QUESTIONS
- Give three methods of controlling cannibalism in a flock of layers in deep litter system. (3mks)
- Describe four characteristics of a poor layer which should be considered during culling (4mks)
- The diagram below is a cross section of part of a cow’s udder
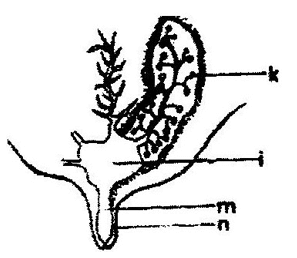
- Label on the diagram the parts marked k, I, m and n. (2mks)
-
- What is milk let down? (1mk)
- Which hormone stimulates milk let down. (1mk)
- State three practices which are carried out to control mastitis in lactating cows. (3mks)
- Explain three qualities that make colostrum suitable for newly born calves. (3mks)
- State any five practices that would ensure clean milk production (5mks)
- State six reasons why agriculture is important in Kenya economy. (3mks)
- State two methods of increasing ploughing depth when using a disc plough. (2 mks)
- State four ways of improving the labour productivity of farm labour. (4mks)
-
- Define opportunity cost as used in Agricultural economics (1mk)
- State two situations under which the opportunity cost is nil (2mks)
- State four variable costs in bean production (2mks)
- Below is a graphical representation of the law of diminishing returns.
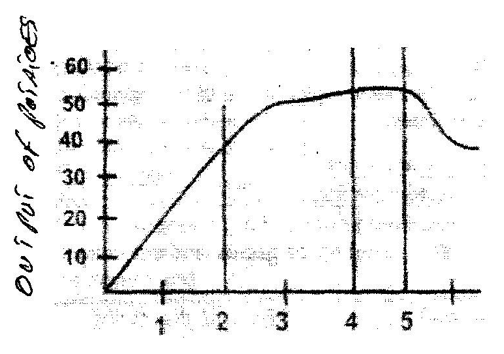
- Explain what happens in each of the Zones marked by lines in relation to output. (3mks)
- Which of the three is a rational zone of production? (1mks)
- State any three precautions a potatoes farmer would take to minimize risks in the production of potatoes. (2mks)
- Compare the use of an ox-drawn mould board plough with that of a tractor-drawn mould board plough (8 mks)
MARKING SCHEME
- Give three methods of controlling cannibalism in a flock of layers in deep litter system. (3mks)
- Feeding on balanced diet
- Hanging green vegetation to keep birds busy scatter grains on the floor
- Isolating and treating cannibalized birds
- Control external parasites
- Keeping birds according to age/ avoid introducing new birds
- Provide adequate space
- Describe four characteristics of a poor layer which should be considered during culling (4mks)
- Combs and wattles are small, dry and cold/ combs have white scales
- The space between the pelvic bones is narrow 2-3 fingers cannot fit in the space between the pelvic bones
- Plumage is shiny, well preened/ sometimes moulting
- Yellowish pigmentation in the vent, shanks and beak
- Space between the keel bone and pelvic bone is small / 3-4 fingers cannot fit in the space
- Eyes are dull and yellow
- Abdomen is hard
- The layer is lazy and dull
- The hen becomes broody
- The diagram below is a cross section of part of a cow’s udder
- Label on the diagram the parts marked k, I, m and n. (2mks)
- K- Alveolus
- L- Gland cistern
- M – Teat cistern
- N – Teat
-
- what is milk let down? (1mk)
- Milk let down is the flow of milk from the upper/ alveolar region of the udder to the gland and teat cisterns
- Which hormone stimulates milk let down. (1mk)
- Oxytocin
- what is milk let down? (1mk)
- State three practices which are carried out to control mastitis in lactating cows. (3mks)
- Practice farm hygiene/ milk infested cows last/ use a separate udder towel for each cow/ use disposable udder towel
- Immediate treatment of infected cows to avoid spread of the diseases/ treat any wounds on the teat/ udder
- Practice teat dips after milking
- Applying milk salve/ jelly to prevent drying and cracking of teats
- Practice good milking techniques
- Label on the diagram the parts marked k, I, m and n. (2mks)
- Explain three qualities that make colostrum suitable for newly born calves. (3mks)
- Has a laxative and helps to remove the faecal meconium/ first faecal matter/ opens up the alimentary canal/ cleanse the digestive system/ prevent constipation
- It is rich in antibiotics that offers temporary immunity against diseases
- It is rich digestible proteins/ fats/ minerals/ vitamin/ highly nutritious
- It is highly digestible
- State any five practices that would ensure clean milk production (5mks)
- The milk person should be clean
- Test for mastitis before milking
- Milk person should be healthy
- Ensure utensils/ equipment are clean
- Ensure milking parlor is clean
- Ensure milking heard is free from zoonotic disease e.g. TB
- Cows with mastitis should be milked last
- Clean the udder
- Sieve the milk
- Cover the milk
- Avoid feeds/ weeds that would taint the milk just before milking
- Proper storage of milk/ cool, dry place.
