Stella
Creative Arts, Social Studies & Religious Education Questions and Answers - Grade 5 Mid Term 2 Exam 2023 Set 3
SECTION 1:ART AND CRAFT.
- Which one of the following is not an element of art?
- Line
- Shape
- Value
- Form
- The following are principles that should guide an artist when creating a still life compositing except __________________________.
- balance
- proportion
- overlapping
- texture
- The following diagram shows a ____________________________.
- collage
- painting
- still life drawing
- crayon etched picture
- What is cross hatching?
- Using parallel intersecting lines to shade a drawn object
- Using water colours to decorate a drawing
- Smearing a drawing made using dry media
- Using a sharp object to draw on a crayon waxed surface
- What is a tertiary colour?
- A colour created by mixing two primary colours
- A colour created by mixing two secondary colours
- A colour created by mixing a primary and secondary colour
- A colour created by mixing black or white to any colour
- Which of the following colour combinations wrong?
- Yellow + orange = yellow-orange
- Red + violet = red-orange
- Yellow+green green-yellow
- Blue + green = blue-green
- A lighter tone of a colour can be created by adding _______________________________.
- water to it
- black colour to it
- white colour to it
- both black and white colours to it
- What is collage?
- pasting textured materials on a surface to create a picture
- cutting and pasting related pictures to make an artwor
- making a picture by drawing with a pencil before painting
- drawing on a crayon waxed surface covered in black ink using a sharp object
- Textured materials from the environment that can be used to make a collage include all of the following except ___________________.
- leaves
- ree bark
- inedible seeds
- old newspapers
- Pictures A and B below show ________________________ and _______________________methods of weaving respectively. B
- coil and plain
- twine and plain
- plain and twine
- twine and coil
- Which one of the following not a method used to prepare weaving materials?
- Splitting
- Soaking
- Stripping
- Smoking
- Pots made using the pinch technique can be decorated in the following ways except by _________________________.
- stamping
- scratching
- incising
- beading
- In pottery, the mud-like clay used as glue for sticking slabs together is called ____________________________.
- grog
- mud
- slip
- adhesiv
- Grade 5 leaners in Al Hadasa School collected the following materials for an Art and Craft lesson:
- Carving tool
- Soft wood
- Sand paper
- Mallet
Which activity were they preparing for?- Weaving
- Carving
- Pottery
- Painting
- Which of the following are not techniques used to decorate a ladle?
- Smoking and texturing
- Burning and polishing
- Incising and embossing
- Beading and piercing
SECTION 2:MUSIC
For questions 16-19, choose the correct answer out of the four options given below to complete the table.
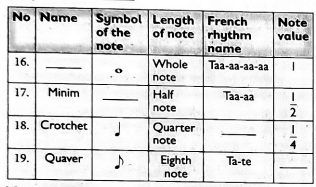
-
- quaver
- semibreve
- Crotchet
- Dotted minim
-
-
- taa
- ta-te
- taa-aa
- taa-aa-aa
-
- 1/8
- 2
- 1½
- 2/8
- Melody of a song is referred to
- pitch and rhythm
- dynamics and tempo
- pitch and dynamics
- tempo and pitch
- Complete the ladder below
- d, r
- r, d
- f, s
- f, r
- Which of the following is not a wind instrument?
- Guitar
- Horn
- Descant recorder
- Flute
- What type of instrument is a descant recorder?
- Percussion
- String
- Wind
- Idiophone
- What is a duet?
- A performance for four people
- A performance for two people
- A performance for five people
- A performance for one person
- When singing, doh is lower in ___________________ than re.
- Melody
- Pitch
- Volume
- Rhythm
SECTION 3: SOCIAL STUDIES.
Study the map below and answer the questions that follow.
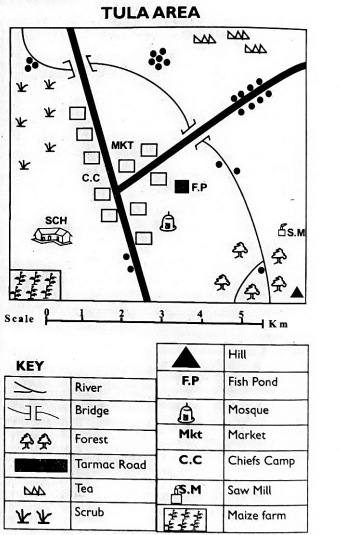
- What is the title of this map?
- County
- Key
- Tula Area
- Bondeni Area
- The following economic activities are carried out in area shown. Which one is not true?
- Farming
- Worshipping
- Trading
- Lumbering
- Who is the head of the area shown above?
- Chief
- Governor
- MCA
- District Commissioner
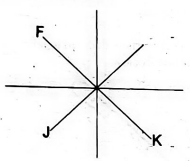
- Kerubo wanted to visit Tula Area to start a business activity in the market. What could give her direction to her place of destination?
- Compass
- Scale
- Title
- Frame
- Which lake is shared by two countries that border Kenya to the South and to the West?
- Lake Turkana
- Lake Victoria
- Lake Baringo
- Lake Nakuru
- Mt Elgon is found at the border of Kenya and ___________________________.
- Tanzania
- Somalia
- Ethiopia
- Uganda
- Which of the following weather elements is not correctly described?
A. Rainfall Rain supports the growth of vegetation. B. Wind Warm and moist winds bring rain. C. Cloud cover Heavy cloud cover brings heavy rainfall. D. Temperature Refers to ice on the mountain. - Muuo wrote the following characteristics to describe a climatic region in Kenya.
- The windward side receives relief rainfall while the leeward side is drier.
- Temperatures range from 0°C - 15°C.
- Experiences cool and wet conditions.
The climatic region described above is ____________________________.- Mountain climate
- Tropical climate
- Modified Equatorial climate
- Desert climate
- Who among the following learners did not give the correct importance of historic built environments?
