INSTRUCTION TO CANDIDATES
- This paper consists of TWO sections: A and B
- Answer ALL questions in section A and B in the spaces provided.
- ALL workings MUST be clearly shown.
- Mathematical tables and electronic calculators may be used.
SECTION A 25MARKS
- At what angle should two plane mirrors be inclined at to produce 5 images? (2marks)
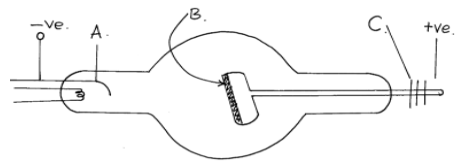
- In a simple cell consisting of copper and zinc plates, bubbles of gas are seen forming around the copper plate
- What is the name given to this defect (1mk)
- Suggest how the defect you have named in 1 (i) above can be minimized (1mk)
- In an experiment to determine the focal length of a converging lens using the lens formula, several values of image distance corresponding to value of object distance U were determined and a graph of magnification m against image distance v, plotted as shown in Figure 11 below
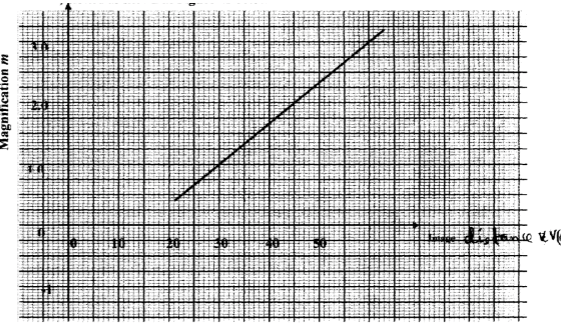
The equation of the graph can be represented by the equation
m = v/f − 1- What does the gradient of the graph represent? (1mk)
- Determine the focal length of the lens. (2mks)
- One way of magnetizing a magnet is hammering. Explain how the magnetization is achieved (2marks)
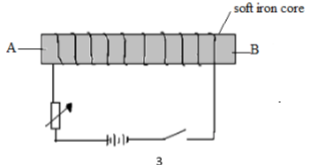
- Figure below shows a solenoid wound on a soft iron core
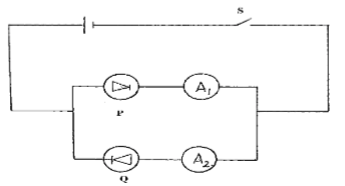
State the polarities at point A and B when the switch is closed (2mark) - Figure below shows a circle with two diodes P and Q and a cell:-
Explain the observation which would be made if S is closed (2mks) - The following is a part of a radio – active series.
Identify the radiation r, find the values of c and d. (3 marks) - State one reasons why Alluminium is preferred to copper in transmission of power ( as overhead cables) (1mark)
- Define the term ‘wavelength’ of a transverse wave (1mark)
- A boy standing 400m away from a cliff claps his hands and hears an echo 2.5s late
- Velocity of light in water is 2.2×108m/s while in glass velocity is 2.0×108m/s. Calculate the angle of incidence in water which could produce an angle of 300 in glass (3marks)
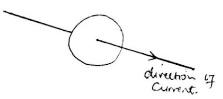
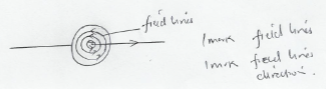
- The figure 10 below shows a current carrying conductor
- On the same diagram draw, the magnetic field pattern produced. (1mk)
- State one possible rule that can be used to predict the field direction produced in the above diagram. (1mk)
- State one advantages of using a convex mirror as a driving mirror. (1mk)
- Table below shows part of the electromagnetic spectrum
Name part labelled A (1mark)Microwave Infra-red Visible light A X-ray
SECTION B 55 MARKS
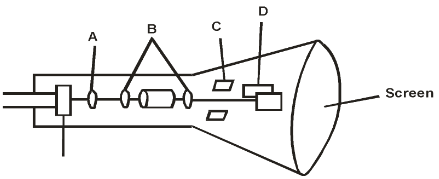
- The figure below represents a cathode ray oscilloscope (C.R.O). use it to answer the questions that follows.
