INSTRUCTIONS
- Sign and write the data of the examination.
- Answer all the questions in the spaces provided.
- You are not supposed to start working with the apparatus for the first 15 minutes of 2¼ hours allowed for this paper. This time is meant to read through the paper and ensure you have all the chemicals and apparatus require.
- All working must be clearly shown
- KNEC mathematical tables and silent electronic calculations may be used.
- All questions should be answered in English
FOR EXAMINERS USE ONLY
|
QUESTIONS |
MAXIMUM |
CANDIDATE’S SCORE |
|
1 |
21 |
|
|
2 |
11 |
|
|
3 |
08 |
|
|
TOTAL SCORE |
40 |

QUESTIONS
QUESTION 1
You are provided with:
- Solid A 5.0g (COOH)2· H2O
- Solution B 0.13M KMnO4
Task
- You are supposed to determine the solubility of A at different temperatures.
- Determine the number of moles of water of crystallization in solid A.
PROCEDURE 1
- Using a burette, add 4cm3 of distilled water to solid A in a boiling tube.
- Head the mixture while stirring with the thermometer to about 800
- When the whole solid dissolves, allow the solution to cool while stirring with the thermometer
- Note the temperature at which crystals first appear and record this temperature in the table 1 below.
- Using aburrete add 2cm3more into the content of the boiling tube and warm until the solid dissolve.
- Remove from the flame and allow the solution to cool in air while stirring.
- Record the temperature at which crystal first appear in table 1.
- Repeat procedure (b) 3 more times and complete table 1 below.
- Retain the content of the boiling tube for procedure II
Table 1
|
Volume of water in the boiling tube (cm3) |
Temperature at which crystals of solid A appear (0C) |
Solubility o solid A g/100g of water |
|
4 6 8 10 12 |
-
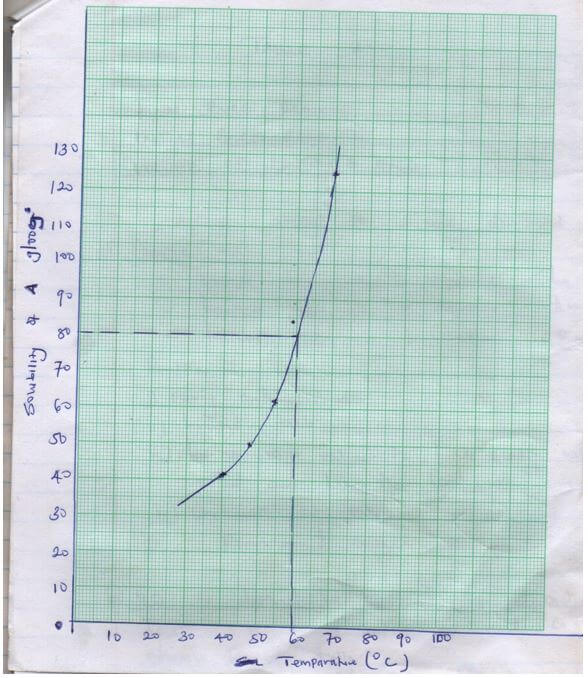
- Draw a graph of solubility of solid A (vertical axis) against temperature (3mks)
- From your graph determine the solubility of solid A at 600C (1mk)
PROCEDURE II
-
- Transfer the contents of the boiling tube into a 250ml volumetric flask.
- Add distilled water up to the mark
- Label this solution A
-
- Using a clean pipette and a pipette filler, transfer 25ml of solution A into a conical flask.
- Warm the mixture up to 600C
- Fill a burette with solution B
- Titrate B against the hot solution A until a permanent pink colour persist
- Read your results in Table 2 below
- Repeat (b) 2 more times are record your results in the table 2 below.
- Transfer the contents of the boiling tube into a 250ml volumetric flask.
TABLE 2
|
I |
II |
III |
|
|
FINAL BURETTE READING |
|||
|
INITIAL BURETTE READING |
|||
|
VOLUME OF SOLUTION B USED (CM3) |
II)
- Calculate the average volume of solution B used (1mk
- Calculate the number of moles of B used (1mk)
- Given 2 moles of Kmno4 react with 5 moles of A, calculate the number of moles of A in 25cm3 (1mk)
- Calculate the molarity of A (1mk)
- Determine the molar mass of A (1mk)
- Determine the value of X (1mk)
(C=12, O=16 H=1)
QUESTION 2
You are provided with solid C. Use it to carry the test below.
Dissolve the whole of C into 10cm3 of water and divide it into five portions.
a) To the 1st portion add sodium sulphate solution.
|
Observations |
Inferences |
|
(1mk) |
(1½mks) |
b) To the 2nd portion add Ammonia solution dropwise until in Excess.
|
Observations |
Inferences |
|
1mk) |
1mk |
c) To the 3rd portion add sodium Hydroxide dropwise until in Excess.
|
Observations |
Inferences |
|
(1mk) |
(1mk) |
d) To the forth portion add Lead (II) Nitrate solution
|
Observations |
Inferences |
|
(½mk) |
(2mks) |
e)To the last portion add Barium Nitrate solution
|
Observations |
Inferences |
|
(1mk) |
(1mk) |
QUESTION 3
You are provided with liquid D use it to carry the test below.
