- Answer all the questions in the spaces provided
- Candidates should answer the questions in English.
-
- What is meant by the term genetic counseling? (1mk)
- State two examples of discontinuous variation in humans. (2mks)
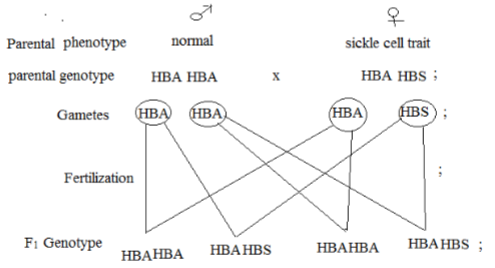
- A female with sickle cell trait marries a normal man. The allele for sickle cell is HbS and the normal allele is HbA. Determine the probability that their first born will have the sickle cell trait. Show your working. (5mks)
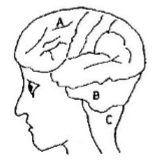
- The diagram below shows surface view of a human brain.
- Name the parts labeled B and C. (2mk)
- State three functions of the part labelled A (3mk)
- State what would happen if the part labelled A was damaged (1mk)
- Name any two tactic responses of plants (2mks)
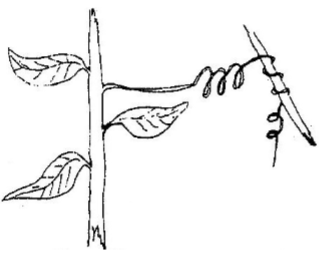
- A response exhibited by a certain plant tendril is illustrated below
-
- Name the type of response (1mk)
- Explain how the response named in (a)(i) above occurs. (2mk)
- What is the importance of tactic responses to microscopic organisms? (1mk)
- State four applications of plant hormones in agriculture. (4mk)
-
-
-
- How do animals obtain nitrogen element in their bodies? (1mk)
- State the importance of the process of denitrification in nitrogen cycle. (2mks)
- In what form is the protein material in dead organism converted into by saprophytic bacteria and Fungi? (1mk)
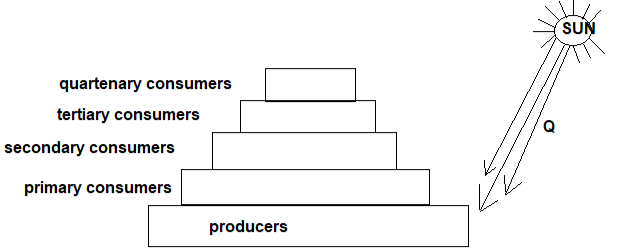
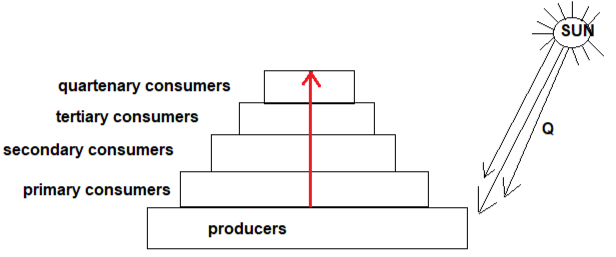
- Study the pyramid of numbers below and answer the questions that follow.
- Identify energy Q (1mk)
- What is the role of energy Q in producers? (1mk)
- Using an arrow of about 1cm indicate the energy flow in the pyramid. (1mk)
- Through which process is energy lost in a food chain. Name one. (1mk)
-
- The table below shows the approximate percent concentration of various components in blood plasma entering the kidney glomerular filtrate and urine of a healthy human being.
Component Plasma Glomerular Urine Filtrate Water 90 90 94 Glucose 0.1 0.1 0 Amino Acids 0.05 0.05 0 Plasma proteins 8.0 0 0 Urea 0.03 0.03 2.0 In organic ions 0.72 0.72 1.5 - Name the process responsible for the formation of glomerular filtrate. (1mk)
- What process is responsible for the absence of glucose and amino acids in urine? (1mk)
- Explain why there are no plasma proteins in the glomerular filtrate. (1mk)
- Besides plasma proteins what other major component of blood is absent in the glomerular filtrate. (1mk)
- Why is the concentration of urea in urine much higher than its concentration in the glomerular filtrate? (2mk)
- Name the tubules that drain:-
- Urine from kidney to urinary bladder (1mk)
- Urine from urinary bladder to external environment (1mk)
SECTION B
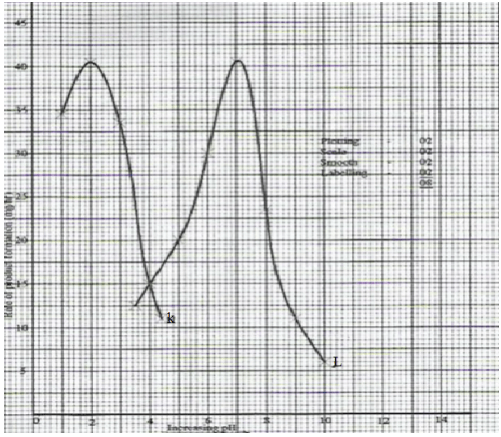
- The table below shows the rate of product formation for two enzymes, K and L over a range of pH values.
