- This paper consists of TWO sections: A and B
- Answer ALL questions in section A and B in the spaces provided.
- ALL workings MUST be clearly shown.
- Mathematical tables and electronic calculators may be used.
SECTION 1 (25 MARKS)
- State one conditions necessary for the occurrence of an annular eclipse (1mk)
- Two plane mirrors are inclined at an angle of 120° to each other such that their reflecting surfaces face each other. An object pins stands midway between the mirrors.
Calculate the number of images formed. (2mks) - Distinguish between hard and soft magnetic materials. (2marks)
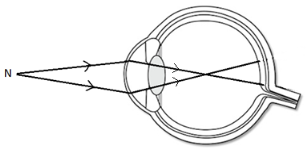
- The figure shows the eye defect
Name the defect and state how it can be corrected. (2marks) - State two defects of a simple cell and how each can be minimized. (2mks)
- Differentiate between electromotive force and potential difference. (2mks)
- An electric bulb rated, 40W is operating on 240V mains. Determine the resistance of its filament. (3mks)
- State one factor other than thickness, which determines the frequency of sound from stretched wire at room temperature. (1mk)
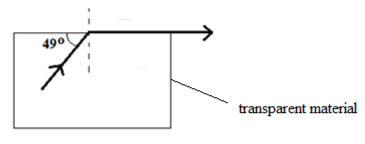
- The figure below shows a ray of light passing through a transparent material placed in air.
Calculate the refractive index of the transparent material. (2 marks) - The force on a conductor carrying a current in a magnetic field can be varied by changing, among others, the magnitude of the current and the magnetic field strength. Name any other factor that can be changed to vary the force. (1marks)
- Arrange the following electromagnetic waves in the order of increasing wavelength.
Ultraviolet, X –rays, radio waves, γ-rays. (1mk) - State one causes of power loss in long distance transmission wires and how these loses can be minimized. (2mks)
- The table below carries information on the type of radiation, detector and use for some of the electromagnetic radiations.
Fill in the blank spaces. (2mks).Type of radiation Detector Use Microwave Crystal detector, solid state diodes ______________________ ___________________ Thermopile, blackened bulb thermometer Warmth sensation
SECTION B (55 MARKS)
Answer all the questions in this section in the spaces provided.
-
- Figure 7 shows a simple electric bell circuit.
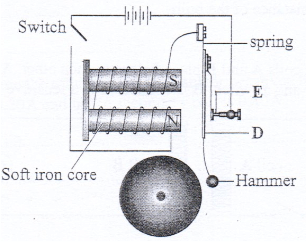
- Name the parts labelled
- D ………………………………………………………. (1 mark)
- E ……………………………………………………….. (1 mark)
- When the switch is closed, the hammer hits the gong repeatedly. Explain why:
- The hammer hits the gong. (2 marks)
- The hammer hits the gong repeatedly. (2 marks)
- Name the parts labelled
- An electric bulb is rated 60W, 240V. Determine:
- the current that flows through it when it is connected to a 240V supply. (2 marks)
- The resistance of the bulb. (2 marks)
- Figure 7 shows a simple electric bell circuit.
-
- State Faradays law of electromagnetic induction. (1 mark)
- The primary coil of a transformer has 1200 turns and the secondary coil has 60 turns. The transformer is connected to a 240V a.c source. Determine
- The output voltage. (2 marks)
- The output current when the primary coil has a current of 0.5A (Assume there is no energy losses) (2 marks)
- One of the primary ways in which power is lost in transformers is through eddy currents. State how eddy currents can be minimized. (1 mark)
- Determine the cost of using an electric iron rated 1500W, for a total of 30 hours given that the cost of electricity per kwh is Ksh 8. (2 marks).
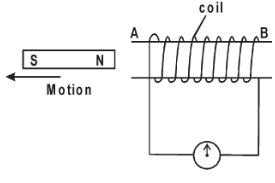
- The figure below shows a coil and a magnet being removed from the coil.
Indicate the direction of flow of current on the coil. (1 mark).
-
- State Ohms’ law (1mark).
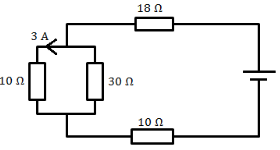
- From the circuit diagram below
Determine- The current through the 30Ω resistor (2 marks)
- The total current in the circuit (2 marks)
- The total resistance in the circuit (2 marks)
- The total P.d in the circuit (2 marks).
- The graph below shows relationship between voltage and the current obtained from an experiment performed by form 4 students.
