- This paper consists of three sections A, B and C.
- Answer all questions in sections A and B and any two questions in section C.
- All answers must be written in the spaces provided.
SECTION A: (30 MARKS)
Answer all the questions from this section.
- Name three types of specialized feeding carried out in livestock management. (1 ½ mks)
- Name the breed of sheep adapted to wet and marshy conditions of Kenya highlands. (1 mk)
- Give two ways of sterilizing a milk churn. (1 mk)
- Define the term epistasis as used in livestock production. (1mk)
- Name two methods used in ration computation. (1mk)
- Give five reasons for care and maintenance of farm tools and equipment (2½ mks)
- Give two reasons for throwing grains to poultry on the litter in a deep litter poultry house. (2mks)
- What are the terms used to describe the young ones of the following livestock. (2mk)
- Rabbits –
- Fish –
- Goat –
- Donkey -
- Name the causal organisms of the following diseases in livestock. (2mk)
- East coast fever -
- Trypanosomiasis -
- Rift Valley fever -
- Anaplasmosis -
- Give four reasons for castrating farm animals. (2mk)
- List any three light breads of poultry (1½)
- Give two qualities of a creep feed that makes it suitable for piglets (2mk)
- State four management practices carried out in sheep during preparation for tupping. (2mk)
- Name any two plumbing tools (1mk)
- List two symptoms of bloat attack in cattle (1mk)
- What do you understand by the following terms as used in livestock health? (2mk)
- Predisposing factors –
- Rigor mortise -
- Name four control measures of fleas in a flock of layers (2mk)
- Differentiate between the following tools (2mk)
- A sickle and secateurs -
- A pair of tin snip and a pipe wrench -
- What is the vector of Nagana? (½ mk)
SECTION B: (20MARKS)
Answer all the questions in the spaces provided.
-
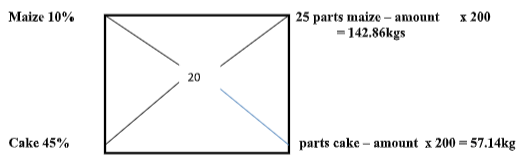
- Compute 200kg feed ration with 20% DCP from maize with 10% DCP and cotton seed cake containing 45% DCP. (4mk)
- Name two feed ingredients that should be added to balance the feed ration above. (2mk)
- Name two advantages of using a sub-soiler during land preparation (2mk)
- The diagram H and J show two types of fences
- Identify each type of fence (2mk)
- H -
- J -
- Name the correct material and correct tool for fastening wooden posts when constructing the types of fence illustrated in diagram H. (2mk)
- Material –
- Tool -
- State three advantages that fence J may have over fence H (3mk)
- Identify each type of fence (2mk)
- Study the diagram below and answer the questions that follow
- Name the type of identification illustrated above (1mk)
- Give the identification number of the pig illustrated above (1mk)
- Using a diagram, illustrate how animal number 83 can be identified using the above method. (2mk)
- What is the use of metal rails in a farrowing pen (1mk)
SECTION C: (40 MARKS)
Answer any two questions from this section.
-
- Describe any four general effects of parasites on livestock (8mk)
- Name two causes of livestock diseases (2mk)
- Describe East Coast Fever (E.C.F.) under the following subheadings
- Animals attacked (1mk)
- Causal agent (1mk)
- Vector (1mk)
- Symptoms (5mk)
- Control (2mk)
-
- Explain the uses of the various hand tools in the construction of the Kenya top bar hive. (12mk)
- Describe the management practices that would ensure maximum yield of fish in a fish pond. (8mk)
-
- Describe various cultural uses of livestock (8mk)
- Describe various livestock rearing practices (12mk)

MARKING SCHEME
SECTION A: (30 MARKS)
Answer all the questions in the spaces provided.