Divide liquid D into four equal portions
To the 1st portion add sodium hydrogen carbonate
|
Observations |
Inferences |
|
(1mk) |
(1mk) |
- To the 2nd portion add acidified potassium manganite (VII) (KmnO4)
|
Observations |
Inferences |
|
(1mk) |
(1mk) |
- To the 3rd portion add Bromine water
|
Observations |
Inferences |
|
(1mk) |
(1mk) |
- To the last portion add potassium dichromate(VI) and warm.
|
Observations |
Inferences |
|
(1mk) |
(1mk) |

MARKING SCHEME
QUESTION 1
You are provided with:
- Solid A 5.0g (COOH)2· H2O
- Solution B 0.13M KMnO4
Task
- You are supposed to determine the solubility of A at different temperatures.
- Determine the number of moles of water of crystallization in solid A.
PROCEDURE 1
- Using a burette, add 4cm3 of distilled water to solid A in a boiling tube.
- Head the mixture while stirring with the thermometer to about 800
- When the whole solid dissolves, allow the solution to cool while stirring with the thermometer
- Note the temperature at which crystals first appear and record this temperature in the table 1 below.
- Using aburrete add 2cm3more into the content of the boiling tube and warm until the solid dissolve.
- Remove from the flame and allow the solution to cool in air while stirring.
- Record the temperature at which crystal first appear in table 1.
- Repeat procedure (b) 3 more times and complete table 1 below.
- Retain the content of the boiling tube for procedure II
Table 1
|
VOLUME OF WATER IN THE BOILING TUBE |
TEMPERATURE AT WHICH CRYSTALS OF A APPEAR |
SOLUBILITY OF SOLID A g/100g of water |
|
4 |
70.0 |
125.0 |
|
6 |
59.0 |
83.3 |
|
8 |
54.0 |
62.5 |
|
10 |
47.0 |
50.0 |
|
12 |
40.0 |
41.7 |
- Complete table – 4mks
Condition and penalties
- A table with 8-10 values award 4
- A table with 6-7 values a ward 3
- A table with 4- 5 values award 2
- A table with 2-3 values award 1
- A table with 1 value award ½
- A table with no value a ward 0
Penalties
- Draw a graph of solubility of solid A (vertical axis) against temperature (3mks)
- Penalize ½ mk for each wrong value of solubility
- From your graph determine the solubility of solid A at 600C (1mk)
- Penalize ½ one for unrealistic temperature readings ½ above 900C and below 100C
- DECIMALS TIED TO TEMPARATURE -1Mk
Accept;
- i) Whole numbers
- Idecimal place where the decimal should be 0 or 5 i.e 70.0 or 70.5
iii. Accept 2 decimal places where it should be .00, .25,.50 or .75
NB: If no consistence penalize fully.
- TREND – Tied to temperature i.e it should be decreasing (1mk)
- Accuracy – tied to temperature when 4cm3 of water was added
Accept 20C of the school value.
1a) GRAPH – award a total of 3mks distributed as follows.
- Labeling (½mks)
- Both axis should be labeled if one is not or wrongly labeled award O
- Ignore units but if indicated they should be right otherwise penalize fully
- Scale – (½mks)
- The actual plotting should be half of the page
- Paralyze fully if scale changes on the way both axis must be correct.
- Plots (1mk)
4-5 correct plots award (1mk)
3 correct plots award (½mks)
Less than 3 correct plots award 0
- Line – a smooth curve passing through 3 or more correct plots award 1mk
Otherwise award 0
- b) – award ½ mk for sloping or the graph
- award ½ mk for calculating
NB:
- Award fully for calculation from correct graph even if not shown on the graph
- Reject any value from a wrong graph.
PROCEDURE II
-
- Transfer the contents of the boiling tube into a 250ml volumetric flask.
- Add distilled water up to the mark
- Label this solution A
-
- Using a clean pipette and a pipette filler, transfer 25ml of solution A into a conical flask.
- Warm the mixture up to 600C
- Fill a burette with solution B
- Titrate B against the hot solution A until a permanent pink colour persist
- Read your results in Table 2 below
- Repeat (b) 2 more times are record your results in the table 2 below.
- Transfer the contents of the boiling tube into a 250ml volumetric flask.
