Questions
SECTION A: (40 MARKS)
Answer all questions in the spaces provided.
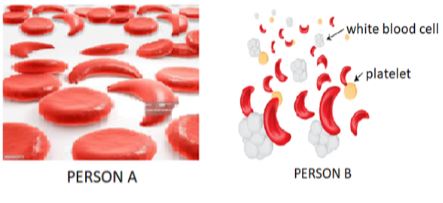
- The diagrams below show samples of blood obtained from two different persons A and B.
- What genetic disorder is person B suffering from? (1 mark)
- State one advantage and one disadvantage of the disorder exhibited in person A (2 mark)
- Work out the genotypes and phenotypes of the resulting offsprings of a marriage between person A and person B (5 marks)
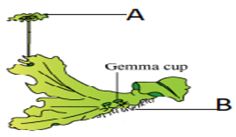
- Study the diagram below and answer the questions that follow.
- Name the division to which the organism belongs giving two reasons for your answer (3 marks)
Division:
Reasons - Name the function of the parts labelled
A (1 mark)
B (1 mark) - State three differences between the process of fertilization in the above named division and in a flowering plant. (3 marks)
- Name the division to which the organism belongs giving two reasons for your answer (3 marks)
-
- Explain the meaning of the term tropism or tropic response .1mk
- Explain how tendrils of climbing plants coil around a support.4mks
- The leaves of some insectivorous plants make very rapid movements when they are touched byan insect.
- Give an example of such plants.1mk.
- How does the response come about? 1mk.
- What is the importance of the response? 2mks
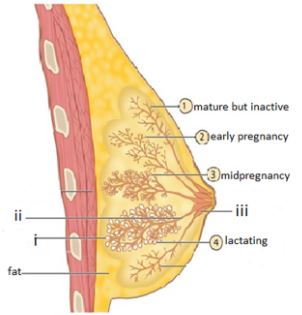
- The diagram below is a section from the mammalian body. Study and use it to answer the questions that follow.
- Name the parts labelled;
(i) (1 mark)
(ii) (1 mark)
(iii) (1 mark) - Describe the process of milk letdown (5 marks)
- Name the parts labelled;
-
- In an experiment, food sample A was respired by an organism and the gaseous product was directed into a test tube containing calcium hydroxide solution through a glass capillary tube.
The same experiment was repeated using the same amount of food sample B. It was noted that it takes 15 minutes for the gaseous product of food sample A to turn calcium hydroxide solution white and 50 minutes by gaseous product of food sample B to do the same.- Suggest with a reason, the possible identity of food sample A and B (4 marks)
- Suggest the possible identity of the gaseous product of food samples A and B. (1 mark)
- Explain how anaerobic respiration has been applied in making of beer and wines. (3 marks)
- In an experiment, food sample A was respired by an organism and the gaseous product was directed into a test tube containing calcium hydroxide solution through a glass capillary tube.
SECTION B: (40 MARKS)
Answer question 6 (COMPULSORY) in the spaces provided and either question 7 or 8
- The table below shows results of an experiment in which small pieces of tradescantia stems were placed in different salt concentrations. After 6 hours they were removed from the solutions, wiped to dry and weighed. The results are as shown below. Study the table and answer the questions that follow.
Salt concentration(mg) Percentage change in weight 2.5 +11 5.0 +8 7.5 +5 10.0 +3 12.5 +2 15.0 +1 17.5 -2 20.0 -8 22.5 -9.5 25.0 -11 -
- Draw a graph of the percentage change in weight against salt concentration. (6 marks)
- From the graph determine the salt concentration that is equal to the concentration of the tradescantia cell sap. (1 mark)
- Account for the following changes in the weight.
- Percentage positive change (4marks)
- Percentage negative change (3 marks)
- Briefly describe how the above physiological process brings about upright posture in seedlings (3 marks)
-
- Define the physiological process in (c) above (1 mark)
- State any two differences between the physiological process above and the physiological process that root hairs use to absorb mineral salts from a soil solution that is hypertonic to their cell saps (2 marks)
-
-
- Explain the biological importance of abiotic factors in seed germination. (12 marks)
- Explain the following evidences of organic evolution.
- Comparative anatomy (5 marks)
- Geographical distribution (3 marks)
- In terms of homeostatic balance in the body, describe the function of the following body systems in regulation of blood sugar level. (20 marks)
- Digestive system
- Circulatory system
- Respiratory system
- Nervous system
- Hormonal system
Marking Scheme
-
- Sickle cell anaemia;
- Advantage – Individuals having this trait hardly/rarely suffer from malaria;
Disadvantages – Suffocation due to insufficient supply of oxygen during straneous activity; -
-
- Division: Bryophyta;
Reasons: Have developed rhizoids for anchoring & absorbing water;
They are thalloid;
Show alternation of generation; - A - Produces spores;
B – Anchorage and absorption of water and mineral salts; -
Bryophytes Flowering plants Antheridia release mobile sperm which swim in water to fertilize the egg in the archegonia Pollen tubes carrying male gametes grow down the style to ovary, to bring about double fertilization. Male gametes are produced in antheridia while female egg in archegonia Pollen grains in anthers and eggs are produced in ovary Zygote formed develops into young sporophyte plant which grows upwards while still attached on the female gametophyte plant The formed zygote develops into a seed in a fruit.