A. Manasseh They remind and teach us about our culture. B. Sharon They bring rain to our land. C. Baraka They are sources of information for learning. D. Gakii They are sources of employment for people who work there. - The following are ways in which language groups depend on each other. Which of them is not correct?
- Treatment
- Trading
- Iron making
- Tribalism
- Learning from specialists was a method of instruction used in African traditional education. Boys and girls were taught the following skills except.
- Pottery
- Basketry
- Singing
- Beading
- Mukabane is the head teacher of Bidii Primary School. Which of them is not one of his duties to perform in school?
- Secretary of the staff meetings.
- Overall in charge of the school.
- Maintains school records.
- In charge of funds and security.
- Danilo listed the following importance of resources in our environment. Which of them is not correct?
A. LAND We grow crops and keep animals on it. B. MINERALS Valuable substances like soda ash beautify our environment. C. WATER Source of water for crops and animals and fish such as tilapia. D. FOREST It is a home for wild animals. - Identify the crop that is not grown in small quantity for use at home among the following.
- Arrowroots
- Yams
- Cassava
- Tea
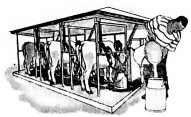
- Joseph rears a few cattle to provide milk as shown below. Which of the following is not a factor that favours his dairy farming?
- Plenty of water for animals.
- Cool temperatures which discourage ticks.
- High and reliable rainfall for pasture growth.
- A small market for dairy products.
SECTION 4:
CHRISTIAN RELIGIOUS EDUCATION.
- Which of the following cannot be learnt from the Bible?
- Wisdom
- Courage
- Pride
- Compassion
- Which of the following activities does not show good stewardship?
- Planting trees in the community
- Polluting the rivers in your area
- Caring for our domestic animals
- Protecting the wild animals in the forest
- Which punishment was given to Adam and Eve after they ate the forbidden fruit?
- They were chased out of the Garden of Eden
- They were beaten
- The snake bit them
- They became naked
- Select the statement that best describes a marriage.
- Two adult people that live together
- A union between an adult male and female that is recognised by law
- A union between two young people
- A sexual relationship between two people
- How does a teacher use their talent and ability to fulfill God's purpose?
- By teaching and helping learners nurture their talents
- By making friends in school
- By reporting to school early
- By greeting the learners
- Which of the following is not a cause of child labour?
- Wealth
- Poverty
- Death of parent or guardian
- Irresponsible parents
- Why did Eve agree to eat the forbidden fruit?
- She was not hungry
- She wanted to be foolish
- She did not know it was forbidden
- She wanted to be wise like God
- Which of these values can we use to nurture our talents and abilities?
- Honesty
- Fear
- Laziness
- Irresponsibility
- We should always read the Bible for _______________________
- Guidance
- Leisure
- Entertainment
- Exams
- Select an effect of child labour from the following.
- Good health
- School drop outs
- Excellent performance in school
- Unity within the family
SECTION 4:
ISLAMIC RELIGIOUS EDUCATION.
- Complete. Hata zurtumul__________________________.
- kalla saufa
- makaabir
- Thuma kalla sanfa ta taalamun
- Al-haqumutakathun
- Which one of the following names means the creator?
- Al-Ghaffar
- Al-Baar
- Al-Khaaliq
- Al-Qahhar
- The Quran teaches us to show ______________________ to our neighbours.
- magic
- kindness
- cruelty
- hatred
- The mid-morning prayer is called _______________________
- Asr
- Tahajjud
- Dhuha
- Taraweh
- The main two tribes in Yathrib were _____________________
- Quraish and Aus
- Aus and Khazraj
- Khazraj and Amhara
- Jews and Amhara
- Which one of the following is not an obligation to our neighbours?
- Assist poor neighbours
- Bury and accompany their coffins
- Annoy them with what we cook
- Give them loans
- _____________________ was sent to Madina to teach Islam.
- Abu Hanifa
- Ali
- Saad bin Muadh
- Musab bin Umeir
- Who among the following refused to bow down to Adam as commanded by Allah?
- Hawa
- Jibril
- Iblis
- Muhammad (SAW)
- ____________________________ is a shield in Islam.
- Swalah
- Saum
- Zakat
- Shahadah
- Which one of the following does not spoil sawm?
- Backbiting
- Lying
- Eating
- Sleeping
MARKING SCHEME
ART
- B
- D
- C
- A
- C
- C
- C
- A
- D
- B
- D
- D
- C
- B
- D
MUSIC
- B
- A
- A
- A
- A
- B
- A
- C
- B
- B
SOCIAL
- C
- B
- A
- A
- B
- D
- D
- A
- B
- D
- C
- A
- B
- D
- D
C.R.E
- C
- B
- A
- B
- A
- A
- D
- A
- A
- B
I.R.E
- B
- C
- B
- C
- B
- C
- D
- C
- B
- D
Integrated Science Questions and Answers - Grade 5 Mid Term 2 Exam 2023 Set 3
SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY
- A computer program that can be used to create, edit, save, retrieve and print documents is known as __________________
- spreadsheets
- word processor
- data base systems
- graphics programs
- Fanaka inflated a balloon as shown in the diagram below.
From what Fanaka did, it can be concluded that;- air is a gas.
- gases have mass.
- gases occupy space.
- gases have indefinite volume.
- Grade 4 learners from Kifaru Primary observed one of the school workers using a wheelbarrow as shown below.
Which other lever has the position of the Load, Fulcrum and Effort at the same point as the wheelbarrow?- nutcracker
- fishing rod
- a spade
- a seesaw
- Mwanaisha discovered that force can change the size of ar object. Which of the following statements can be used to demonstrate what Mwanaisha discovered?