- Name the parts labelled A and B. (2mks)
- What are the functions of parts labelled C and D? (2mks)
- Explain how electrons are produced . (1mk)
- Give a reason why the tube is evacuated. (1mk)
- The potential between the anode and the cathode of an X-ray tube is 80kv. Calculate;
- The energy of an electron accelerated in the tube. (Electronic charge e = 1.6 x 10-19 C) (3mks)
- The velocity of electrons in the tube. (Mass of an electron = 9.11 x 10-31kg ) (3mks)
-
- The refractive index of glass is 3/2 and that of water is 4/3 . Calculate the refractive index of glass with respect to water. (2 mks)
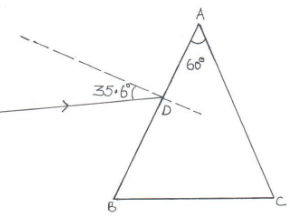
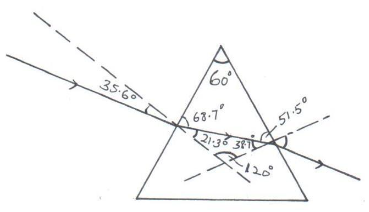
- The figure below shows a ray of light incident at an angle of 35.6° at point D on the first face of a glass prism ABC. The refractive index of the prism is 1.6.
- Determine the angle of refraction at point D. (2 mks)
- Find the angle of incidence of the refracted ray on the face AC to 1 decimal point. (2 mks)
- Complete the ray diagram to show the emergent ray from the face AC. (2 mks)
- State two conditions necessary for total internal reflection to occur. (2 mks)
-
- State one application of a capacitor. (1 mk)
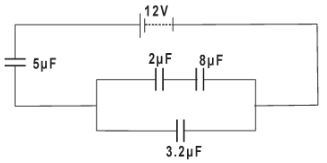
- Figure 7 shows four capacitors connected to a battery of 12 volts.
Calculate:- Effective capacitance. (2 mks)
- Charge on 3.2µF (2 mks)
- Potential Difference across 5µF (2 mks)
- The energy stored by 2µF (2 mks)
- What are effects on capacitance of a parallel plate capacitor when :
- Increasing the area overlap of the plates ? (1mk)
- Increasing the distance of separation between plates ? (1mk)
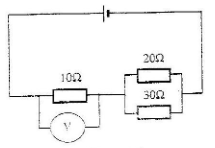
- The cell in figure 10 has an e.m.f of 2.1 V and negligible internal resistance.
Determine the- Total resistance in the circuit (2 marks)
- Current in the circuit (1 mark)
- Reading of the voltmeter (2 marks)
-
- State Lenz’s law of electromagnetic induction. (1mk)
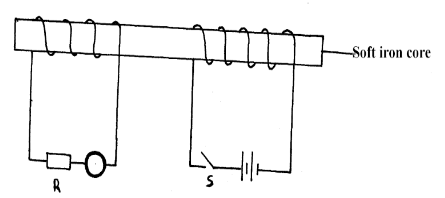
- The figure shows two coils of insulated copper wires wound on a single soft iron core. One coil is connected to a battery through a switch and the other is connected to a resister through a galvanometer.
It is observed that as the switch is closed, the pointer of the galvanometer deflects momentarily. The same as when the switch is opened.- Explain why the pointer deflects momentarily. (2mks)
- State one way in which the current through R can be increased. (1mk)
-
- State one way in which power is lost in a transformer. (1mk)
- A transformer uses 240V ac supply to deliver 9A at 80V to a heating coil. If 10% of the energy taken from the supply is lost in the transformer itself, What is the current in the primary winding? (2mks)
- The diagram below shows simplified diagram of an x-ray tube,
- Name the parts A, B, and C. (3mks)
- What adjustments would be made to:
- Increase the penetrating power of the x-rays produced. (1mk)
- Increase the intensity of the rays produced. (1mk)
- Name a suitable material for the part marked B and give a reason for your choice. (2mk)
- Name a suitable material for the part marked C and state its purpose. (2mk)
- Why is it necessary to maintain a vacuum inside the tube? (1mk)
- In a certain X- ray tube electrons are accelerated by p.d of 12 kV. Assuming all energy goes to produce X-rays, determine the frequency of the X-rays produced
(Planck’s constant =6.63x10-34 Js. Charge of an electron=1.6x10-19C) (3 mks)
MARKING SCHEME
SECTION A
- n = 360/? - 1 √1
S = 360
? -1
θ = 360
6
= 60°√1 -
- Polarization√1
- Add a depolarizer/ an oxidizing agent√1
-
- Reciprocal of the focal length power of the lens
- 1/f = gradient => f = 1/gradient
f= 13cm
-
- Hammering makes the dipoles to vibrate√1
- Earth magnetic field aligns the dipoles√1
-
- B- North pole√1
- A- South pole – Allow correct pole at one end
- A1 will shows a reading while A2 will not show any reading. This is the fact that P will be forward biased hence conducting while Q is reverse biased hence it wil not conduct.