- Name three types of specialized feeding carried out in livestock management. (1 ½ mks)
- Creep feeding
- Flushing
- Steaming up
- Name the breed of sheep adapted to wet and marshy conditions of Kenya highlands. (1 mk)
- Romney marsh / kent
- Give two ways of sterilizing a milk churn. (1 mk)
- Wash with hot and suitable detergent
- Use chemical sterilizers
- Drying in the sun
- Define the term epistasis as used in livestock production. (1mk)
- Combination of genes which individually could be undesired
- Name two methods used in ration computation. (1mk)
- Trial and error
- Pearson’s square method
- Give five reasons for care and maintenance of farm tools and equipment (2½ mks)
- To reduce cost of replacement
- To increase durability
- Increase efficiency
- Prevent injury to the user
- Avoid damages to the tool
- Give two reasons for throwing grains to poultry on the litter in a deep litter poultry house. (2mks)
- To help turn the litter to keep id dry
- To keep poultry busy
- What are the terms used to describe the young ones of the following livestock. (2mk)
- Rabbits - Kindling
- Fish - Fingerling
- Goat - Kid
- Donkey - Foal
- Name the causal organisms of the following diseases in livestock. (2mk)
- East coast fever - Protozoan/ Theirelia parva
- Tryponosomiasis - Protozoan/ Trypanosome
- Rift Valley fever - Virus
- Anaplasmosis - Protozoan/ Anaplasma marginale
- Give four reasons for castrating farm animals. (2mk)
- Control breeding diseases
- Makes animal docile
- improves meat quality
- Control inbreeding
- Increases weight gain
- . List any three light breeds of poultry (1½)
- Minorca - Sykes
- Ancona
- Give two qualities of a creep feed that makes it suitable for piglets (2mk)
- Highly palatable
- Highly digestible
- Rich in proteins
- State four management practices carried out in sheep during preparation for tupping (2mk)
- Crutching/tagging/barling
- Raddling
- Hoof trimming
- Ringing
- Name any two plumbing tools (1mk)
- Stock and die
- Pipe wrench
- Pipe cutter
- List two symptoms of bloat attack in cattle (1mk)
- Distended left side of belly
- Immobility
- Digestive complication
- Constipation
- What do you understand by the following terms as used in livestock health? (2mk)
- Predisposing factors:
- Conditions inside or outside the body of animal which lead to the animal contracting a disease or injury.
- Rigor mortise:
- Stiffening of joints
- Predisposing factors:
- Name four control measures of fleas in a flock of layers (2mk)
- Dusting the poultry house/nest
- Ensure cleanliness
- Apply petroleum jelly on infected parts
- Dust birds with insecticide
- Differentiate between the following tools (2mk)
-
- Sickle - cutting back pyrethrum stack/harvesting rice, grass
- Secateurs - soft branches /tungs
(mark whole)
- A pair of tin snip and a pipe wrench
- Tinsnips – Cutting through sheet of metal,
- Pipe wrench: - Loosening or tightening metal pipes.
-
- What is the vector of Nagana? (½ mk)
- Tsetsefly
SECTION B: (20MARKS)
Answer all the questions in the spaces provided.
-
- Compute 200kg feed ration with 20% DCP from maize with 10% DCP and cotton seed cake containing 45% DCP. (4mk)
- Name two feed ingredients that should be added to balance the feed ration above. (2mk)
- Vitamins; minerals
- Name two advantages of using a sub-soiler during land preparation (2mk)
- Breaks hardpans
- Cultivate compacted soil
- Compute 200kg feed ration with 20% DCP from maize with 10% DCP and cotton seed cake containing 45% DCP. (4mk)
- The diagram H and J show two types of fences
- Identify each type of fence (2mk)
- H – Chain link/woven wire fence
- J – Live fence/hedge
- Name the correct material and correct tool for fastening wooden posts when constructing the types of fence illustrated in diagram H. (2mk)
- Material – U – nails/staples
- Tool: Claw hammer/fencing hammer/pliers
- State three advantages that fence J may have over fence H (3mk)
- More aesthetic value
- Act as wind break
- Source of livestock feed
- Cheaper to establish
- Source of fruits
- Source of firewood
- Provides organic matter
- Identify each type of fence (2mk)
- Study the diagram below and answer the questions that follow
- Name the type of identification illustrated above (1mk)
- Ear notching
- Give the identification number of the pig illustrated above (1mk)
- 110
- Using a diagram, illustrate how animal number 83 can be identified using the above method. (2mk)
- What is the use of metal rails in a farrowing pen? (1mk)
- Prevents sow from crushing the piglets.