II)
TABLE 2
- Complete table with 3 titration 1mk
- Incomplete table with 2 titrations ½ mk
- Incomplete table with 1 titration 0 mks
Penalties
- Wrong arithmetic
- Invented table
- Unrealistic values i.e burette reading with more than 50cm3 and less than 1cm3
- Unrealistic titre values
NB: PENETICE ½ once
b) Use of decimals (1mk) (Tied to the 1st and 2nd row only)
Accept 1 or 2 decimal places used consistently otherwise penalize fully
- If 2 dp are used the 2nd should be a “O” OR “5” e.g 20.10 or 20.15 otherwise penalize fully
- Accept the use of Zero as the initial burette reading i.e 0,0.0 or 0.0
C) Accuracy (1mk)
Complete the candidate value with the school value (S.V)
- If within 1 of the school value award 1mk
- If within 2 of S.V ward ½mk otherwise award 0
NB: Tick the candidate value that deserves a credit
D) PRINCIPLE OF AVERAGING ------------------------1MK
Conditions
- If 3 titration done but only two are consistence and averaged award 1mk
- If 3 titration are done and consistency and averaged award 1mk
- If two titration are done and are consistency and averaged award 1mk
- If three consistency titration one done but 2 are averaged award 0
- If three 3 titration are done and are inconsistence and are done averaged award zero
- If two titration are done and are inconsistence and are averaged award 0
PERALTIES
- Penalize ½ for wrong arithmetic
- penalize ½mk if no working is shown and answer is correct
- penalize fully if no working is shown and answer given is wrong
- Accept rounding off or truncation to the 2ndd.p
e.g 12.666 12.67
or
12.66 12.66
NB:
- The working of average must be marked before the mark for averaging is award in table 2.
- Accept the average volume if it work out exactly to a whole number.
FINAL ACCURACY ----------------------(1MK) Tiled to correct average time.
Compare the candidate average time to the school value.
- If within 1 award 1mks
- If with n 2 award ½ mk
Otherwise award 0
NB:
- If there are 2 possible correct average titre, use the one the one close to the school value and award accordingly.
- If wrong value are averaged, pick the correct values average for the candidate and award accordingly.
- Record the marks as follows besides the table to the right.
CT – 1mk
D - 1mk
A -1mk
PA -1mk
FA - 1mk
Total 05 mks
|
1 |
11 |
111 |
|
|
FINAL BURET READING |
12.5 |
12.5 |
12.5 |
|
INITIAL BURET READING |
0.0 |
0.0 |
0.0 |
|
VOLUME OF SOLUTION B USED |
12.5 |
12.5 |
12.5 |
- Calculate the average volume of solution B used (1mk
1000-0.13
12.5 ?
= 12.5 x 0.13 ½
1000
0.001625 moles ½
= 0.0040625 - Calculate the number of moles of B used (1mk)
ans = b x 5
2
= 0.0040625 - Given 2 moles of Kmno4 react with 5 moles of A, calculate the number of moles of A in 25cm3 (1mk)
ans c x 1000
= 0.1626m - Calculate the molarity of A (1mk)
- Determine the molar mass of A (1mk)
5g 250cm3
20g – 1000
(1×20)/0.1625
= 123.07 - Determine the value of X (1mk)
(C=12, O=16 H=1)- 90 + 18 =123
18 = 33
= 33
18
= 1.83
= 2
QUESTION 2
|
A) OBSERVATION |
INFERENCES |
|
No white precipitate Formed (1mk) |
Ba2+ Ca2+ and Pb2+ Absent Each ½ mks Penalize ½mk to a maximum of 1 ½ mks for any contradictory ion |
|
B) OBSERVATION |
INFERENCES |
|
No white precipitate insoluble in excess NB: White precipitate ½ mk - Insoluble in excess ½ mk |
Zn2+ absent (1mk) Penalize 1mk for each contradicting ion to a maximum of (1mk) |
|
C) OBSERVATION |
INFERENCES |
|
A white precipitate ½ Insoluble in excess ½ |
Mg2+ present (1mk) - Accept Al3+ absent for ½mk - Panelize 1mks for any contracting ion to a Maximum of 1mks |
|
D) OBSERVATION |
INFERENCES |
|
A white precipitate is formed ½ mks - |
C1-, So32- , SO4 2- and CO32- present – ½ mk each Penalize ½mk for any contradictory ion to a maximum of (2mks) |
|
E) OBSERVATION |
INFERENCES |
|
No white precipitate formed |
CI- Present (1mks) -accept SO42- AND SO32- OR CO32- absent for fully marks penalize 1mks for any contradictory ion to a maximum of 1mks
|
QUESTION 3
|
a) OBSERVATION |
INFERENCES |
|
No fizzing/bubbling /hissing (1mk) Reject -fissiling -Sizzling |
R- CooH Absent (1mk) NB: Ignore H3O+ & H+ |
|
b) OBSERVATION |
INFERENCES |
|
KMno4 get decolorized
|
C= C OR –C= C- (½mk) |
|
c) OBSERVATION |
INFERENCES |
|
Yellow /orange bromine water does not get decolonized It remains yellow or orange |
C= C or –C C- |
|
d) OBSERVATION |
INFERENCES |
|
K2CrO7 turns from orange to green(1mk) |
R-OH Present (1mk) Penalize 1mk for any contradictory group to a maximum of 1mk |
Download Chemistry Paper 3 Questions and Answers - Form 4 Term 2 Opener Exams 2022.
Tap Here to Download for 50/-
Get on WhatsApp for 50/-
Why download?
- ✔ To read offline at any time.
- ✔ To Print at your convenience
- ✔ Share Easily with Friends / Students