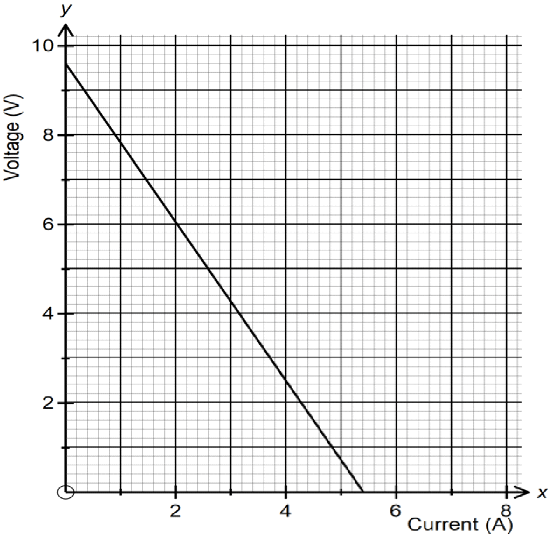
- Draw a circuit that could be used to obtain the results shown on the graph. (1 mark)
- From the graph determine the emf of the battery used give the relation (2 marks)
E = IR + Ir - Determine the internal resistance of the battery. (2 marks)
-
- distinguish between hard and soft x-rays . (1mk)
- Figure below shows a circuit of a modern x-ray tube.
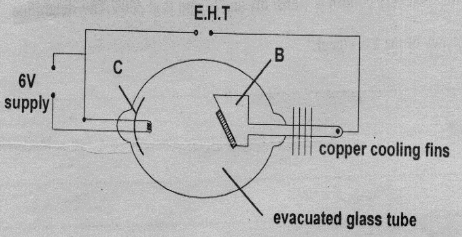
- Indicate the path of the x-ray beam produced by the tube. (1mk)
- Give the function of the part labelled C. (1mk)
- Identify part labelled B. (1mk)
- In modern models of x-ray tubes, part B rotates, Give a reason for this rotation. (1mk)
- How can the intensity of the x-rays be increased (1mk)
- An x-ray tube operates at 30k V and a current of 20m A, calculate the electric power dissipated. (2mks)
- Give a reason why C.R.O is a more accurate device as a voltmeter than a moving coil meter. (1mk)
- Give one difference between x-rays and cathode rays. (1mk)
- Figure below shows the trace on the screen of an a.c signal connected to Y-plates of a C.R.O
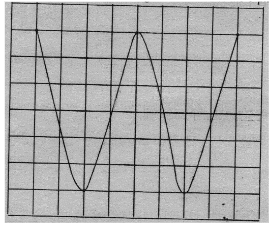
Given that the time base control is 10ms/div and y gains200V/div. Determine;- The frequency of the a.c signal. (2mks)
- The peak voltage of the signal. (2mks)
-
- When a radiation was released into a diffusion chamber, short, thick tracks were observed. State with reason, the type of radiation was detected. (2mks)
- The half-life of a certain radioactive element is 8 years.What fraction of the element will be remaining after 32 years. (2mks)
- State what is meant by an extrinsic semi-conductor. (1 mark)
- Figure 11 shows a depletion layer in an unbiased p-n junction.
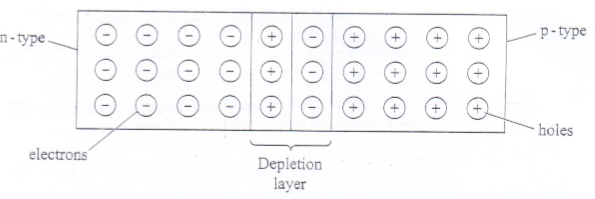
Figure 11
State how a battery can be used to make the depletion layer narrower. (1 mark) - Figure 12 shows an incomplete circuit of a full wave rectified.
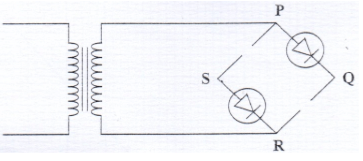
Figure 12- Draw in the Figure 12 two more diodes to complete the circuit. (2 marks)
- Show on the Figure 12 the points across which the output of the rectifier should be obtained (1 marks)
MARKING SCHEME
Section 1 (25 marks)
-
- Moon is between sun and the Earth
- During new moon
- Moon far from the Earth
- Number of images = 360° = I
ϴ
360° = I
120
= 21 Images -
- Hard magnetic material – hard/difficult to magnetize but once magnetized retains the magnetism for a long time.
- Soft magnetic materials – magnetized easily but do not retain their magnetism for long.
