INSTRUCTIONS TO CANDIDATES: -
- Answer all the questions in the spaces provided
- Candidates should answer the questions in English.
- Give a reason why using a sharp blade is necessary when sectioning during preparation of specimens for observation under the microscope. (1mk)
- The following reaction may occur in a forward and backward direction
Water + Carbon (IV) OxideGlucose + Oxygen + Energy
- Name the organelle where the above reaction occurs.
- Forward direction (1mk)
- Backward direction (1mk)
- Give one difference for the two organelles named in (a) above (1mk)
Chloroplast Mitochondrion
- Name the organelle where the above reaction occurs.
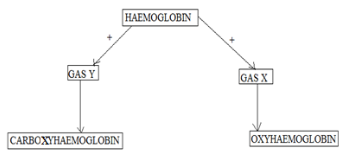
- The chart below represents how respiratory gases are transported in the human blood.
- Identify gas Y. (1mk)
- Name the advantages that oxyhaemoglobin has over carboxyhaemoglobin. (2mks)
- The paddles of whales and the fins of fish adapt these organisms to aquatic habitats.
- Name the evolutionary process that may have given rise to these structures. (1mk)
- What is the name given to such structures? (1mk)
- Give two examples of vestigial organs in man. (2mks)
- State one physiological and one structural difference between a cell wall and cell membrane. (2mks)
Cell wall Cell membrane Physiological Structural - Name the organelles that carry out the following functions (2mks)
- Formation of spindle fibres
- Osmoregulation
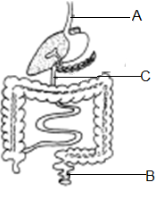
- The diagram below shows part of alimentary canal of a mammal
- Name the parts labeled A and C (2mks)
- State the function of the part labeled B. (1mk)
- Name the part of the chloroplast where the following reactions occur.
- Carbon (IV) oxide fixation. (1mk)
- Photolysis. (1mk)
- Polydactyl is a genetic disorder in which people inherit an extra digit. Polydactyl is caused by a dominant allele (B). The table below describes the different genotypes for polydactyl.
- Complete the table below by giving the correct genotype, alleles of each genotype and the expected number of fingers per hand. (4mks)
Genotype Alleles Expected number of digits per hand Homozygous dominant Six bb Heterozygous Bb - The table below shows results of marriages between various parents. Complete the table by writing the probability of each marriage producing a child with polydactyl. One has been done for you. (2mks)
Parental genotypes. Probability of child with polydactyl Bb X BB 1 Bb X bb Bb X Bb
- Complete the table below by giving the correct genotype, alleles of each genotype and the expected number of fingers per hand. (4mks)
- What are the end-products of respiration in animals when there is sufficient oxygen supply? (1mks)
- State two characteristic of visking tubing used in osmosis process? (2mks)
- Explain the physiological process responsible for keeping the seedlings upright. (3mks)
- List down substances that depend on diffusion, to be exchanged across the placenta of a female Human being. (3mks)
-
- What is meant by the term seed dormancy? (1mk)
- State any two external causes of seed dormancy (2mks)
- Explain what is meant by the following terms?
- Plasmolysed cell (2mks)
- A crenated cell (2mks)
- List down any two domestic applications of anaerobic respiration (2mks)
- State two processes through which heat energy produced by respiration lost from human body?(2mks)
- Account for the absence of glucose and proteins in the glomerular filtrate.
- Glucose (1mk)
- Proteins (1mk)
- Plants relatively have less waste to excrete than animals. Give two reasons to explain this observation. (2marks)
- Homeostasis is defined as the maintenance of a stable internal environment in the body. What is meant by expression ‘internal environment’? (1 mk)
- Name one factor that is maintained at a relatively constant level in the body by the following organs. (2mks)
- Liver
- Kidneys
- Explain two ways in which the trachea is adapted to perform its functions. (2mks)
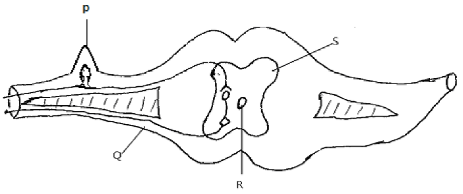
- The diagram below represent the reflex arc in human
- Name the parts labelled P and S (2mks)
- State the function of the part labelled Q (1mk)
- Name the fluid contained in part labelled R. (1mk)
- State two classes of the classes of the phylum Arthropoda in which the body is divided into cephalothorax and abdomen. (2mks)
- Briefly explain two adaptive features present in animal respiratory surfaces that are absent in plant respiratory surfaces. (2mks)
- State two external characteristics that distinguish mammals from other vertebrata (2mks)
- State two functions of the choroids in the human eye. (2mks)
- Explain the effect of temperature above 40°C to the germinating seed. (4mks)
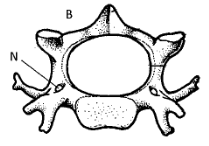
- Examine the diagrams below and answer the questions that follow.
- Give the identity of bone shown in the diagram above (1mks)
- Give two reasons for your answer in a(i) above ( 2mks)
-
- State two effects of dumping untreated sewage into a river. (2 mks)
- Name the causative agents of amoebic dysentery disease in human. (1 mk)
- What is the importance of the following in external fertilization?
