QUESTIONS
- State two ways in which agriculture contributes directly to the development of Industries. (1mk)
-
- Why is it necessary to cultivate land before planting? (2mks)
- Give four advantages of mechanizing seedbed. (2mks)
- Explain the following terms as used in crop production. (11/2mks)
- State four factors which determine the depth of ploughing. (2mks)
- State four factors that determine the spacing of annual crop. (2mks)
- State four deficiency symptoms of phosphorous in crop. (2mks)
-
- List two factors that are considered when selecting planting material. (1mk)
- Distinguish between seed dressing and seed inoculation. (1mk)
- Give two reasons why care must be taken not to injure the crop during pruning. (1mk)
-
- State three advantages of drip irrigation in a farm. (11/2mks)
- Give any three methods of storing water in the farm. (11/2mks)
- State four characteristics of a good root stock for grafting. (2mks)
-
- Differentiate between a seedbed and a seedling bed. (1mk)
- State three factors considered in sitting a nursery bed. (11/2mks)
- How can damping off disease be controlled in a vegetable nursery? (1mk)
-
- What is soil texture? (½mks)
- State three properties of soil that are influenced by the parent material. (1½mks)
- Name a physiological disease in tomato crop. (½mks)
- Name two pruning system in coffee. (1mk)
- State two advantages of using tissue culture in crop propagation. (1mk)
- Give three advantages of using vegetative propagation in crop production. (1½mks)
SECTION B
- A farmer was advised to apply 40kg of P2O5 per hectare of maize at planting time. The phosphatic fertilizer available was single super phosphate 20% P2O5.
- Calculate how much single super phosphate fertilizer he should apply in two acres. (2mks)
- Why is it advisable to apply phosphatic at planting? (1mk)
- Study the diagram below of a soil profile and answer the questions that follows:-
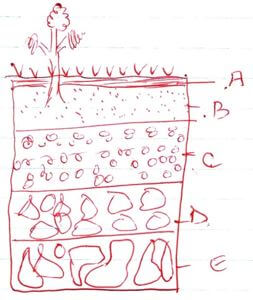
- Name the Horizon labeled A,B,C, & D (4mks)
- What does the term transition zone refers to in soil profile?
- State three distinct features of Horizon B. (3mks)
- How does the soil profile above help in determining the type of crop to be grown in an area? (2mks)
- Study the illustrations below and answer the questions that follows:-
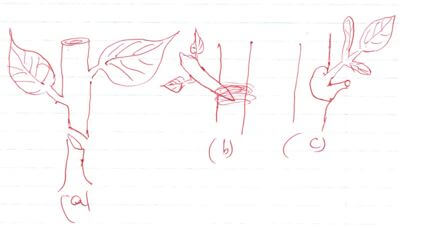
- Name the propagation methods labeled A,B & C. (3mks)
- Name any two crops propagated by Method C. (2mks)
- Name any two tools/ materials used in carrying out methods B. (2mks)
SECTION C (40 MKS)
-
- Describe the preparation of a vegetable nursery bed. (10mks)
- Describe the procedure of transplanting vegetable seedling. (10mks)
-
- Explain the factors that determine the time of harvesting the crop produce. (10mks)
- Explain the various post – harvest practices done on the crop produce after harvesting. (10mks)
- Describe the production of tomatoes under the following sub – headings;-
- Ecological requirement. (4mks)
- Seedbed preparation and planting. (6mks)
- Field management practices. (7mks)
- Harvesting. (3mks)
MARKING SCHEME
- State two ways in which agriculture contributes directly to the Development of Industries.
- Source of raw material for industries.
- Provision of market for industrial goods.
- Source of food for labour in industries
- Income from export of agricultural products is used to set up industries
-
- Why is it necessary to cultivate land before planting?
- To kill weeds.
- To incorporate manure and other organic matter.
- To destroy different stages of crop pests.
- To aerate the soil.
- To encourage the penetration of roots in soil.
- To make subsequent operation possible.
- To encourage water infiltration.
- Give four advantages of mechanizing seedbed. Makes the operation to be timely.
- It is less labourious.
- It accomplishes the work efficiently.
- It is cheaper per unit work done in large operation.
- Can perform more heavy tasks than human labour.
- Why is it necessary to cultivate land before planting?
-
- Explain the following terms as used in Crop Production:-
- Threshing: Removal of seeds of pulses and cereal from pods and grains head respectively.
- Shelling: Removal of maize grains from cobs by use of maize shellers.
- Trellising: Practice of providing support of crops with vines using wire e.g. passion fruits.
- Explain the following terms as used in Crop Production:-
- State four factors which determine the depth of ploughing.
- Soil type.
- Soil moisture content.
- Size of the seed.
- Type of germination.
- State four factors that determine the spacing of an annual crop.
- Type of machinery used.