- A goalkeeper stopping a ball that has been shot towards the goal.
- A toy car that stops moving after hitting the wall.
- A leaner that squeezes a circular clay ball using his hands.
- A girl who pulls a rubber band to its full length.
- Which of the following statements is true?
- Digestion of proteins takes place in the mouth.
- Absorption of digested food takes place in the stomach.
- Vitamins are directly absorbed into the body without being digested.
- Water is absorbed back into the body in the ileum.
- The following are uses of the Save As command. Which one is not?
- Saving a document using a new file name.
- Changing the location where the document is to be saved.
- Saving the changes that have been made on an existing document.
- Saving a document for the first time.
- The following are ways of managing solid waste. Which of the ways shows recycling?
- Making compost manure from organic waste.
- Making a pencil holder from metallic cans.
- Selling old newspapers to shopkeepers for wrapping.
- Using plastic containers that had cooking oil to carry water
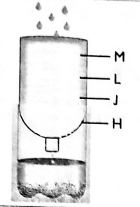
- Grade 4 learners from Kamagambo Junior School made a water filter as shown below.
At what point do you think the learners put small stones?- L
- H
- J
- M
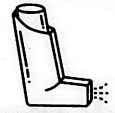
- Which of the following diseases can be managed by the use the item shown in the diagram?
- Pneumonia
- Asthma
- Influenza
- Tuberculosis
- The amount or quantity of matter in an object is known as;
- mass
- volume
- weight
- shape
- Which of the following materials is translucent?
- car windscreen
- frosted glass
- mirror
- a brick wall
- Zawadi wanted to save his work on the computer. Which short cut would you advise him to use?
- Ctrl + C
- Ctrl + V
- Ctrl + N
- Ctrl + S
- I am a part of the breathing system. I allow lungs to contract and expand during the breathing process. Who am I?
- bronchi
- diaphragm
- windpipe
- air sacs
- Mulwa had the following signs and symptoms.
- Stomach pains
- Appetite loss
- Skin rashes
- Red area on the skin that is itchy
- General body weakness
- Weight loss
- Paleness of the skin
- Wheezing when breathing
It is likely that Mulwa had;- hookworms.
- tapeworms.
- roundworms.
- pinworms
- Scabies are caused by _______________________________.
- jiggers
- lice
- mites
- bedbugs
AGRICULTURE
- It is necessary to recover eroded soil because;
- it prevents soil erosion.
- it has nutrients.
- it is not fertile.
- it easily carried by water.
- In container gardening, we make holes at the bottom of the bucket because;
- the roots of the crops should get out of the bucket.
- nutrients get in through the holes.
- water gets in through the holes.
- excess water gets out through the holes.
- Mary and Molly constructed some shade above the young fruit plants that had been planted. What is the purpose of what they did?
- to reduce soil erosion
- to reduce the rate of water evaporation in the soil
- to increase soil fertility
- to improve soil texture
- Which of the following ways does not conserve water in the soil?
- irrigation
- mulching
- shading
- planting cover crops
- Compost manure is ready for use after how long?
- 3 months
- 6 months
- 1 month
- 6 weeks
- What should Nuru use to protect his feet when working on the farm?
- Mzee Odongo noticed that the seedlings on the nursery bed were congested and weak. What would you advisable him to do?
- weeding
- thinning
- shading
- watering
- The following are examples of cereals, except;
- maize
- millet
- sorghum
- beans
- Which of the following equipment or tools can be used to maintain seedlings on the seed bed?
- Teacher Muhindi wanted to buy animals that could be used for digging and give them meat when they are slaughtered. Which of the following animals should Teacher Muhindi buy?
- cows
- oxen
- ram
- buck
- Which of the following is not a climbing
- grapes
- kiwi
- raspberries
- apples
- Grade 5 learners were asked to name planting materials for climbing fruit plants. Who gave the correct planting materials only?
- Abbie: roots, stem cuttings, vine cutting
- Wesly: stem cuttings, vine cutting, roots
- James: vine cutting, buds, roots
- Tes: seeds, stem cuttings, vine cutting
- When controlling small wild animals that harm our crops, it is not advisable to;
- plant chilli plants around the crop field.
- kill the small wild animals that we trap.
- use loud sound to scare the animals.
- use dogs to scare the wild animals.
- Which of the following statements is true?
- The soil with the smallest particles retains the highest amount of water.
- Rice grows well on the soil with medium particles.
- The soil with the largest particles retains the highest amount of water.
- The soil with medium particles does not retain water.
- Soil erosion is likely to take place on the part of the farm that;
- has not have clay soil.
- have nothing growing on it.
- has grass growing on it.
- is very fertile.
HOME SCIENCE
- Which of the following is a way of caring for enamel earthenware?
- Do not wash in warm water.
- Avoid knocking them.
- Do not use them frequently.
- Hang them upside down.
- Kheri would wish to preserve milk which he has to use two days later. Which of the following is the best method of preservation?
- Refrigeration
- Fermentation
- Canning
- Boiling
- Grade 4 learners grouped fuels as shown in the table below.
Electricity can be represented by letter _______________________.Type of fuel Used to cook Warms the house Provides light Fuel X Yes Yes Yes Fuel P Yes Yes No Fuel R Yes No Yes Fuel B Yes No Yes - B
- P
- R
- X
- The following is the importance of making a shopping list except;
- It saves money.
- It helps in buying the most important items.
- It saves time.
- It helps in buying items that are cheaper.
- It is true that glasses should;
- be stacked.
- not be washed one at a time.
- be washed using a soft material.
- be washed in very hot water.
- Suctioning is done by use of ______________________________
- a broom
- a mop
- a vacuum cleaner
- brush
- Which of the following cooking facilities can be used anywhere, it is quick to use, it is clean in use, it is locally and readily available?