- State six reasons why agriculture is important in Kenya economy. (3mks)
- Provides employment
- Source of food
- Earns the country foreign exchange
- Source-of raw materials for industries
- Provide market for industrial goods
- Source of income for farmers
- State two methods of increasing ploughing depth when using a disc plough. (2 mks)
- Decrease the angle of cut
- Use of hydraulic/ draught control lever
- Adding weights on the plough beam
- Raising the land wheel
- State four ways of improving the labour productivity of farm labour. (4mks)
- Training the labour force
- Giving incentives to employees
- Efficient supervision of labour
- Assigning specific tasks to workers
- Proper remuneration of a worker
- Provide efficient tools
- Mechanization of some operations
- Provide transport within the farm
-
- Define opportunity cost as used in Agricultural economics (1mk)
- It is the value of the best alternative foregone
- State two situations under which the opportunity cost is nil (2mks)
- Where there is no alternative
- where the resources are free/gift
- Where the resources are in excess/ unlimited
- Define opportunity cost as used in Agricultural economics (1mk)
- State four variable costs in bean production (2mks)
- Casual labour costs
- Fertilizer/ manure costs
- Costs of agro chemicals
- Costs of repair of farm tools used
- Cost of hiring machinery
- Costs of seeds
- Below is a graphical representation of the law of diminishing returns
- Explain what happens in each of the Zones marked by lines in relation to output. (3mks)
- Zone I. For each addition unit of fertilizer applied, the output of potatoes increases at an increasing rate because resources are under utilized
- Zone II. For each additional unit of fertilizer applied, the output of potatoes increases at a decreasing rate as the resources are utilized to the maximum
- Zone III. For each additional unit of fertilizer applied the output of potatoes decreases since the resource is excessively applied.
- Which of the three is a rational zone of production? (1mks)
- Zone II
- State any three precautions a potatoes farmer would take to minimize risks in the production of potatoes. (2mks)
- Flexibility in production.
- Produce under contract
- Input rationing/appropriate allocation of resource input.
- Insurance of the crop.
- Use of modern technology e.g. disease resistant varieties,
- Use of pesticides and fungicides, use of fertilizers.
- Compare the use of an ox-drawn mould board plough with that of a tractor-drawn mould board plough (8 mks)
- Ox- drawn mould board is lighter hence does not compact the soil as much as the tractor – drawn mould board plough
- Ox – plough can be use for more farm operations e.g. weeding, ploughing harvesting roots crops than tractor mould board.
- Ox- plough requires less skills to operate compared to the tractor plough
- Tractor plough is faster than ox- plough hence can plough a large area with a short time
- Source of power for ox- plough is not as reliable as the source of power for tractor plough
- Ox- plough relatively shallow compared to tractor plough that plough deeper
- Ox- plough can be used in steeper lands where tractor plough cannot plough
- Ox- plough requires more people to operate than tractor plough
- Ox - plough is cheaper to buy than tractor plough
- Ox - plough is cheaper to maintain than tractor plough
- Explain what happens in each of the Zones marked by lines in relation to output. (3mks)
Join our whatsapp group for latest updates
Tap Here to Download for 50/-
Get on WhatsApp for 50/-
Download Agriculture Questions and Answers - Form 4 Mid-term Exams Term 1 2022.
Tap Here to Download for 50/-
Get on WhatsApp for 50/-
Why download?
- ✔ To read offline at any time.
- ✔ To Print at your convenience
- ✔ Share Easily with Friends / Students

