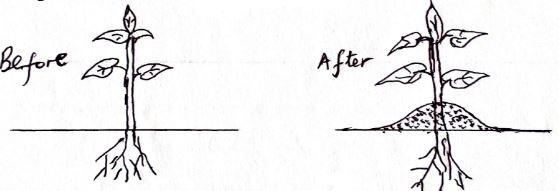Questions
SECTION A: (30MKS)
- State four advantages of using farm yard manure. (2mks)
- State four merits of minimum tillage in crop production. (2mks)
- Mention four practices carried out to maintain grass pastures. (2mks)
- State four disadvantages of nomadic pastoralism. (2mks)
- Mention four cultural methods of used control in crop production. (2mks)
- State four ways of overcoming extremes of temperature in crop production. (2mks)
- List five precautions observed in harvesting tea to ensure high quality produce. (21/2mks)
- List three ways in which primary cultivation can be achieved. (11/2mks)
- An agriculture student was advised to apply complete fertilizer 40:30:10 in a (20x10) M plot and at the rate of 40kg per hectare.
- Calculate the percentage of P2O5 in the complete fertilizer. (2mks)
- Calculate the amount of fertilizer the student would require for the plot. (2mks)
- State four divisions of livestock farming. (2mks)
- List four methods commonly used for applying nitrogenous fertilizers. (2mks)
- Name four factors influencing soil formation. (2mks)
- A farmer owns one hectare on which he can grow maize whose yield is 15 bags/hectare but has chosen to grow sorghum whose yield is 20 bags/hectare. If maize is sold at shs 1200 per bag while sorghum is sold at shs 700 per bag. Calculate the opportunity cost. (2mks)
- State four characteristics of plants used for preparation of green manure. (2mks)
SECTION B (20MKS)
- Students in an agriculture class set out to investigate the constituents of soil sample from school. They carried out a series of tests on various portions of the sample. They then prepared a table a shows below:
Description Quantity Mass of an empty evaporating disk
Fresh soil on evaporating disk
Mass of dried soil at 105oC on evaporating disk
Vol. of water in the tin
Vol. of water and soil after stirring
Mass of empty silica disk
Mass of silica disk and soil after ignition
Mass of silica disk and dried soil before ignition
Volume of water and soil before stirring10g
35g
28g
250cm3
410cm3
15g
45g
65g
500cm3- Calculate the percentage of soil water in the sample. (1mk)
- Why was soil heated at 105oC? (1mk)
- Calculate the percentage of soil air in the sample? (1mk)
- Calculate the percentage of soil organic matter in the sample. (1mk)
- Name one other soil constituent not tested above. (1mk)
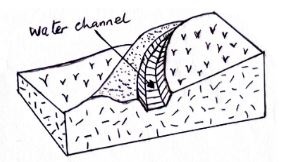
- The diagram below shows a construction on farm. Use it to answer the questions that follow.
- Identify the above structure. (1mk)
- State four areas where water in the channel is directed to: (4mks)
- The diagram below shows a field practice in crop production.
- Identify the practice. (1mk)
- State two advantages of the practice named in (a) above to Irish potatoes. (2mks)
- Name two other crops that require the above practice. (2mks)
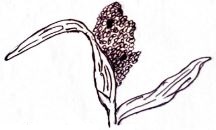
- Use the diagram below to answer the questions.
- Identify the sorghum variety shown above. (1mk)
- State two bird pests that commonly attack the crop. (2mks)
- Name two other varieties commonly grown by farmers. (2mks)
SECTION C (40MKS)
-
- Outline the procedure for soil sampling. (8mks)
- Give five reasons for ridging sweet potatoes. (5mks)
- Outline seven properties of nitrogenous fertilizers. (7mks)
-
- Discuss five benefits of weeds to the farmer. (10mks)
- Discuss five importance of draining a waterlogged area. (10mks)
-
- Discuss five factors influencing crop rotation. (10mks)
- Discuss five government policies that regulate production, marketing and distribution of agricultural products. (10mks)
Marking Scheme
-
- Improves soil structure/ water -holding capacity
- Supply variety of soil nutrients
- Locally/easily available
- Long residual effect
- Promotes microbial activity
- Buffers soil pH
-
- Reduce cost of production
- Control soil erosion
- Maintain soil structure
- Prevents exposure of humus
- conserve moisture
- Pr events disturbance of roots
-
- Top dressing
- Controlled grazing
- Topping/ cutting back
- Re-seeding
- Control of pests eg moles
- Control of weeds
- Irrigation
-
- Low production
- uncontrollable mating
- Difficult to control parasite and diseases
- Leads to overgrazing and soil erosion
-
- Mulching
- Cover cropping
- Crop rotation
- Timely planting
- Use of clean seeds
- Proper spacing
- Clean seedbed
- Flooding.