- Name the type of identification illustrated above (1mk)
SECTION C: (40 MKS)
Answer any two questions from this section.
-
- Describe any four general effects of parasites on livestock (8mk)
- Sucking blood: Some parasites suck blood from their hosts causing Anaemia and death
- Parasites eat food intended for livestock – this an lead to malnutrition and weakness in the host.
- Obstruction: Internal parasites block the alimentary canal which can cause death.
- Transmission of disease – can cause death or lower production in livestock.
- Damage internal tissues and organs preventing proper functioning
- Irritation to animals : some parasites make animals uncomfortable
(4 x 2 = 8 mks)
(Exaplanation 1 mk)
(Stating 1 mk)
- Name two causes of livestock diseases (2mk)
- Pathogens eg bacteria, virus, protozoa and fungi
- Chemicals
- Physical eg injuries
- Nutritional causes
- Describe East Coast Fever (ECF) under the following subheadings
- Animals attacked - Cattle (1mk)
- Causal agent - Theirelia parva (1mk)
- Vector – Brown ear tick (1mk)
- Symptoms
- High fever
- Lachrymal discharge
- Swelling of lymph nodes
- Difficult breathing
- Self- isolation from others
- Haemorrhage in the vulva and mouth (5mk)
- Coughing
- Sight impairment
- Control (2mk)
- Eradication of ticks
- Intra-muscular injection of antibiotics and iron
- Control strange animals from the farm
- Describe any four general effects of parasites on livestock (8mk)
-
- Explain the uses of the various hand tools in the construction of the Kenya top bar hive. (12mk)
- Claw hammer – driving nails in and out of wood
- Tape measure/metre rule – measuring length of pieces of material
- Clamp – holding pieces of wood together when joining
- Pliers – cutting wires
- Try square – determining right angles on cutting points
- Marking/mortise gauge – marking points to cut/plane
- Ball pen hammer – Straightening/shaping sheet of metal
- Hand saw/Tenon saw – cutting pieces of wood
- Tinsnips – cutting roofing sheet/metal sheet
(8 x 1 ½ mks = 12 mks)
(1/2 mk) – naming
(1mk – explaining)
- Describe the management practices that would ensure maximum yield of fish in a fish pond. (8mk)
- Control stocking rate
- Control water pollution
- Supply adequate feed
- Provide appropriate feed
- Aerate the water by ensuring constant inflow and outflow
- Crop at correct stage
- Maintain water level
- Repair broken/cracked dykes
- Clear vegetation around the pond
- Control predators
(8 x 1 = 8 mks)
- Explain the uses of the various hand tools in the construction of the Kenya top bar hive. (12mk)
-
- Describe various cultural uses of livestock (8mk)
- Status symbol – One is regarded wealthy on owning large herds of cattle, sheep or goats.
- Medium of exchange – livestock were used during barter trade
- Social ceremonies – ceremonies like marriage and funerals had live or slaughtered animals
- Recreational purpose – some activities like cock fighting, bull fighting may utilize their time constructively.
- Describe various livestock rearing practices (12mk)
- Feeding – It enhances maintenance and productivity of the animal. Also important in preventing diseases in animals.
- Parasite and disease control – Ensures animals remain healthy and productive.
- Breeding practices – Ensures multiplication of healthy animals
- Identification – Facilitates record keeping and other aspects of livestock management
- Debeaking – Important in poultry to control vices e.g cannibalism and egg eating.
- Tooth clipping – Removal of canine teeth in piglet 24 hours after birth
- Culling – Removal of unproductive animals from a breeding herd.
- Describe various cultural uses of livestock (8mk)
Download Agriculture Paper 2 Questions and Answers - Form 4 Term 1 Opener Exams 2023.
Tap Here to Download for 50/-
Get on WhatsApp for 50/-
Why download?
- ✔ To read offline at any time.
- ✔ To Print at your convenience
- ✔ Share Easily with Friends / Students