- Soil fertility.
- Size of the plant.
- Moisture availability.
- Use of the crop.
- Pest and disease control.
- Growth habit
- State four deficiency symptoms of phosphorous in crops.
- Production of anthocyanin i.e. purplish colour in plant.
- Stunted growth.
- Poor root development.
- Inhibited fruit and seed formation.
-
- List two factors that are considered when selecting planting materials.
- Suitability to the ecological condition.
- Purity of the materials.
- Germination percentage.
- Certified seeds.
- Distinguish between seed dressing and seed inoculation.
- Seed inoculation coating the legume seeds with right strain of Rhizobium to nodulation. (1⁄2 x 2 = 1mk)
- Give two reasons why care must be taken not to injure the crop during pruning.
- Production is lowered as it tries to heal the wound.
- Cut surface may become entry points of diseases causing organism. (Any 2 x = Imk)
- List two factors that are considered when selecting planting materials.
-
- State three advantages of drip irrigation in a farm.
- Little amount of water is required.
- Water under low pressure can be used.
- It discourages fungal diseases such as blight.
- It does not encourage the growth of weeds between the rows.
- Give any three methods of storing water in the farm.
- Water tanks
- Dams
- Weirs
- Ponds
- State three advantages of drip irrigation in a farm.
- State four characteristics of a good root stock for grafting.
- Tolerate to drought.
- Resistant to soil borne diseases.
- Compatible with the scion.
- Deep rooted.
-
- Differentiate between a Seedbed and a seedling bed.
- Seedbed-prepared piece of land used for raising crops.
- Seedling bed type of nursery bed used for excess seedlings which have been removed from the nursery bed due to overcrowding.
- State three factors considered in siting a nursery bed.
- Nearness to source of water.
- Sheltered site.
- Leveled ground.
- Fertile and well drained soil.
- Nearness to the planting field.
- Secure place.
- How can damping off disease be controlled in a vegetable nursery?
- Reduce frequency of watering.
- Observe nursery hygiene.
- Routine fungal spray.
- Practice thinning to reduce overcrowding.
- Differentiate between a Seedbed and a seedling bed.
-
- What is soil texture?
- Refers to relative proportions of soil particles in a sample of soil/coarseness of fineness of a soil when felt between the fingers.
- State three properties of soil that are influenced by the parent material.
- Soil nutrient status.
- Soil physical properties.
- Soil colour.
- Name a Physiological disease in tomato crop.
- Blossom end rot.
- What is soil texture?
- Name two pruning system in coffee.
- Single stem pruning system.
- Multiple stem pruning system.
- State two advantages of using tissue culture in crop propagation.
- Establishes nathogen-free plants.
- Mature faster than those from seeds.
- Easier and faster i.e. does not show dormancy.
- Facilitate propagation of seedless crops.
- Show uniformity such as disease resistance, seed, size, colour.
- Possible to produce many varieties of compatible crops on the same root stock.
- A farmer was advised to apply 40kg of P2O5 per hectare of maize at planting time. The phosphatic fertilizer available was single super phosphate containing 20% P2O5
- Calculate how much single super phosphate fertilizer he should apply in two acres20 kgs P2O5 contained in 100kg single super phosphate.
- 40kgs P2O5 = 40/20 x 100 x 2 √(1 mk)
=400kgs
- 40kgs P2O5 = 40/20 x 100 x 2 √(1 mk)
- Why is it advisable to apply phosphatic fertilizer at planting?
- For seedling root development.
- It is slightly soluble in soil moisture thus requires near root zone.
- Calculate how much single super phosphate fertilizer he should apply in two acres20 kgs P2O5 contained in 100kg single super phosphate.
- Study the diagram below of a soil profile and answer the questions that follows:-
- Name the Horizons labeled A, B, C & D.
- A-Top Soil
- B-Sub Soil
- C-Weathered Rock
- D-Bedrock
- What does the term transition zone refers to in a soil profile?
- A merging zone between two horizontal layers in which one horizon gives rise to another.
- State three distinct features of Horizon B.
- Layer of nutrient accumulation.
- Layer of clay pan.
- Light coloured.
- Low organic matter content.
- How does the soil profile above help in determining the type of crop to be grown in an area?
- Deeper profile suit deep rooted crops.
- Deeper profile encourages high water infiltration thus reducing soil erosion.
- Deeper profile has larger soil volume hence more nutrients.
- Deeper profile has higher water retention.
- Name the Horizons labeled A, B, C & D.
- Study the illustrations below and answer the questions that follows:-
- Name the propagation methods labeled A, B and C.
- A-Side grafting.
- B-Whip/tongue grafting.
- C-Budding
- Name any two crops propagated by Method C.
- Pear; Plum
- Orange, Lemon
- Name any two tools/materials used in carrying out method B.