- Laying of many eggs (1 mark)
- Mention two adaptations of human sperm to its function ( 2 mks)

MARKING SCHEME
- Give a reason why using a sharp blade is necessary when sectioning during preparation of specimens for observation under the microscope. (1mk)
- Avoid distortion of the specimen;
- The following reaction may occur in a forward and backward direction
- Name the organelle where the above reaction occurs.
- Forward direction (1mk)
- Chloroplast;
- Backward direction (1mk)
- Mitochondrion;
- Forward direction (1mk)
- Give one difference and one similarity for the two organelles named in (a) above (2mks)
- Similarity
- Both have a double membrane;
- Both have fluid filled cavity;
- Differences
Chloroplast Mitochondrion Has Grana
Has fluid Stromahas Cristae;
Has fluid Matrix;
- Similarity
- Name the organelle where the above reaction occurs.
- The chart below represents how respiratory gasses are transported in the human blood.
- Identify gas Y. (1mk)
- Carbon (II) oxide;
- Name the advantages that oxyhaemoglobin has over carboxyhaemoglobin. (2mks)
Oxyhaemoglobin Carboxyhaemoglobin Unstable hence dissociates releasing oxygen to the tissues Stable hence does not easily dissociate;
- Identify gas Y. (1mk)
- The paddles of whales and the fins of fish adapt these organisms to aquatic habitats.
- Name the evolutionary process that may have given rise to these structures. (1mk)
- Convergent evolution;
- What is the name given to such structures? (1mk)
- Analogous structures;
- Give two examples of vestigial organs in man. (2mks)
- Coccyx; appendix; reduced ear muscles/nictating membrane/reduced body hair;
- Name the evolutionary process that may have given rise to these structures. (1mk)
- State one physiological and one structural difference between a cell wall and cell membrane. (2mks)
Cell wall Cell membrane Physiological Fully permeable Semipermeable; Structural Made of cellulose Made of lipoprotein; - Name the organelles that carry out the following functions (2mks)
- Formation of spindle fibres
- Centrioles
- Osmoregulation
- Contractile vacuole
- Formation of spindle fibres
- The diagram below shows part of alimentary canal of a mammal
- Name the parts labeled A and C (2mks)
- A - oesophagus /gullet (reject food pipe)
- C - duodenum
- State the function of the part labeled B. (1mk)
- Temporally storage of feaces / undigested /indigestible materials /Absorption of water;
- Name the parts labeled A and C (2mks)
- Name the part of the chloroplast where the following reactions occur.
- Carbon (IV) oxide fixation. (1mk)
- Stroma;
- Photolysis. (1mk)
- Grana;
- Carbon (IV) oxide fixation. (1mk)
- Polydactyl is a genetic disorder in which people inherit an extra digit. Polydactyl is caused by a dominant allele (B). The table below describes the different genotypes for polydactyl.
- Complete the table below by giving the correct genotype, alleles of each genotype and the expected number of fingers per hand. (4mks)
Genotype Alleles Expected number of digits per hand Homozygous dominant BB Six Homozygous recessive bb Five Heterozygous Bb Six - The table below shows results of marriages between various parents. Complete the table by writing the probability of each marriage producing a child with polydactyl. One has been done for you. (2mks)
Parental genotypes. Probability of child with polydactyl Bb X BB 1 Bb X bb 0.5/ 50%/ ½; Bb X Bb 0.75/ 75%/ ¾;
- Complete the table below by giving the correct genotype, alleles of each genotype and the expected number of fingers per hand. (4mks)
- What are the end-products of respiration in animals when there is sufficient oxygen supply? (3mks)
- Energy/heat;
- Carbon (iv) oxide;
- Water;
- state two characteristics of visking tubing used in osmosis process? (2mks)
- Its semi-permeable;
- It’s a thin membrane;
- Its synthetic;
- Explain the physiological process responsible for keeping the seedlings upright (3mks)
- Its due to osmosis; water is drawn into the cells; becoming turgid providing mechanical support;
- List down substances that depend on diffusion, to be exchanged across the placenta of a female Human being. (3mks)
- O2 gas (from the maternal blood to foetal blood)
- CO2 gas (from the foetal blood to maternal blood)’
- Some digested foods;
-
- What is meant by the term seed dormancy? (1mk)
- A period (of rest) in which a seed performs its physiological processes slowly (and utilize little food);
- State any two external causes of seed dormancy (2mks)
- Low/freezing temperatures;
- Lack of appropriate light wavelength
- What is meant by the term seed dormancy? (1mk)
- Explain what is meant by the following terms?
- Plasmolysed cell (2mks)
- A plant cell that has lost water by osmosis; and has become flabby/ shrunk;
- A crenated cell (2mks)
- an animal cell that has lost water by osmosis; anad shrunk;
- Plasmolysed cell (2mks)
- List down any two domestic applications of anaerobic respiration (2mks)
- Fermentation of dairy products yoghurt, sour milk etc
- Fermentation of porridge;
- Production of biogas;
- Preparation of sillage;
- Baking of cakes/bread;
- State two processes is heat energy produced by respiration lost from human body? (2mks)
- Conduction
- Convection/sweating/perspiration;
- Radiation;
- urination
- Defaecation;
- Account for the absence of glucose and proteins in the glomerular filtrate.