- Division: Bryophyta;
-
- A tropism is a growth movement in a plant brought about by exposure of a unidirectional stimulus.1mk.
- Contact causes auxins to migrate from the side in contact to the opposite side. The opposite side away from contact grows faster .The tendrils of climbing plant coil around the support due to the reduction of the growth on the side in the contact.
-
- Venus flytrap.
- As a result of rapid changes in the turgor pressure of a certain cells in the leaf.
- Once the insects is trapped ,the plants secretes enzymes that digests it.The soluble products are absorbed.
-
-
- Lobule/Alveoli;
- Lacteferous duct;
- Lacteferous sinus;
- A (IV) oxide gas;
-
- Carbon (IV) oxide;
- Sugar in fruits or barley seeds;is fermented/broken down anaerobically; to produce ethanol in wines;
-
-
-
- 16.25% salt;
-
- The salt solution is hypotonic; to the cell sap of the tradescantia, water molecules moved from the solution into the cells by osmosis; making the cells turgid hence increase in size;
- The salt solution is hypertonic; to the cell sap of the tradescantia, water molecules moved from the cells into the solution by osmosis; making the cells flaccid to reduce in size;
- The plants absorb water from the soil by osmosis;the water is transported to cells; the cells become turgidmaking the plant upright;
-
- Movement of water molecules from a region of low concentration to a region of high across a semi permeable membrane.
-
Osmosis Diffusion Involves movement of water
Should be across a semi Permeable membraneInvolves movement of other substances apart From water
It should not be across a semi permeable membrane.
-
-
- Water; Activation of enzymes to hydrolyze food materials;
Transport of hydrolyzed food;
Dissolve the stored food;
Softens the seed coat to allow for imbibition;
Oxygen: For aerobic respiration to supply energy (for formation of new cells and tissues).
Optimum/favorable temperature
Germination enzymes require optimum temperature for maximum activity.
Low temperature inactivate the enzymes.
High temperatures beyond optimum denatures/destroy enzymes
The embryo is also killed at high temperatures.
pH ;change from optimumpH denatures enzymes responsible for germination. Optimum pH activates the enzymes and the rate of germination will be faster.
Light: Light induces the formation of gibberellins which stimulate seed germination by breaking seed dormancy.
It is also a requirement of photosynthesis by the young growing leaves of the developing seedlings. -
- Comparative anatomy
The study of internal structures reveal that certain body structures or organs found in different species of organisms have similar internal structure or plan; eg pentadactyl limbs in vertebrates.
Such similar structures with similar origin but have undergone structural modifications to perform different functions in different organisms are called homologous structures, and the basis of their origin is called divergent evolution.
Some organs have different embryonic origin but perform similar functions hence such organs are called analogous structures, and basis of their origin is called convergent evolution.
Some body parts or structures become vestigial in the course of development and reduce in size due to disuse. - Geographical distribution
initially organisms occupied one big land mass, drifting of centinents isolated organisms from common ancestry leading to speciation/formation of new species due to adaptive radiation.
- Comparative anatomy
- Water; Activation of enzymes to hydrolyze food materials;
-
- Digestive system
Ingested carbohydrates are digested to glucose in the gut; glucose is absorbed into the bloodstream; raising blood glucose levels; Pancreas secretes insulin; thus stimulates liver cells to convert excess sugar to glycogen, fats and increase rate of respiration; restoring the level to normal;(6marks) - Transport system
Capillaries in small intestines join the hepatic portal vein which transports absorbed glucose to the liver directly;
Transport system also transport hormones insulin and glucagon from the pancreas to the liver; transports glycogen from liver to muscles in the body for storage; hepatic vein transport glucose from the liver to other parts of the body for respiration; (4marks) - Respiratory system
When level of glucose in blood increases beyond normal, insulin stimulate liver cells;to increase breakdown of excess glucose to water carbon(IV)oxide and energy; hence lowering the concentration of sugar in blood to normal levels ;
When the level of glucose in blood falls below normal,pancreas is stimulated to secrete glucagon hormone; which stimulate liver cells to reduce breakdown /metabolism of glucose into water ,carbon(IV)oxide and energy; restoring the amount of glucose in blood to normal.(5marks) - Nervous system
The hypothalamus detects levels of blood sugar in blood; sends impulses to the pituitary gland; which generates impulses and sends to the pancreas; to secrete insulin/glucagon; to stimulate liver cells to lower or raise blood sugar; (5marks) - Hormonal system
The pancreas as an endocrine gland secretes ;( the following hormones involved in regulation of blood glucose levels)
Insulin stimulates liver cells; (to convert excess glucose to fat or glycogen thus lowering its concentration)
Glucagon stimulates liver cells ;( to carry out activities that release glucose to blood thus increasing its concentration)
Adrenaline hormone; secreted by adrenal glands; increase hydrolysis of glycogen into glucose; and inhibits release of insulin resulting to increase in blood sugar level. (6marks)
Maximum 20 marks
- Digestive system
Download Biology Paper 2 Questions and Answers - Form 4 End Term 1 Exams 2022.
Tap Here to Download for 50/-
Get on WhatsApp for 50/-
Why download?
- ✔ To read offline at any time.
- ✔ To Print at your convenience
- ✔ Share Easily with Friends / Students