INSTRUCTION.
- Answer all questions in the spaces provided.
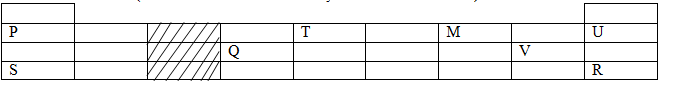
- The table below shows some elements in the periodic table. Use it to answer the question that follow. (The letter are not the actual symbols of the elements)
- Identify the elements in the same group. (2mks)
- Give the name of the family to which elements P and S belong. (1mk)
- Write the electron configuration of ions of elements; (2mks)
- V
- Q
- Given that isotopes of element S are as follows 39S(93.1%), xS(0.01%) and 41S(6.89%), calculate x given that the relative atomic mass of element S is 39.1349. (3mks)
- Elements Q and V react to form a compound.
- Write an equation for the reaction. (1mk)
- What is the nature of the compound formed in (i) above. Explain. (2mks)
- Element T forms covalent bond with element V. Using dot (.) and cross (x) diagram show bonding in the compound formed. (2mks
-
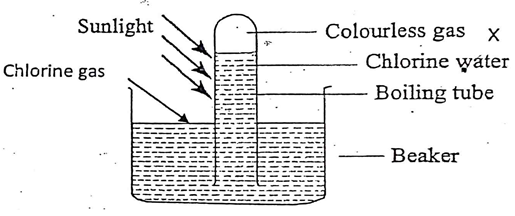
- The following set up was carried out by students in form two in the open air in the presence of sunlight to investigate a certain property of the halogen. Study it answer the questions.
- Which property of the halogen was being investigated? (1mk)
- Name the gas which was colourless. (1mk)
- Chlorine water is yellow in colour. However, in the presence of light it is decolourised. Explain. (2mks)
- Comment on the effect of chlorine water on red and blue litmus paper. (2mks)
- The following diagram represents a section of the plant for the large scale manufacture of hydrochloric acid.
- Name gases A and B. (2mks)
- State the role of glass beads in the plant. (1mk)
- Explain why gas A is introduced into the reaction chamber through a jet. (1mk)
- Write the chemical equation for the reaction between gas A and B. (1mk)
- Determine the volume of hydrochloric acid gas formed when 3600cm3 of gas B react with gas A at stp (MGV at stp = 22.4dm3) (2mks)
- CFC’S and DDT are chlorine compounds with long life span and so affects both plants and animal life. Write their full names. (2mks)
- The following set up was carried out by students in form two in the open air in the presence of sunlight to investigate a certain property of the halogen. Study it answer the questions.
-
- Butane and bromine react according to the equation below.
CH3CH2CH2CH3 + Br2 → CH3CH2CH2CH2Br + HBr- Name the type of reaction taking place in the equation above. (1mk)
- State the condition under which the above reaction takes place. Explain. (2mks)
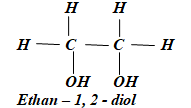
- Name the following compounds:
-
(1mk)
-
(1mk)
-
(1mk)
-
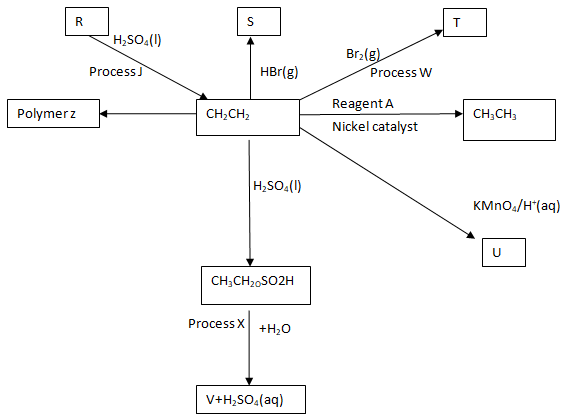
- Study the reaction scheme shown and answer the questions that follow.
- Identify reagent A. (1mk)
- Name process;
- X (1mk)
- W (1mk)
- Write the equation for the process J. (1mk)
- Name products: (3mks)
- S
- T
- V
- Draw and name the structure of:
- Polymer Z (1 ½ mks)
- Product U (1 ½ mks)
- Butane and bromine react according to the equation below.