pH 1.0 2.0 3.0 4.0 5.0 6.0 7.0 8.0 9.0 10.0 Rate of product formation for enzyme K ( mg/hr) 34.5 40.5 35.5 15.0 Rate of product formation for enzyme L (mg/hr) 15.0 20.0 30.0 40.5 23.5 11.0 6.0 - On the same axis, plot graphs of the rate of product formation against pH. (8mks)
- Account for the rate of product formation for enzyme K between
- pH 1.0 and 3.0 (3mks)
- pH 3.0 and 7.0 (3mks)
- From the graph, determine
- The pH value at which the rate of product formation of the two enzymes was the same. (1mk
- The value of the rate of product formation for enzyme K and L at the pH value stated in c (i) above. (1mk)
- The optimum pH value for enzyme L. (1mk)
- State one variable that may lead to the change in the optimum rate of product formation of the two enzymes. (1mk)
- Suggest with a reason, the likely part of the human alimentary canal where enzyme K would be found. ( 2mks)
- Explain the various ways in which a typical cell is adapted to its functions (20mks)
- Describe the structure and functions of the various parts of the mammalian ear (20mks)
MARKING SCHEME
-
- What is meant by the term genetic counseling? (1mk)
- Offering information about a genetic disorder to patients to enable them make informed decisions;
- State two examples of discontinuous variation in humans. (2mks)
- sex; ABO blood group system;
- ability to roll the tongue;
- free or attached ear lobe;
- finger prints;
- presence or absence of hair in the nose and ear pinna;
- A female with sickle cell trait marries a normal man. The allele for sickle cell is Hbs and the normal allele is HbA. Determine the probability that their first born will have the sickle cell trait. Show your working. (5mks)
- What is meant by the term genetic counseling? (1mk)
- The diagram below shows surface view of a human brain.
- Name the parts labeled B and C. (2mk)
- B- Cerebellum
- C – Medulla oblongata: Acc Oblongata alone. Rej. Medulla alone
- State three functions of the part labelled A (3mk)
- Control locomotion;
- motor area/sends impulse to affectors/controls
- Voluntary
- Vision/hearing/smell/taste.
- Personality speech;
- Mediates cranial (any three)
- State what would happen if the part labelled A was damaged (1mk)
- Loss of muscle co-ordination/balance
- Name any two tactic responses of plants (2mks)
- phototaxis;
- chemotaxis;
- aerotaxis;
- osmotaxis;
- Name the parts labeled B and C. (2mk)
- A response exhibited by a certain plant tendril is illustrated below
-
- Name the type of response (1mk)
- Thigmotropism / haptotropism
- Explain how the response named in (a)(i) above occurs. (2mk)
- Contact with support; causes migration of auxin to the other side; causing faster growth on the side away from contact surface; (causing tendrils curl around support.)
- Name the type of response (1mk)
- What is the importance of tactic responses to microscopic organisms? (1mk)
- Escape injurious stimuli / seek favorable habitats; move towards light / stimuli
- State four applications of plant hormones in agriculture. (4mk)
- Induce root growth in stem cutting
- Selective weed killers
- Encourage apical dominance
- Encourage sprouting of side branches
- Breaking seeds dormancy
- Induce parthenocarpy
- Promotes flowering
- Induce fruit fall
- Accelerates ripening of fruits.
-
-
-
- How do animals obtain nitrogen element in their bodies? (1mk)
- By eating /feeding food that contain proteins; either plant maternal (herbivorous) or feeding on other animals (carnivorous)
- State the importance of the process of denitrification in nitrogen cycle. (2mks)
- It facilitates the release of free nitrogen into the atmosphere; Hence the nitrogen is made available for cycling;
- In what form is the protein material in dead organism converted into by saprophytic bacteria and Fungi? (1mk)
- Ammonia (NH3)
- How do animals obtain nitrogen element in their bodies? (1mk)
- Study the pyramid of numbers below and answer the questions that follow.
- Identify energy Q (1mk)
- Light energy/solar
- What is the role of energy Q in producers? (1mk)
- Photolysis
- Identify energy Q (1mk)
- Using an arrow of about 1cm indicate the energy flow in the pyramid. (1mk)
- Through which process is energy lost in a food chain. Name one. (1mk)
- Respiration/ (heat)
- Excretion/sweating/urination/exhalation/
- Defaecation/
- Some animal parts are not consumed as horns, hair-indigestable foods
-
- The table below shows the approximate percent concentration of various components in blood plasma entering the kidney glomerular filtrate and urine of a healthy human being.