- electric cooker
- charcoal jiko
- firewood jiko
- cooking gas
- When taking care of the bedroom, which of the following should be done weekly?
- Spreading the bed.
- Fixing the mosquito net.
- Changing the bed sheets.
- Opening the windows and the door.
- A kitchen should not be close to the _____________________________.
- living room
- food store
- toilet
- back door
- Fragile utensils are those that;
- break easily.
- are expensive.
- are brightly coloured.
- are very important.
PHYSICAL AND HEALTH EDUCATION
- The following are hurdling stages. Which of the stages in the second one?
- Landing
- Take off and flight
- Approach
- Hurdle clearance
- ______________________________ is the act of sending the ball to the batsman using a continuous smooth under arm action.
- Batting
- Bowling
- Attacking
- Defending
- The following happens to someone during exercise. Which one does not?
- The heart beats faster.
- The person feels thirsty.
- The body temperature rises.
- The blood flow reduces.
- Dhahabu's group of muscle can perform a repeated action without getting tired. This means that Dhahabu has;
- cardiovascular strength.
- muscular endurance.
- muscular hard work.
- cardiac stamina.
- Kipkoech is an athlete. Which of the following does he need in very small quantities?
- Carbohydrates
- Vitamins
- Proteins
- Fats and oils
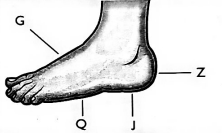
- Grade 4 learners were practicing how to make an instep pass. Which of the parts shown should they use?
- G
- Z
- J
- Q
- In _________________________ technique, the athlete crosses the finish line at top speed when the trunk is leaning forward with shoulders and chest.
- elongated start
- medium start
- standing finish
- run through finish
- In long jump, the sprinting or approach area is known as _____________________________________
- take off board
- landing area
- runway
- sprint zone
- When performing standing discuss, the score cards are used for;
- marking several throws that are made.
- recording the scores that are made.
- measuring the distance of each throw.
- writing the names of the participants.
- In which style of rope skipping does one jump the rope alternating the right and left foot in front and back in a repeated rhythm?
- straddle
- skier
- straddle cross
- flip flop
MARKING SCHEME
- B
- C
- A
- D
- C
- C
- A
- D
- B
- A
- B
- D
- B
- A
- C
- B
- D
- B
- A
- A
- A
- B
- D
- C
- B
- D
- D
- B
- A
- B
- B
- A
- D
- D
- C
- C
- D
- C
- C
- A
- B
- B
- D
- B
- B
- A
- D
- C
- B
- C
Shughuli za Kiswahili Questions and Answers - Grade 5 Mid Term 2 Exam 2023 Set 3
Soma kifungu kifuatacho kisha ujibu maswali yanayofuata.
Wanyama wa porini ni rasilimali tuliyopewa na Mwenyezi Mungu. Wanyama hao wana umuhimu mkubwa katika taifa lolote. Umewahi kuwaona nyumbu wakivuka kutoka Kenya na kuingia Tanzania au kutoka Tanzania kuingia Kenya? Hali hiyo hutoa utulivu mkubwa katika moyo. Kuwaona simba wakiwawinda na kuwala wanyama wengine husababisha furaha kubwa. Hili lina maana kuwa kule kuwatazama wanyama wa porini huleta utulivu. Faida nyingine ya wanyamapori ni kule kuwavutia watalii. Watalii wanaotoka nchini na katika mataifa ya nje humiminika nchini ili kujionea wanyama hao.
Manufaa makubwa ambayo sisi hupata kutokana na watalii ni pesa za kigeni. Watalii wanapotuletea pesa za kigeni, serikali yetu huweza kupiga hatua kubwa kimaendeleo. Ni kutokana na pesa hizo ndipo tunapoweza kujenga barabara, shule, hospitali na kadhalika. Wakenya wengi wameajiriwa kufanya kazi zinazohusiana na wanyamapori. Hao ni kama vile madereva, walinzi, wanaowatembeza watalii na wanaofanya kazi katika hoteli za watalii hao.Wafanyakazi hao hufanya kazi kwa bidii ili kufaulu katika maisha yao.Wafanyakazi hao hupata pesa za kusaidia familia zao ili waishi maisha mazuri. Tatizo hutokea wakati tamaa inapofanya tuwinde na kuwaua wanyama hao. Majangili huwawinda wanyamapori wakiwa na lengo la kupata vipusa, pembe za ndovu na ngozi za wanyama hao. Uovu huo unafaa kukomeshwa haraka mno. Ni vyema kuelewa kuwa kuwaangamiza wanyamapori ni kuiletea nchi yetu hasara. Kila mkenya ajitolee kuwatunza wanyamapori.
- Pesa za kigeni ambazo huletwa na watalii hutumiwa na;
- watalii
- shule
- wakenya
- serikali
- Ni kweli kwamba tusipokuwa na wanyamapori;
- watalii wataongezeka nchini.
- majangili watatajirika.
- kiwango cha maendeleo kitarudi chini.
- watu wengi wataajiriwa.
- Ufuatao ni umuhimu wa wanyamapori isipokuwa;
- hutuliza moyo
- huwaletea majangili faida
- huvutia watalii
- huwapa watu ajira
- Kifungu kinaeleza kuwa wanaowinda wanyamapori huongozwa na nini?
- umaskini
- njaa
- tamaa
- kutojua
- Wafanyakazi hao hufanya kazi kwa bidii ili kufaulu katika maisha yao. Maneno haya yanaweza kuelezwa kwa methali gani?
- Asiyefunzwa na mamaye hufunzwa na ulimwengu.
- Achanikaye kwenye mpini hafi njaa.
- Mtoto wa nyoka ni nyoka.
- Mtaka yote hukosa yote.
- Tambua maana ya 'majangili' kulingana na kifungu.