-
- Planting crops adaptable
- Planting early maturing crops
- Irrigation
- Timely planting
- Planting drought resustant crop varieties
- Growing crops under greenhouses
-
- Pick two leaves and a bud
- Put in woven basket
- Do not compress leaves
- Keep under shade as pickign continues
- Deliver to factory same day
-
- Hand digging
- Mechanical cultivation
- Use of an ox-plough
-
- Total Ratio= 40 + 30 + 10 = 80
30/80 x 100 = 37.5% - 1 hac = 10,000m2
Area of plot = 20 x 10= 200 m2
1 hac = 10,000m2 = 40kg
200→ 40 x 200 = 8kg
10,000
- Total Ratio= 40 + 30 + 10 = 80
-
- Pastoralism(mammalian livestock keeping)
- Fish farming
- Poultry farming
- Bee keeping
-
- Broadcasting
- Side dressing
- Folier spraying
- Drip
- fertigation
-
- Parent rock
- Living organism
- Time
- Climate
- Topography
-
- Returns for maize = 15 x 1200 = 1800
Returns for sorghum = 20 x 700 = 14000
- Returns for maize = 15 x 1200 = 1800
-
- Highly vegetative/ leafy
- Fast growth rate
- High N2 content
- High rate of decomposition
- Hardy
-
- 7/35 x 100 = 20%
- to evaporate/ expel the moisture
- 90/250 x 100= 36%
- 20/50x100=40%
- Soil living organisms
Soil mineral matter/ inorganic
- 7/35 x 100 = 20%
-
- Cut- off drain/ diversion ditch
-
- Natural water ways eg river
- non-erodable story/ rock ground
- grass land with grass cover
- artificial water way.
- Cut- off drain/ diversion ditch
-
- Eating up
-
- Improves tuber formation
- Promotes production of seeds
- Improves drainage
- Provides support
-
- Cassava
- Groundnuts
- Sweet potatoes
- Eating up
-
- Compact paricle
-
- Sudan Dioch
- Weavers
- Starlings
-
- Open paricle
- Goose necked
-
- Procedure of soil sampling
- Clear the vegetation from sampling spot
- Make a vertical cut 15-25cm from crop land and 5cm fro pasture land
- Take a slice from vertical cut using a spade/ soil auger.
- Put the soil in clean suitable container
- Repeat the above steps in 15-20 spots
- Soil from all the spots is mixed, dried and crushed.
- A sub-sample from the mixture is taken
- Its clearly labelled and taken to the laboratory for testing.
- Reason for ridging
- Allows tuber expansion
- Allows easy harvesting
- Prevents greening of tubers
- Conserve moisture
- Controls drainage
- Prevents pest attack.
- Properties of nitrogenous fertilizers
- Highly soluble in water
- Easily leached to lower horizons
- Have short residual effect
- Have scorching effect/ burning effect
- Are highly corrosive
- Are highly volatile hence applied on moist soils
- Are hygroscopic hence absorb moisture from atmosphere
- Procedure of soil sampling
-
- Benefits of weeds
- Some weeds are edible to man and livestock eg pigweed. They are used as food.
- Some weeds have medicinal value. Weeds are known to provide gherbal medicine to man and livestock eg sodom apple.
- Weed acts as soil cover, preventing loss of moisture , soil capping and impact of raindrops
- Weeds add organic matter to the soil when they decompose hence enriching soil humus/ soil nutrients.
- Leguminious weeds fix nitrogen in the soil hence enriching soil with nitrates. [students to give proper explanation]
- Importance of drainage
- To increase soil volume: Soil around the root zone increases making it easy for plants to get nutients
- To reduce soil erosion: This increases water holding capacity and infiltration
- To increase microbial activities: Drainage increases aeration in soil ⇒ to increase in number of micro-oragnisms
- To remove toxic substances: Salts such as those of sodium increase in waterlogged conditions.
- To raise soil temp: improves the rate at which soil warms up.
- To increase soil aeration: When excess water is removed, plant roots get enough air for proper growth.
- Benefits of weeds
Join our whatsapp group for latest updates
Tap Here to Download for 50/-
Get on WhatsApp for 50/-
Download Agriculture Paper 1 Questions and Answers - Form 4 End Term 1 Exams 2022.
Tap Here to Download for 50/-
Get on WhatsApp for 50/-
Why download?
- ✔ To read offline at any time.
- ✔ To Print at your convenience
- ✔ Share Easily with Friends / Students