-
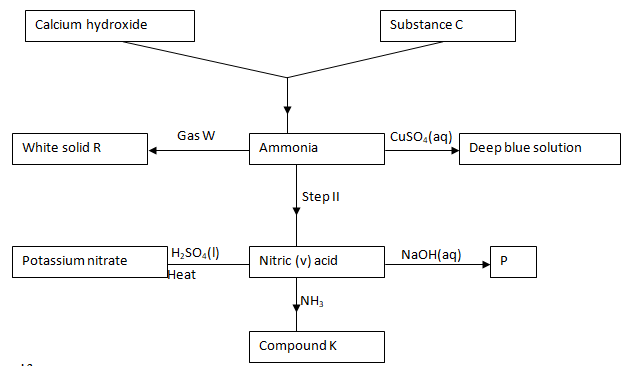
- Use the flow chart drawn to answer the questions that follow:
- Identify:
- Compound C (1mk)
- Compound K (1mk)
- Write the equation for the following:
- Calcium hydroxide and substance C. (1mk)
- Gas W and ammonia. (1mk)
- Identify the catalyst in step II. (1mk)
- Write the formula of the deep blue solution and compound K. (2mks)
- State the type of reaction that produces P. (1mk)
- State one use of compound K. (1mk)
- Identify:
- When compound N is heated, a red-brown gas is evolved and a yellow residue is left on cooling.
- Name:
- The red-brown gas. (1mk)
- The ions present in the residue. (1mk)
- Write equation for decomposition of solid N. (1mk)
- Name:
- Use the flow chart drawn to answer the questions that follow:
-
- Candle wax is mainly a compound consisting of two elements. Name the two elements. (2mks)
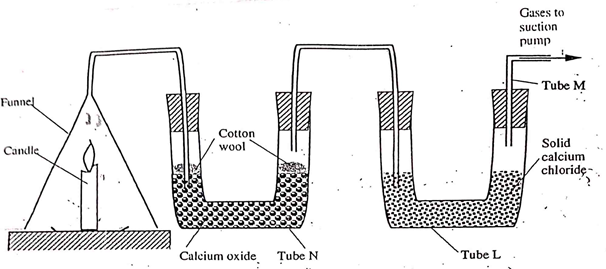
- The set – up below was used to investigate the burning of a candle. Study it and answer the questions that follow.
- What would happen to the burning candle if the pump was turned off? Give reasons. (3mks)
- State and explain the changes in mass that are likely to occur in tube N by the end of the experiment. (3mks)
- Name two gases that come out through tube M. (2mks)
- What is the purpose of calcium chloride in tube L? (1mk)
- Name another substance that could be used in the place of calcium oxide in tube N. (1mk)
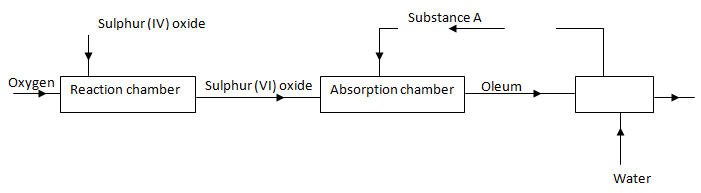
- The flow chart below shows some of the processes involved in large scale production of sulphuric (VI) acid. Use it to answer the questions that follow.
- Describe how oxygen is obtained from air on a large scale. (3mks)
-
- Name substance A. (1mk)
- Write an equation for the process that takes place in the absorption chamber. (1mk)
- Vanadium (V) oxide is a commonly used catalyst in the contact process.
- Name another catalyst which can be used for this process. (1mk)
- Give two reasons why vanadium (V) oxide is the commonly used catalyst. (2mks)
- State and explain the observations made when concentrated sulphuric (VI) acid is added to crystals of copper (II) Sulphate in a beaker. (1mk)
- The reaction of concentrated sulphuric (VI) acid with sodium chloride procduces hydrogen chloride gas. State the property of concentrated sulphuric (VI) acid illustrate in this reaction. (1mk)
- Name four uses of sulphuric (VI) acid. (2mks)


MARKING SCHEME
INSTRUCTION.
Answer all questions in the spaces provided.
- The table below shows some elements in the periodic table. Use it to answer the question that follow. (The letter are not the actual symbols of the elements)
-
- Identify the elements in the same group. (2mks)
- P & S
- U and R
- Give the name of the family to which elements P and S belong. (1mk)
- Alkali metals
- Write the electron configuration of ions of elements; (2mks)
- V
- V- 2.8.8
- Q
- Q3+ 2.8
- V
- Given that isotopes of element S are as follows 39S(93.1%), xS(0.01%) and 41S(6.89%), calculate x given that the relative atomic mass of element S is 39.1349. (3mks)
= (93.1 x 39) + (0.01Xx) + (6.89 x 41)
100
= 39.1379
= 3630.9 + 0.01x + 282.49 = 39.1379
100
= 3913.39 + 0.01x = 3913.79
=0.01x = 0.40 = 40
0.01
x =40 - Elements Q and V react to form a compound.