- Wezi wa wanyamapori
- Wawindaji haramu
- Askari wa wanyamapori
- Watalii katika mbuga
- Chagua kichwa kinachofaa kwa makala haya.
- umuhimu wa watalii
- faida na hasara za wanyamapori
- umuhimu wa wanyamapori
- kuwinda, wanyamapori
Soma kifungu kifuatacho kisha ujibu maswali yanayofuata.
Kutoka kwa: This email address is being protected from spambots. You need JavaScript enabled to view it.
Kwenda kwa: This email address is being protected from spambots. You need JavaScript enabled to view it.
MADA: MWALIKO WA KUPATA MAFUNZO
Kwa Bwana/Bi,
Jina langu ni Mapato Mapesa. Mimi ndimi katibu wa chama cha Akiba Haiozi. Chama cha Akiba Haiozi ni chama cha wafanyabiashara wa biashara ndogondogo katika mji wa Mumias. Sisi hujihusisha na biashara za rejareja, uchuuzi na shughuli za juakali. Tumekuwa tukiweka akiba kidogo katika benki yenu ya Wekeza. Kwa sasa, tuna akiba ya kima cha shilingi milioni moja. Tuna hamu ya kuwekeza katika miradi mbalimbali ya maendeleo ili kujipa faida zaidi. Hata hivyo, hatuna ujuzi wa kutosha kuhusu uwekezaji. Kwa kuwa kuuliza si ujinga, tumeamua kutoa ombi ili mtutumie afisa au maafisa ambao watatueleza mengi kuhusu uwekezaji. Vilevile, tugependa kujua iwapo tunaweza tukapewa mkopo. Tatizo jingine ni kwamba hatujui aina za mikopo mnayotoa na riba inayohusiana na kila aina ya mkopo.
Tuna matumaini makubwa kuwa mtalikubali ombi letu na kukifaa chama hiki. Tunatoa ahadi ya kuendelea kushirikiana na benki yenu pamoja na maafisa wenu. Isitoshe, tutazidi kuweka akiba katika banki iyo hiyo nyakati zote. Iwapo ombi letu litakubalika, tafadhali tupeni ujumbe na wakati mnaopatikana ili tujiendae. Tunawapa shukrani za awali kutoka katika vilindi vya mioyo yetu. Kwaherini.
Wenu mwaminifu,
Mapato Mapesa (katibu)
- Kifungu hiki ni mfano wa;
- barua ya kirafiki.
- barua rasmi.
- baruapepe.
- barua ya kiofisi.
- Ni kweli kuwa anayeandikiwa barua hii ni wa jinsia gani?
- ya kike
- ya kiume
- haijulinani
- katibu
- kulingana na kifungu, kwa nini mwandishi na wenzake wana hamu ya kuwekeza katika miradi mbalimbali?
- ili wajue mengi kuhusu uwekezaji
- ili wapate faida
- ili watembelewe na maafisa wa benki
- ili waweke akiba
- Wanachama wa chama cha Akiba Haiozi wanafahamu kuwa;
- Akufaaye kwa dhiki ndiye rafiki.
- Majuto ni mjukuu huja baadaye.
- Ngoja ngoja huumiza matumbo.
- Haba na haba hujaza kibaba.
Soma shairi lifuatalo kisha ujibu maswali yanayofuata.
Familia kuteseka, sababu umasikini,
Chakula wanaposaka, ni ukweli hawaoni,
Mavazi yameraruka, kichwa hadi mguuni,
Bidii yahitajika, kuushinda uchochole.
Kuanza kule shuleni, kujikaza ni lazima,
Shambani pia kazini, tukilala tutazama,
Bidii iwe moyoni, kujitolea daima,
Bidii yahitajika, kuushinda uchochole.
- Chagua kina cha kati cha ubeti wa kwanza.
- na
- ma
- ni
- ka
- Mwandishi wa shairi hili angetumia neno gani jingine badala ya neno 'familia'?
- ayali
- jamii
- ndugu
- sahibu
- Umaskini husababisha nini kutokana na ubeti wa kwanza?
- ukosefu wa mavazi na chakula
- ukosefu wa elimu na amani
- ukosefu wa chakula na elimu
- ukosefu wa mavazi na amani
- Kibwagizo cha shairi hili kina mizani mingapi?
- 10
- 2
- 14
- 16
Chagua jibu lifaalo ili kujazia nafasi zilizoachwa.
Mtu __16__ anayetaka kufaulu __17__ lazima awe mwenye bidii. Bidii ni muhimu sana kwetu. Tunafaa kuwa wenye bidii masomoni, kazini __18__ michezoni. Mtu asiyependa bidii hawezi akafaulu katika __19__ lolote. Je __20__ wewe ni mwenye bidii au unapenda uzembe?
| A | B | C | D | |
| 16. | yoyote | yeyote | wowote | ambaye |
| 17. | kwenye maisha | kwa maisha | katika maisha | katika maishani |
| 18. | lakini | au | wala | na |
| 19. | kitu | shughuli | mambo | jambo |
| 20. | , | ? | ! | : |
- Tambua aina za nomino zilizopigiwa mistari. Mtoto alijawa na furaha alipokunywa maziwa.
- pekee, wingi, dhahania
- kawaida, wingi, shahania
- pekee, dhahania, wingi
- kawaida, dhahania, wingi
- Chagua neno lenye silabi nne kati ya maneno yafuatayo.
- beba
- wekea
- tembelea
- hajaja
- Tambua sentensi iliyotumia koma.
- Amemaliza chakula.
- Wewe ni nani?
- Amenunua kitabu, kalamu na kichongeo.
- Ala! Wacha kuharibu mazingira.
- Ikiwa jana ilikuwa Jumatatu, keshokutwa itakuwa lini?