- Name the process responsible for the formation of glomerular filtrate. (1mk)
- Ultra filtration
- What process is responsible for the absence of glucose and amino acids in urine? (1mk)
- Selective reabsorption
- Explain why there are no plasma proteins in the glomerular filtrate. (1mk)
- Because the pores in the glomerular capillaries are too small for plasma protein to pass through;
- Besides plasma proteins what other major component of blood is absent in the glomerular filtrate. (1mk)
- Blood cells
- Why is the concentration of urea in urine much higher than its concentration in the glomerular filtrate? (2mk)
- Most of the water in the glomerular filtrate is reabsorbed back into blood stream; whereas very little or no urea is reabsorbed;
- Name the tubules that drain:-
- Urine from kidney to urinary bladder (1mk)
- Ureter
- Urine from urinary bladder to external environment (1mk)
- Urethra
- Urine from kidney to urinary bladder (1mk)
- Name the process responsible for the formation of glomerular filtrate. (1mk)
SECTION B
Answer question 6 compulsory and either question 7 or 8 in the spaces provided after question 8
- The table below shows the rate of product formation for two enzymes, k and L over a range of pH values.
- On the same axis, plot graphs of the rate of product formation against pH. (8mks)
Plotting – all points 2mks
(smooth) curves ½ mark each 1mk
Appropriate scales – X ad Y (2mks)
(correct) labeling of axes – (2mk)
Identity of curves (1mk) -
- Account for the rate of product formation for enzyme K between pH 1.0 and 3.0 (3mks)
- Rate product formation increases with increase in pH up to the optimum/ then decreases; pH 2.0 is the optimum pH value for the activity of enzyme K; between pH 1 and 2, the enzyme molecules are activated;
- pH 3.0 and 7.0 (3mks)
- Rate of product formation (sharply) decreases with the increase in pH; enzyme K is not favoured by the increase in pH, hence is denatured; no product forms above/beyond pH 4.0 and 7.0(all enzyme molecules will have denatured);
- Account for the rate of product formation for enzyme K between pH 1.0 and 3.0 (3mks)
- From the graph, determine
- The pH value at which the rate of product formation of the two enzymes was the same. (1mk
- pH 4;
- The value the rate of product formation for enzyme K and L at the pH value stated in c(i) above. (1mk)
- 15mg/hr;
- the optimum pH value for enzyme L. (1mk)
- 7.0;
- The pH value at which the rate of product formation of the two enzymes was the same. (1mk
- State one valuable that may lead to the change in the optimum rate of product formation of the two enzymes. (1mk)
- temperature( increase beyond 40oC or extremely lowering it);
- (varying )substrate concentration;
- Enzyme concentration;
- suggest with a reason, the likely part of the human alimentary canal where enzyme K would be found. ( 2mks)
- stomach;
- acidic medium /low pH;
- On the same axis, plot graphs of the rate of product formation against pH. (8mks)
- Explain the various ways in which a typical cell is adapted to its functions (20mks)
- Has a cell membrane; with pores; that regulates substances entering and leaving the cell;
- cytoplasm; contain sugars and salts; for maintaining its osmotic pressure; also has a liquid medium; for all biochemical reactions;
- nucleus; contain chromosomes having hereditary material; and controls all the activities of the cell;
- ribosomes; are sites for protein synthesis;
- golgi bodies/apparatus; for secretion of hormones and enzymes; formation of lysosomes;
- lysosomes; contain lytic enzymes for breaking down worn-out organelles;
- secretory vesicles; formed from golgi apparatus for secreting substances;
- smooth endoplasmic reticulum; synthesizes and transports lipids;
- rough endoplasmic reticulum; transport proteins;
- nucleolus; controls the activities of the nucleus; produces ribosomes;
- mitochondria; form sites for energy production; c
- centrioles; formation of cilia and flagella; forms spindle fibres used in cell division;
- plant sap vacuoles; store salts and other dissolved substances; controls osmotic pressure and turgidity of cells;
- food vacuoles involved in digestion of engulfed food;
- chloroplasts; form sites for photosynthesis in plant cells; Max.20mks
- Describe the structure and functions of the various parts of the mammalian ear (20mks)
- Pinna; is wide/funnel-shaped to collect/gather sound waves; and direct them to the auditory canal into the ear;
- Eardrum/tympanic membrane is thin and light; to convert sound waves into vibrations;
- Ear ossicles/ malleus, incus and stapes are of high density; to magnify/amplify sound waves;
- Oval window is smaller than eardrum; to magnify the sound waves; and direct them to the inner ear;
- Cochlea is long and coiled; to increase surface area; for attachment of receptor cells/sensory hairs; cochlea has many sensory hairs; which receive sound vibrations and generate impulses;
- Liquid or fluid/endolymph in cochlea; transmit sound vibrations;
- Auditory nerve; transmit impulses to the brain for interpretation;
- Eustachian tube; link the mouth and middle ear to equalise pressure; between middle and outer ear to prevent damage to delicate eardrum;
- Round window; lose excess vibrations; to avoid continuous stimulation;
- Semi-circular canals; contain receptors for body balance and posture;
- External auditory canal cells produce/secrete wax; to trap dust particles/solid/micro-organisms that can damage eardrum; Max.20mks
Download Biology Paper 2 Questions and Answers - Form 4 Term 3 Opener Exams 2023.
Tap Here to Download for 50/-
Get on WhatsApp for 50/-
Why download?
- ✔ To read offline at any time.
- ✔ To Print at your convenience
- ✔ Share Easily with Friends / Students