- Write an equation for the reaction. (1mk)
- 2Q(s) + 3V2(g) → 2QV3
- What is the nature of the compound formed in (i) above. Explain. (2mks)
- Acidic; QV3/AlCl3 hydrolyses in water to form H+ions, hence the acidic nature of the chloride.
- Write an equation for the reaction. (1mk)
- Element T forms covalent bond with element V. Using dot (.) and cross (x) diagram show bonding in the compound formed. (2mks)
- Identify the elements in the same group. (2mks)
-
- The following set up was carried out by students in form two in the open air in the presence of sunlight to investigate a certain property of the halogen. Study it answer the questions.
- Which property of the halogen was being investigated? (1mk)
- Solubility in water.
- Name the gas which was colourless. (1mk)
- Oxygen
- Chlorine water is yellow in colour. However, in the presence of light it is decolourised. Explain. (2mks)
- The yellow colour is due to presence of chloric (I) acid; in the presence of light the chloric (I) acid decompose to form hydrochloric acid, hence the solution turn colourless.
- Comment on the effect of chlorine water on red and blue litmus paper. (2mks)
- Blue litmus paper turns red then both litmus papers are bleached to white; chlorine water is acidic and has bleaching properties due to presence of chloric (I) acid/ hypochlorous acid.
- Which property of the halogen was being investigated? (1mk)
- The following diagram represents a section of the plant for the large scale manufacture of hydrochloric acid.
- Name gases A and B. (2mks)
- A – Hydrogen
- B – Chlorine
- State the role of glass beads in the plant. (1mk)
- To increase the surface area over which the gas dissolves in water.
- Explain why gas A is introduced into the reaction chamber through a jet. (1mk)
- To prevent an explosion since the mixture of chlorine and hydrogen react explosively.
- Write the chemical equation for the reaction between gas A and B. (1mk)
- H2(g) + Cl2(g) → 2HCl(g)
- Determine the volume of hydrochloric acid gas formed when 3600cm3 of gas B react with gas A at stp (MGV at stp = 22.4dm3) (2mks)
Moles of B = Vol
MGV
= 3600
22400
= 0.1607 moles
Moles of HCl produced = (0.1607 x 2)
= 0.3214 moles
Volume of HCl gas = moles x MGV
= 0.3214 x 22400
= 7200cm3 - CFC’S and DDT are chlorine compounds with long life span and so affects both plants and animal life. Write their full names. (2mks)
- CFC - chlorofluorocarbons
- DDT – Dichlorodiphenytrichloroethane
- Name gases A and B. (2mks)
- The following set up was carried out by students in form two in the open air in the presence of sunlight to investigate a certain property of the halogen. Study it answer the questions.
-
- Butane and bromine react according to the equation below.
CH3CH2CH2CH3 + Br2 → CH3CH2CH2CH2Br + HBr- Name the type of reaction taking place in the equation above. (1mk)
- Substitution
- State the condition under which the above reaction takes place. Explain. (2mks)
- U.V light/ sunlight; presence of sunlight splits the halogen (bromine) molecules into free atoms which are very reactive hence they replace the hydrogen atoms in an alkane.
- Name the following compounds:
- Name 2,3 - dimethylpentane
- Name 1,3 – dichloro – 2 - methylbutane
- Name: 5 – methylhex-1-ene
- Name the type of reaction taking place in the equation above. (1mk)
- Study the reaction scheme shown and answer the questions that follow.
- Identify reagent A. (1mk)
- Hydrogen
- Name process;
- X - Hydrolysis (1mk)
- W - Halogenation (1mk)
- Write the equation for the process J. (1mk)
- C2H5OH(l)
C2H4(g) + H2O(l)
- C2H5OH(l)
- Name products: (3mks)
- S - Bromoethane
- T – 1, 2 - dibromoethane
- V - Ethanol
- Draw and name the structure of:
- Polymer Z (1 ½ mks)
Polythene
- Product U (1 ½ mks)
- Polymer Z (1 ½ mks)
- Identify reagent A. (1mk)
- Butane and bromine react according to the equation below.