- Alhamisi
- Jumatano
- Jumanne
- Ijumaa
- Chagua wingi wa;
Ubao wenyewe una ufa mkubwa.- Mbao zenyewe zina maufa makubwa.
- Mabao yenyewe yana nyufa kubwa.
- Mabao yenyewe yana maufa makubwa.
- Mbao zenyewe zina nyufa kubwa.
- Tegua kitendawili.
Dhahabu yangu ya thamani haisimami.- shamba
- mkufu
- siafu
- maji
- Nomino gani isiyopatikana katika ngeli ya I-ZI?
- kabati
- kalamu
- karatasi
- kamba
- Tambua aina za maneno yaliyopigiwa mistari. Lo! Kumbe wote wamelala ndani ya chandarua.
- kiwakilishi, kihusishi
- kihisishi, kivumishi
- kihusishi, kihisishi
- kihisishi, kihusishi
- Bwana harusi alivaa ______________________________ shingoni.
- koja la maua
- shada la maua
- mkungu wa maua
- kishazi cha maua
- Chagua kitenzi kilichonyambuliwa katika kauli ya kutendeka.
- pika
- weka
- fulika
- cheka
INSHA
Andika insha ya masimulizi kuhusu;
SAFARI YA KUFURAHISHA
MARKING SCHEME
- D
- C
- B
- C
- B
- B
- C
- C
- C
- B
- D
- D
- A
- A
- D
- B
- C
- D
- D
- A
- D
- C
- C
- A
- D
- B
- A
- D
- A
- C
English Questions and Answers - Grade 5 Mid Term 2 Exam 2023 Set 3
Read the conversation below and then answer questions 1-5.
Teacher: Good morning, Marion?
Marion : __1__
Teacher: You did the assignment, didn't you?
Marion : __2__
Teacher : Why didn't you complete your work?
Marion : I was unable to because I did not understand what immunisation is.
Teacher : Immunisation is a process through which a person becomes protected against a disease through vaccination.
Marion : Thank you teacher. I shall now be able to complete the work. Teacher : ___5___
- How should Marion respond to the teacher's greetings?
- Good morning.
- Good afternoon.
- Lovely day
- There is nothing good about this morning.
- Fill in the blank space in question 2 in the conversation above
- Yes, I did it.
- No, I did not.
- Yes, I did.
- No, I didn't do it.
- What is immunisation according to the dialogue?
- Medicine that kills diseases instantly.
- What causes germs in the body.
- Whatever fight parasites.
- Protection against diseases through vaccination.
- How best can we describe Marion in the conversation?
- She is very rude.
- She is very lazy and disobedient.
- She is intelligent and respectful.
- She is humble but lazy.
- What is the best response the teacher can give to Marion in the blank space numbered 5?
- Thank you for your time.
- Yes, you will do it now.
- Most welcome.
- I appreciate it.
Read the passage below and then questions 6 - 9.
It is important to take care of one's teeth right from childhood. Taking good care of one's teeth will ensure that the teeth do not develop problems later in life. When one eats too many sweets and does not brush every day, it is likely that they will have problems in life such as toothaches, cavities, swelling and pain. One should visit the dentist at least once a year to ensure that their mouth is healthy. A dentist is a person who treats diseases and other conditions affecting the mouth, teeth and the gums.
There was once a boy in our class whose mouth smelt all through. Whenever he opened his mouth to answer a question, everyone held their nose. The stench that came out could not be withstood. The teacher took action at once and helped him. Besides advising him to brush after every meal, he also took him to the dentist himself for treatment. Many learners were beginning to withdraw from the class.
After a certain period of time of taking care of his teeth, the problem was taken care of and normalcy returned. All the learners freely interacted with the boy and made friends with him. All thanks to our class teacher
- According to the passage, a dentist is _____________________________.
- a person who takes care of people in a hospital.
- a person who treats diseases and other conditions affecting the mouth, teeth and gums.
- a person who takes care of our eyes.
- a person who ensures that we brush our teeth.
- Why is it important to take care of our teeth?
- To ensure there is no problem later on in life.
- To smell good.
- So that we are able to eat many sweets.
- In order not to brush our teeth every day.
- How many times should we visit the dentist?
- Once a year.
- Once a month.
- Once every six months.
- Every week.
- Which one among the following does not happen when we fail to brush our teeth every day?
- We get cavities.
- Swelling and pain.
- We have a lovely smile.
- Our teeth might start to rot.
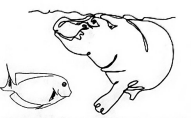
Read the passage below and then answer questions 10 - 12.
A long time ago the fish were able to walk on land together with their friends the hippopotamuses. They were very good friends and did almost everything together. They went hunting for food together and shared whatever they were lucky to get. One day, the sun did not rise early as it usually did, so the fish were not able to see their way through the darkness like their friends the hippopotamuses.
When their friend the hippopotamuses came back that evening with food, they all shared and retired. The same thing happened the following day. Their faithful friend was there for the fish again. This went on until the hippopotamuses got fed up. He said he could not go on feeding the fish as they sat back at home doing nothing.
The fish then decided to go to their leader to ask him why the sun had refused to shine for all those days. They were starving due to lack of food. Their leader told them that the sun was upset that they were walking on the land because they belonged strictly to the water. This news troubled the fish so much. They did not know what to do. One of them, however, advised that they should follow their leader's advice - never to leave the water. Since that day, the fish have never set their feet on land for fear of making the sun angry.
- Which one of the following was never done by both the fish and their friends the hippopotamuses
- They looked for food together.
- They shared food as a family.
- They shared nearly everything.
- They walked on land together.
- Who according to the passage was able to see through the darkness?
- The hippopotamuses.
- The fish.
- Both animals.
- The leader of the fish.
- It is true to say that Hippopotamuses ________________________.