- Glucose (1mk)
- All glucose reabsorbed at proximal convoluted tubule;
- Proteins (1mk)
- Proteins not filtered into glomerular filtrate as molecules too large to pass through capillary pores;
- Glucose (1mk)
- Plants relatively have less waste to excrete than animals. Give two reasons to explain this observation. (2marks)
- Plants reuse some of their waste products; Plants produce their waste products slowly compared to animals that produce slowly;
- Homeostasis is defined as the maintenance of a stable internal environment in the body. What is meant by expression ‘internal environment’? (1 mark)
- Tissue fluid/ Intercellular fluid/ Interstitial fluid;] Acc. Surrounding of the body cells
- Name one factor that is maintained at a relatively constant level in the body by the following organs. (2mks)
- Liver
- Blood glucose (Reject: sugar) level;
- Kidneys
- Osmotic pressure/ Water content/ Osmolarity of body fluids (Accept: blood and tissue fluid) Accept: pH of body fluids (Accept: blood and tissue fluid);
Reject: Osmoregulation
- Osmotic pressure/ Water content/ Osmolarity of body fluids (Accept: blood and tissue fluid) Accept: pH of body fluids (Accept: blood and tissue fluid);
- Liver
- Explain two ways in which the trachea is adapted to perform its functions. (2marks)
- Made up of rings of cartilage to ensure it does not collapse (or to keep it open always) during breathing. Also they enable the tubes to be stretched e.g. during coughing;
- Hollow tube to allow passage of air into the lungs.
- The incomplete rings (c-shaped) have gaps on the side facing the oesophagus which allow smooth swallowing;
- The inner lining of the trachea has mucus to trap and filter micro-organisms and dust particles preventing them from entering the lungs;
- The trachea is lined with cilia which beat in waves and move mucus and other foreign particles upwards into the pharynx;
- The diagram below represent the reflex arc in human
- Name the parts labelled P and S (2mks)
- P-Dorsal root ganglion
- S-grey matter
- State the function of the part labelled Q (1mk)
- Part through which motor neuron leaves the spinal cord
- Name the fluid contained in part labelled R. (1mk)
- Cerebrospinal fluid
- Name the parts labelled P and S (2mks)
- state two classes of the classes of the phylum Arthropoda in which the body is divided into cephalothorax and abdomen. (2mks)
- Arachnida
- Crustacea
- Briefly explain two adaptive features present in animal respiratory surfaces that are absent in plant respiratory surfaces. (2mks)
- Highly vascularized for transport of respiratory gases;
- thin epithelial lining to reduce diffusion distance;
- State two external characteristics that distinguish mammals from other vertebrates (2mks)
- Body covered with fur/hairs;
- Has external ear/pinna;
- State two functions of the choroids in the human eye. (2 marks)
- Has numerous blood vessels to supply nourishment of the eye cells;
- Has dark pigment to absorb stray light;
- Explain the effect of temperature above 40°C to the germinating seed. (4mks)
- The temperature would denature the respiratory enzymes; the stored food would
- Not be hydrolysed/broken down; leading no germination;
- Higher temperature would kill the embryo;
- Examine the diagrams below and answer the questions that follow.
- Give the identity of bone shown in the diagram above (2marks)
- Cervical vertebra;
- Give two reasons for your answer in a(i) above ( 2marks)
- Presence of branched transverse processes;
- Presence of vertebrarterial canals;
- Give the identity of bone shown in the diagram above (2marks)
-
- State two effects of dumping untreated sewage into a river. (2 marks)
- leads to eutrophication, kills organisms in water;
- Changes the water PH, reduces amount of oxygen in water;
- Causes water borne diseases eg cholera;
- Reduces the quality of water for consuming;
- Name the causative agents of amoebic dysentery disease in human. (1 mk)
- Entamoeba histolytica
- State two effects of dumping untreated sewage into a river. (2 marks)
- What is the importance of the following in external fertilization?
- Laying of many eggs (1 mark)
- to increase chances of survival since the fertilized eggs could be attacked by predators or micro-organisms;
- Mention two adaptations of human sperm to its function ( 2 marks)
- have large nucleus which contains haploid genetic material;
- Has an acrosome which contains lytic enzymes which dissolves the membrane of an ovum for
- Penetration;
- Has a long tail which propel the sperm towards the ovum by its side-to-side movement;
- Has numerous mitochondria to provide the energy necessary for propulsion of the sperm towards the ovum;
- Laying of many eggs (1 mark)
Join our whatsapp group for latest updates
Tap Here to Download for 50/-
Get on WhatsApp for 50/-
Download Biology Paper 1 Questions and Answers - Form 4 Term 3 Opener Exams 2023.
Tap Here to Download for 50/-
Get on WhatsApp for 50/-
Why download?
- ✔ To read offline at any time.
- ✔ To Print at your convenience
- ✔ Share Easily with Friends / Students