- r =beta particle ✔, c=206 ✔ d= 82 ✔
-
- It forms a coating at the surface to prevent rusting and as an insulator
- It is less dense hence easy to carry
- It is easily available/cheaper (Any TWO √1 each)
- Distance between a particle in the wave medium and the next one that is in phase with it or Distance between two successive crest/trough √1
- V = 2nd
t
= 400 × 2
2.5
= 320m/s - n=(2.2x108)/(2.0x108)
=1.1
= sin i
sin 30
Sin I = 1.1 x sin30
= 0.55
I = sin-1 0.55 -
-
-
- Right hand grip rule
- Maxwell – cork screw rule
-
-
- Wide view
- Gives upright image
- ultra violet light
-
-
- A – Grid✔1
- B – Electron gun✔1
-
- C – Vertical deflection of beam of electrons✔1
- D – Horizontal deflection of beam of electrons✔1
- By thermionic emission or heating the filament✔1
- To prevent ionization of electrons as they move to the anode✔1
-
- E = ev✔1
E = 1.6 x 10-19 x 80000✔1
= 1.28 x 10-14 J✔1 - ½ mv2 = 1.28 x 10-14✔1
v2 = 2 ×1.28 × 10-14
9.11 ×10-31
v = √2 ×1.28 ×10-14
9.11 ×10-31 ✔1
v = 2.23 x 108 ms✔1
- E = ev✔1
-
-
- wηg = wηa × aηg
= 3/4 × 3/2
= 9/8
= 1.13 -
- η = Sin i
Sin r
1.6 = Sin 35.6°
Sin r
r = 21.3º - Angle of incidence = 38.7º (show working)
Sin C = 1/η = 1/1.6
= 38.7º -
-
- The critical angle must be exceeded. ✓¹
- Light must be travelling from a dense medium to a less dense medium. ✓¹
- η = Sin i
- wηg = wηa × aηg
-
- Capacitors are used in
- rectification smoothing circuits
- tuning circuits
- camera flash
- reduction of sparking in induction coil contact
any one 1
-
- 2 x 8 = 16 = 1.6μF
2 + 8 10
1.6 + 3.2 = 4.8μF ✔
CT = 5 x 4.8 ✔ = 24 = 2.45 x 10-6F ✔
5 + 4.8 9.8 - Q = CV
= 2.45 x 10-6 x 12 = 2.94 x 10-5C ✔
charge on 3.2μF = 2/3 x 2.94 x 10-5
= 1.96 x 10-5C ✔ - p.d on 5mF = Q = 2.94 x 10-5 = 5.88volts ✔
C 5 x 10-6 - energy = 1/2CV2 ✔
= ½ x 2 x 10-6 x 6.122
= 3.75 x 10-5J ✔
- 2 x 8 = 16 = 1.6μF
-
- Capacitance will also increase
- capacitance will decrease.
-
- Parallel circuit 1/30 + 1/20 = 5/60 or 60/50
R = 12 Ω
Total resistance = 10 + 12 = 22Ω (2 marks) - l = V/R = 2.1/22 = 0.095A (1 mark)
- Reading of the voltmeter
V = lR = 10 x 2.1 = 0.95 (2 marks)
22
- Parallel circuit 1/30 + 1/20 = 5/60 or 60/50
- Capacitors are used in
-
- Lenz’s Law states that the direction of induced current is such that it opposes the charge producing it.✔
-
- When switch S is closed, the magnetic field strength increases (magnetic flux) from zero to maximum ✔½This changing magnetic flux (field) induces an e.m.f in the secondary coil ✔1 When the switch is opened, the magnetic field strength decreases (magnetic flux) from maximum to zero ✔½This produces an induced current in the secondary coil
- Having more turns on the coil connected to the cell ✔
-
-
- Hysterisis
- Eddy currents
- Resistance of wire
- Loss of magnetic flux linkage
- Power Primary x 90/100 = VsIs ✔1
240 x IP x 90/100 = 80 x 9
IP = 80 × 9 × 100 ✔1 = 3.33A ✔1
240 90
-
-
- A – cathode B – Anode C – Cooling fins
-
- increase the p.d at the anode (B)
- increase the cathode heater current
- Tungsten:- It has a high melting point so the heat produced will not melt it easily
- Copper – it is used to cool/conduct heat away from the anode
- So that the electrons do not collide with gas molecules which could result in loss of energy.
- E = QV = hf ✔½
1.6 x 1019 x 1,200 = 6.63 x 1034 x f ✔½
f = 2.9 x 1018 Hz ✔
Join our whatsapp group for latest updates
Tap Here to Download for 50/-
Get on WhatsApp for 50/-
Download Physics Paper 2 Questions and Answers - Form 4 End Term 2 Exams 2023.
Tap Here to Download for 50/-
Get on WhatsApp for 50/-
Why download?
- ✔ To read offline at any time.
- ✔ To Print at your convenience
- ✔ Share Easily with Friends / Students