allow the solid accumulate in the environment. (2mks)
- Non-biodegradable hence pollutes the environment.
Accept does not decompose for non-biodegradable.
- Non-biodegradable hence pollutes the environment.
- Give the name of the solid. (1mk)
- In the Harber process, nitrogen reacts with hydrogen according to the following equation.
3H2(g) + N2(g) → 2NH3(g) ; H= -92KJmol-1- What would be the effect of adding a catalyst on the position of the equilibrium?
- No effect/has no effect on position or equilibrium
- What would be the effect of increasing the pressure to the system on the position of the equilibrium? Explain. (2mks)
- Equilibrium shifts to the right
- Increase in pressure favour the side with fewer molecules.
- Explain why it is not advisable to use temperatures higher that 773K in the haber process. (2mks)
- Forward reaction is exothermic, excessive temperatures would favour backward reaction, it lowers the yield.
- What would be the effect of adding a catalyst on the position of the equilibrium?
- You are provided with solid potassium hydrogen carbonate. Describe how a solid sample of potassium nitrate can be prepared. (2mks)
- Measure a certain volume of dilute nitric (V) acid and place it in a beaker.
- Add potassium hydrogen carbonate little by little as the mixture is stirred until effervescence stops.
- Filter the excess KHCO3
- Evaporate the solution to saturation and allow it to cool for crystals to form.
- Dry the crystals between filter papers.
-
- Define the term molar heat of displacement. (1mk)
- The heat evolved/ the enthalpy change when one mole of a substance is displaced from its ions in solution.
- The following ionic equation represents the reaction between Zinc metal and an aqueous solution of copper ions.
Zn(s) + Cu2+(aq) → Zn2+(aq) + Cu(s) H =-ve
Draw an energy level diagrams to represent the reaction. (2mks)
- Define the term molar heat of displacement. (1mk)
- Study the setup below and answer the questions that follow.
- Name the substance that was collected in test tube A. (1mk)
- Water
- Write an equation for the reaction which occurs in tube B: in
- In the first few minutes of the experiment. (1mk)
- CO2(g) + Ca(OH)2(aq) → CaCO3(s)+H2O(l)
- After a long time. (1mk)
- CaCO3(s) + Ca(OH)2(aq) → CaCO3(s) +H2O(l)
- In the first few minutes of the experiment. (1mk)
- Explain the equations in (b) above. (2mks)
- Carbon (IV) oxide reacts with calcium hydroxide (lime water) to form a white precipitate after a short while; then the precipitate dissolves to form a colourless solution when more carbon (IV) oxide is passed through it due to the formation of the soluble Ca(HCO3)2.
- Give a suitable conclusion for the experiment in the set up. (1mk)
- Burning candle produces water and CO2/ candle contains carbon and hydrogen/ candle is a compound of carbon and hydrogen/candle is a compound of carbon and hydrogen.
- Name the substance that was collected in test tube A. (1mk)
- Explain why a solution of sodium chloride conducts electricity while that of sugar does not. (2mks)
- A solution of NaCl contains free ions/ mobile ions that are free to conduct electricity while sugar contains molecule/no charged ions/ mobile ions/free ions hence cannot conduct electricity.
- Explain why commercial indicators are preferred to flower extracts as acid-base indicators. (2mks)
- The composition of commercial indicators remain constant hence gives consistent results while the composition of flower extracts changes with time giving inconsistent results.
- (NH4)2HPO4 is a fertilizer used by farmers to boost their crop production.
- Calculate the mass of phosphorous in a 20kg packet of (NH4)2HPO4 (N=14, H=1, P=31, O=16) (2mks)
- RFM of (NH4)2 HPO4 = (14x2) + (9x1) +31 (16x4)
= 28+9+31+64
= 132
31g or P = 132
20,000g of P=?
= 20,000 x 132
31
= 4697g/ 4.697kg
Or - 20/132 x 31
= 4.697kg
- RFM of (NH4)2 HPO4 = (14x2) + (9x1) +31 (16x4)
- State one advantage of this fertilizer, (NH4)2HPO4 over urea CO(NH2)2 (1mk)
- (NH4)2 HPO4 has two nutrients available for crops; nitrogen and phosphorus, while urea has only one
- Calculate the mass of phosphorous in a 20kg packet of (NH4)2HPO4 (N=14, H=1, P=31, O=16) (2mks)
- Name the technique used to separate coloured substances in green leaves. (1mk)
- Chromatography
Join our whatsapp group for latest updates
Tap Here to Download for 50/-
Get on WhatsApp for 50/-
Download Chemistry Questions and Answers - Form 4 Mid-term Exams Term 1 2022.
Tap Here to Download for 50/-
Get on WhatsApp for 50/-
Why download?
- ✔ To read offline at any time.
- ✔ To Print at your convenience
- ✔ Share Easily with Friends / Students