-
- Use the flow chart drawn to answer the questions that follow:
- Identify:
- Compound C (1mk)
- Ammonia chloride
- Compound K (1mk)
- Ammonium nitrate
- Compound C (1mk)
- Write the equation for the following:
- Calcium hydroxide and substance C. (1mk)
- Ca(OH)2(s) + 2NH4Cl(s) → CaCl2(aq)+ 2NH3(g) + 2H2O(l)
- Gas W and ammonia. (1mk)
- NH3(g) + HCl(g) → NH4Cl(s)
- Calcium hydroxide and substance C. (1mk)
- Identify the catalyst in step II. (1mk)
- Platinum rhodium
- Write the formula of the deep blue solution and compound K. (2mks)
- (Cu(NH3)4)2+
- NH4NO3
- State the type of reaction that produces P. (1mk)
- Neutralization
- State one use of compound K. (1mk)
- As a fertilizer
- In preparation of nitrogen (I) oxide
- Identify:
- When compound N is heated, a red-brown gas is evolved and a yellow residue is left on cooling.
- Name:
- The red-brown gas. (1mk)
- Nitrogen (IV) oxide
- The ions present in the residue. (1mk)
- Pb2+ and NO-3 ions
- Write equation for decomposition of solid N. (1mk)
- 2Pb(NO3)2(s)
2PbO(s) + 4NO2(g)+ O2(g)
- 2Pb(NO3)2(s)
- The red-brown gas. (1mk)
- Name:
- Use the flow chart drawn to answer the questions that follow:
-
- Candle wax is mainly a compound consisting of two elements. Name the two elements. (2mks)
- Hydrogen
- Carbon
- The set – up below was used to investigate the burning of a candle. Study it and answer the questions that follow.
- What would happen to the burning candle if the pump was turned off? Give reasons. (3mks)
- It extinguishes because carbon (IV) oxide will accumulate around it putting it off.
- State and explain the changes in mass that are likely to occur in tube N by the end of the experiment. (3mks)
- Mass increase since water vapour reacts with calcium oxide, Cao, and forms calcium hydroxide, which then reacts with carbon (IV) oxide to produce calcium carbonate.
- Name two gases that come out through tube M. (2mks)
- Nitrogen, Helium, Neon, Argon
- What is the purpose of calcium chloride in tube L? (1mk)
- It absorbs moisture which is produced from burning candle.
- Name another substance that could be used in the place of calcium oxide in tube N. (1mk)
- Sodium hydroxide
- What would happen to the burning candle if the pump was turned off? Give reasons. (3mks)
- Candle wax is mainly a compound consisting of two elements. Name the two elements. (2mks)
- The flow chart below shows some of the processes involved in large scale production of sulphuric (VI) acid. Use it to answer the questions that follow.
- Describe how oxygen is obtained from air on a large scale. (3mks)
- Air is first passed through concentrated sodium hydroxide to remove carbon (IV) oxide. It is then cooled to -25oC to remove water; through repeated expansion and compression, air is cooled to liquid at -200oC through fractional distillation, nitrogen and oxygen are then separated
-
- Name substance A. (1mk)
- Con. Surphuric (VI) acid
- Write an equation for the process that takes place in the absorption chamber. (1mk)
- H2SO4(l) + SO3(g) → H2S2O7(l)
- Name substance A. (1mk)
- Vanadium (V) oxide is a commonly used catalyst in the contact process.
- Name anther catalyst which can be used for this process. (1mk)
- Platinised asbestos.
- Give two reasons why vanadium (V) oxide is the commonly used catalyst. (2mks)
- Not highly/ easily poisoned by impurities
- It is cheap
- Name anther catalyst which can be used for this process. (1mk)
- State and explain the observations made when concentrated sulphuric (VI) acid is added to crystals of copper (II) sulphate in a beaker. (1mk)
- Crystals turn from blue to white; concentrated sulphuric (VI) acid removes water of crystallization from hydrated copper (II) sulphate.
- The reaction of concentrated sulphuric (VI) acid with sodium chloride procduces hydrogen chloride gas. State the property of concentrated sulphuric (VI) acid illustrate in this reaction. (1mk)
- Concentrated sulphuric (VI) acid is less volatile hence displaces more volatile acids from their salts.
- Name four uses of sulphuric (VI) acid. (2mks)
- manufacture of fertilizers, pigments, dyes, drugs, explosives, detergents, and inorganic salts and acids, as well as in petroleum refining and metallurgical processes.
- Describe how oxygen is obtained from air on a large scale. (3mks)
-
Join our whatsapp group for latest updates
Tap Here to Download for 50/-
Get on WhatsApp for 50/-
Download Chemistry Paper 2 Questions and Answers - Form 4 Term 1 Opener Exams 2023.
Tap Here to Download for 50/-
Get on WhatsApp for 50/-
Why download?
- ✔ To read offline at any time.
- ✔ To Print at your convenience
- ✔ Share Easily with Friends / Students