-
- Short sightedness/Myopia
- Use diverging lens
-
- Polarization – Add a depolarizer e.g. manganese dioxide – react with hydrogen to form water
-
- Local Action – Use pure Zinc
- Alloying Zinc electrode with Mercury
-
- Electromotive force – Voltage between the terminals of a cell when no current is flowing through an external circuit when the circuit is open.
- Potential difference – Voltage across the terminals of a cell when current is being drawn from it (in a closed circuit)
- P = 40W
V = 240v
R = V2/P
R = 2402
40
R = 1440 Ω -
- Length of the wire
- Tension in the wire
- Refractive index η = 1
sin C
C = (90° – 49°) = 41°
η = 1
sin 41°
η = 1.524 - Length of the conductor inside the M.F
- Y-rays, X-rays, UV light, Radio waves
-
- Power loss inform of heat which dissipated due to resistance of the conductor wire.
- Minimized by reducing current and resistance
-
- Radar communication, cooking
- Infrared radiation
Section Two (55 marks).
-
-
-
- D_______soft iron armature.
- E______ contact screw.
-
- Current flows in the circuit and the core becomes magnetized. The electromagnet induces magnetism in the soft iron strip(armature) which is then attracted by the armature striking the gong.
- The attraction of the soft iron armature separates the contacts, breaking the circuit. Magnetism in the core ' dies off' and the spring returns the armature to its original position. Contact is made again and the process is repeated.
-
-
- Power = VI
I = P/V
= 60/240
= 0.25A. - R = V/I
= 240/0.25
= 960 Ohms.
- Power = VI
-
-
- Faraday law of electromagnetic induction states that the magnitude of the induced emf is directly proportional to the rate of charge of magnetic flux linkage.
-
- Np = Vp
Ns = Vs
1200 = 240
60 Vs
Vs = 12V - Ip = 0.5
Ip = Vp
Ip = Vs
Is = 240 × 0.5
12
Is = 10A - The core is laminated
- Np = Vp
- E = PI
P = 3000W
P = 3.0KW
t = 30Hrs
E = 3 × 30
E = 90Kwh
Cost = 90 × 8
= Kshs 720 -
- Current direction in the coil - downwards
- Anticlockwise when viewed from end B
-
- Ohm’s law states that the voltage across a conductor is directly proportional to the current flowing through it provided that all physical conditions and temperature remain constant.
-
- Voltage across 10Ω Resistor
V = 3 × 10 = 30V
Current through the 30Ω
I = V/R
I = 30/30
I = 1A - Total current = 3A +1A = 4A
- Total resistance = 18+ 10+ ( 30×10)
(30+10)
= 35.5 Ohms - V = IR
= 4 × 35.5
=142 V.
- Voltage across 10Ω Resistor
-
- E = IR + Ir
E = V + Ir
V = E − Ir. V = −Ir + E
E = Y intercept
= 9.5 V. - r = gradient
= 1.759 Ohms.
- E = IR + Ir
-
-
- Hard xrays : produced by fast moving electron as a result of high accelerating Voltage. They have Short wavelength and thus high penetrative power.
- Soft x-rays: produced by electrons of low velocities. Have less energy's, longer wavelength thus low penetrative power.
-
- Focusing cathode __focuses electron beam onto the target.
- Copper anode.
- To change the point of impact of the beam,thereby reducing wear and tear.
- Increasing the heating current so as to produce greater number of electrons.
- Electrical power = V X I
= 30000 X 0.02
= 600W. -
- Has infinite resistance and does not therefore take any current.
- Can measure both ac and dc.
- can measure large voltage without damage.
-
- Cathode rays: beam of electrons. Negatively charged particles.
- Xrays. Electromagnetic radiation.
-
- Time base control = 10ms/div
No. of div. = 8
Total time = 8×10
= 8ms
No. of cycles. = 2
Periodic time. = 80/2
=40ms.
Frequency. = 1/40ms
f = 25Hz. - peak voltage = 200 ×3
= 600V.
- Time base control = 10ms/div
-
-
- Alpha particles __. Cause heavy ionisation loosing energy rapidly, hence their short range.
- fraction remaining = [½]^32/8
=½4
= 1/16 - This is an intrinsic semiconductor to which some impurities have been added to enhance conductivity.
- Connecting p-type region to the positive terminal and n-type to the negative terminal.
-
-
Download Physics Paper 2 Questions and Answers - Form 4 Term 3 Opener Exams 2023.
Tap Here to Download for 50/-
Get on WhatsApp for 50/-
Why download?
- ✔ To read offline at any time.
- ✔ To Print at your convenience
- ✔ Share Easily with Friends / Students