- Grafting Knife
- Grafting Tape
- Grafting Wax
- Water
- Name the propagation methods labeled A, B and C.
-
- Describe the Preparation of a vegetable nursery bed.
- Clear the site for nursery preparation.
- Carry out primary cultivation/plough deeply.
- Eradicate rhizomatous root systems/ eradicate perennial weeds.
- Carry out secondary cultivation/harrow to fine tilth.
- Use a rake to remove trash on the nursery bed.
- Incorporate organic manure/improve on the soil texture.
- Determine the extent of the bed.
- Ensure the nursery beds run in an East-West direction.
- Place timber boards on the sides / carry out soil and water conservation measures.
- Raise the shade/make shade material available.
- Provide mulch material.
- Describe the procedure of transplanting vegetable seedlings.
- Transplant late in the evening/ during cold weather.
- Thoroughly water the seedling in nursery bed.
- Apply phosphatic fertilizer in the hole and thorough mix with the soil in the holes.
- Dig out the seedling from the nursery bed with the aid of soil auger.
- Ensure each seedling root system has a ball of soil.
- Place gently each seedling root system in the transplanting hole.
- Cover the roots gently with soil firming it at the top.
- Apply pesticide at base.
- Water each seedling.
- Apply mulch over entire seedbed.
- Shade individual seedlings.
- Describe the Preparation of a vegetable nursery bed.
-
- Explain the factors that determine the time of harvesting the crop produce.
- Moisture content of the produce: Grains and pulses should be dry.
- Colour of leaves/fruits/grains: change in colour/pale or brown fruits.
- Intended use of the produce/market demand/ taste and preference of the consumer.
- The nutrient concentration in the produce:
- Harvest when quality of produce is highest.
- Outbreak of pest/ disease in crops:
- Harvesting done early to avoid damage.
- Escape losses from prevailing weather: Harvesting done early if rain is likely to occur.
(Award Imk for naming factor and Imk for correct explanation) (Any 2 x 5-10mks)
- Explain the various post-harvest practices done on the crop produce after harvesting.
- Drying: Grains, pulses, pyrethrum flowers e.t.c. are dried to low moisture content (11-13%).
- Threshing/Shelling: Removal of seed or grain from pods, cobs etc.
- Winnowing: Removal of Chaff from the grain or seeds.
- Seed dressing: Dusting the seed or grain with appropriate pesticides to prevent attack.
- Sorting: putting the produce in grades according to quality.
- Explain the factors that determine the time of harvesting the crop produce.
- Describe the production of tomatoes under the following sub-headings:-
- Ecological requirement.
- Warm temperatures are ideal.
- Attitude: 0-1200m above sea level.
- Well distributed rainfall during the season.
- 760-1300mm rainfall per annum.
- Free draining fertile loam soil.
- Seedbed Preparation and Planting.
- Clear bushes and remove stumps.
- Plough and harrow/till with fork jembe to medium tilth.
- Remove all perennial weeds.
- Ensure that the land has no solanacae family for 3 years to prevent diseases and pest.
- Dig hole 15cm deep.
- Space the hole at 00cm x 60cm
- Water the nursery thoroughly before uprooting.
- Lift seedlings with as much soil attached to the root.
- Field Management practices.
- Water seedlings especially in dry weather.
- Place thin mulch round seedling.
- Plant soodling at the same depth it was in the nursery.
- Gapping should be done as soon as the seedling dries up.
- Keep the field clear of weed by cultivation.
- Top dress with C.A.N. or ASN when seedling are 25-30cm tall at the rate of 20kg N/ha or 100kg CAN/ha.
- Staking allows plants to grow upright to control blight, dirt and pests.
- Prune tomatoes such that only one to two stem grow.
- In tall varieties cap stems at 1.5-1.8m high.
- Control pests such as American Bollworm, Aphids, Cutworms and nematodes using appropriate method.
- Control diseases using appropriate methods.
- Control blight by routinely spraying copper fungicides every 2 weeks.
- Control bacterial blight by using certified seeds and practicing crop rotation.
- Control blossom end rot by ensuring that soil has plenty of calcium.
- Harvesting.
- Mature at 31/2 months.
- Pick fruits for fresh market when reddish colour start to appear.
- Pick fully ripe fruits for canning purpose.
- Pack fruit in wooden crates when transporting to prevent damage to fruits.
- Expected yield at 75+ per hectare.
- Ecological requirement.
Join our whatsapp group for latest updates
Tap Here to Download for 50/-
Get on WhatsApp for 50/-
Download Agriculture Paper 1 Questions and Answers - Form 4 Term 2 Opener Exams 2023.
Tap Here to Download for 50/-
Get on WhatsApp for 50/-
Why download?
- ✔ To read offline at any time.
- ✔ To Print at your convenience
- ✔ Share Easily with Friends / Students