- are only able to walk at night.
- are the only ones able to see in the darkness.
- are usually afraid of the sun.
- are able to live on land and in water.
Read the following passage and then answer questions 13 - 15.
Environmental Day is the day when the world celebrates the God given environment. Environment refers to all the things found in it; living or otherwise. Normally, we converge as members of the environmental club at the County offices and take part in cleaning the environment as well as planting trees. This exercise does not end there. We enlighten the society on the importance of taking care of the environment. This is done through short skits, plays choral verses and even narratives. People come in large numbers especially the lovers of the environment.
This year we were lucky to be joined by the Governor himself. Some of us had only managed to watch him on television but today we got lucky to set our eyes on him. He is a handsome man with a kind heart. He promised us free scholarship to study further about the environment outside the country. We could not have been happier.
You will not believe it when I say he held a broom and swept the market as a role model. Journalists from various media houses captured him and sent the pictures to their newsrooms. It was a great moment for me when I took a photograph with him.
- The environment is made up of ____________________________.
- Living things and otherwise.
- Both living and non- living things.
- Non-living things only.
- Living things only.
- The scholarship would be given to ______________________________.
- all the primary schools in the writer's neighbourhood.
- the writer only.
- those who will excel in the environmental programme.
- the members of the environmental club to study further about the environment.
- The best title for the passage above would be
- The Governor sweeps the market.
- Getting a scholarship.
- The World's Environmental Day.
- The day I met the Governor.
Read the passage below. It contains blank spaces numbered 16-20. For each blank space, choose the best alternative from the given four.
Have__16__ ever thought of what you want to be __17__ you grow up? Are you working towards achieving your dreams? There are __18__ careers one can pursue, however, you __19__ work harder at school and get good qualifications for you to become what you have always __20__.
| A | B | C | D | |
| 16. | you | he | I | we |
| 17. | if | unless | when | until |
| 18. | differently | diffrent | different | difference |
| 19. | may | must | should | shan't |
| 20. | dreamt | wished | admiring | hoped |
For questions 21 -25. choose the best alternative to complete the given sentence.
- This pen is mine but _______________________ one is yours.
- it
- other one
- this
- that
- There was ________________________ soda in the bottle so she drank it all.
- a little
- little
- a lot
- none
- A person who sells flowers is a ________________________.
- florist
- greengrocer
- flower seller
- trader
- Mary is the ________________________ of the twins.
- tall
- tallest
- taller
- more taller
- Mother bought a _________________________.
- table, long, square
- square, long, table
- long, square, table
- table, square, long
For question 26, choose the alternative with the plural of the given sentence.
- The baby is crying.
- The babies are crying.
- These babies are crying.
- The babies were crying.
- The baby's is crying.
- Which word least fits in the group of words given below?
- Spoons
- Socks
- Shorts
- Trousers
For questions 28 and 29, identify the pronouns in the given sentences.
- He is a good boy.
- is
- he
- boy
- good
- "Mary is a prayerful woman," she said.
- Mary
- woman
- she
- is
- Which is the correctly punctuated sentence?
- Cows eat grass, don't they?
- Cows eat grass don't they.
- Cows eat grass, dont they?
- Cows eat grass. Don't they?
COMPOSITION
Write an interesting composition about:
MY HOBBY
MARKING SCHEME
- A
- C
- D
- D
- C
- B
- A
- A
- C
- C
- A
- D
- B
- D
- C
- A
- C
- C
- B
- B
- D
- B
- A
- C
- C
- A
- A
- B
- C
- A
Mathematics Questions and Answers - Grade 5 Mid Term 2 Exam 2023 Set 3
QUESTIONS
- What is the place value of the underlined digits in the following numbers? 4305
- Ones
- Tens
- Thousands
- Hundreds
- Arrange the following fractions from the smallest to the largest.
2/3,1/4, 5/6, 3/8- 1/4, 3/8, 2/3, 5/6
- 5/6,2/3, 3/8,1/4
- 3/8 ,1/4, 2/3, 5/6
- 2/3,3/8, 5/6,1/4
- Work out
496
+ 39
- 535
- 1934
- 19434
- 18344
- What is the total value of digit 5 in 705378?
- 5000
- 50000
- 5
- 500
- Estimate the sum of the following by rounding off to the nearest ten.
493 + 179- 672
- 680
- 670
- 660
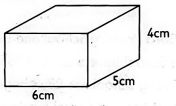
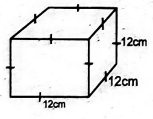
- Calculate the volume of the figure below.
- 20cm3
- 30cm3
- 120cm3
- 15cm3
- James and Matu were asked to circle multiples of 18. Which one of the following was not circled by Matu and James?
- 36
- 9
- 54
- 18
- John had sh 2975. His friend Kaluma had sh 3673. How much money did they have in total?
- 5648
- 4468
- 6648
- 7648
- In a forest, 1/4 of the animals are gazelles, 3/8 are birds and 1/5 are lions. What is the total fraction of gazelles and birds?
- 5/8
- 9/20
- 23/40
- 33/40
- Mwatoo had 784 cows, 385 goats, 998 sheep and 79 donkeys. How many animals did he have altogether?
- 2167
- 2246
- 1169
- 10067
- Msingi Bora Primary School and Bidii Primary School have a total of 7654. Bidii Primary School has 2849 boys and girls. What is the total number of learners in Msingi Bora Primary School?
- 5215
- 4805
- 4815
- 1956
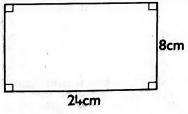
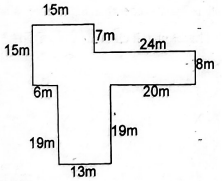
- Work out the area of the figure below
- 192cm
- 32cm
- 32cm2
- 192cm2
- Work out: 9745 − 3816
- 4929
- 5929
- 6131
- 6929
- The government imported three hundred and fifty eight thousand bags of maize to fight hunger. During inspection, the agent found out that one hundred and seventy eight bags of maize were not good for use. Calculate the number of bag of maize that was good.
- 358178
- 536000
- 357822
- 357922
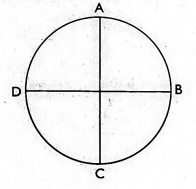
- Look at the circle below
I was at point B. I made a turn to point A. Which turn did I make?- A quarter anticlockwise
- Half anticlockwise
- A quarter clockwise
- Half clockwise
- Work out and write the answer in romans. IX − VI
- II
- III
- IV
- X
- Learners made number digit cards below.
They used the digits to form various 5-digit numbers. Which of the numbers formed was the largest?- 50321
- 53210
- 35201
- 10532
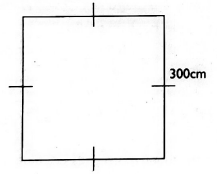
- A tailor made a square table clothe drawn below. Find the areas of the table clothe?
- 600cm2
- 9000cm
- 9000cm3
- 90000cm2
- Work out:
km m
28 400
−10 840
- 27km 560m
- 17km 560m
- 39km 240m
- 18km 560m
- A building block measures 30cm by 15cm by 20cm. Work out its volume. A. 65cm3
- 65cm3
- 900cm3
- 9000m3
- 9000cm3
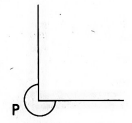
- What is the name of the angle marked by letter p?
- Right angled
- Acute angle
- Obtuse angle
- Reflect angle
- Work out: 15kg 400g + 4kg 700g
- 19kg 1100g
- 20kg 100g
- 19 kg 100g
- 20kg 1100g
- Muchai bought 3kg of meat from a butchery. The bones were 500g. What was the mass of the steak?
- 3kg 500g
- 2kg 500g
- 3kg
- 500kg 3g
- Musa's age is y years. His wife is x years. The son is p years. Find the sum of their ages.
- y + x − p
- y + x + p
- y − x − p
- y × p
- Work out :
min sec
15 25
+ 3 38
- 18 min 63 sec
- 18 min 3 sec
- 19 min 3 sec
- 19 min 63 sec
- Fill in the missing number.
× 14 = 126
- 1764
- 15
- 9
- 6
- What is the L.C.M of 24 and 18?
- 42
- 6
- 72
- 432
- Below is a price list from a shop. Use it to answer question below.
Anne bought 2 pens and a book. How much did she spend?Item
Pen
ruler
Book
RubberPrice
15.00
25.00
30.00
10.00- sh. 45
- sh. 30
- sh. 60
- sh. 90
- Represent the shaded part as a decimal in the diagram below.
- 0.6
- 0.4
- 0.3
- 0.1
- Complete the table below and answer the questions that follow.
Colour Tally Number Green llll llll Yellow llll llll Blue llll llll llll 15
How many more pegs are blue than yellow.- 10
- 15
- 5
- 25
MARKING SCHEME
- D
- A
- A
- A
- C
- C
- B
- C
- A
- B
- B
- D
- B
- C
- A
- B
- B
- D
- B
- D
- D
- B
- B
- B
- B
- C
- C
- C
- B
- C
Creative Arts, Social Studies & Religious Education Questions and Answers - Grade 5 Mid Term 2 Exam 2023 Set 2
SOCIAL STUDIES
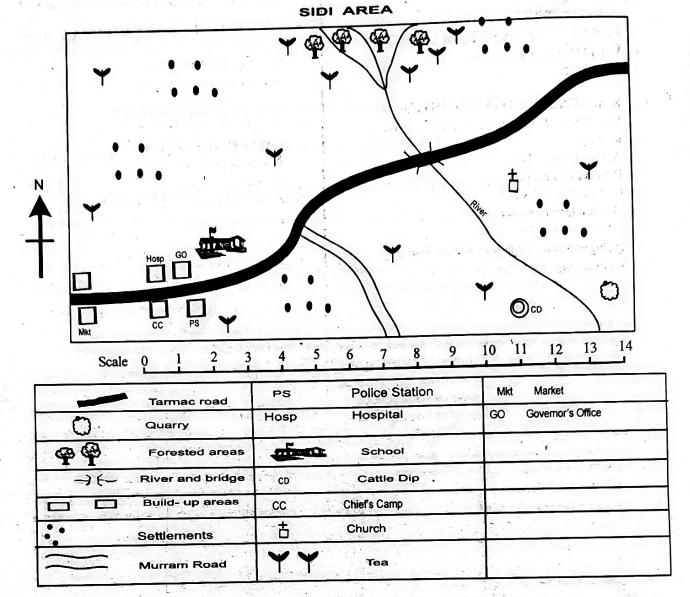
- The settlement pattern in Sidi area can be described as
- linear settlement
- dense settlement
- clustered settlement
- even settlement.
- The highest point in Sidi area is around the
- cattle dip
- shrubs
- forest
- chief's camp
- The flow of the river in Sidi area can be described as from
- North East to South
- North to South East
- South West to North
- North West to South East.
- The people in Sidi area are likely to be
- Hindus
- Muslims
- Pagans
- Christians.
- The location of the market in Sidi area was influenced by
- road passing by
- climate
- type of soil
- security.
- Kamau listed the following types of industries. Which type of industry is also called secondary industry?
- Processing industry
- Service industry
- Assembly industry
- Manufacturing industry.
Achieng drew the figure below. Use it to answer questions 7 to 8.
- The letters F and J respectively represent
- North East ans South West
- South West ans South East
- North West and South East
- North West and South West.
- Below are uses of the above figure. Which one is not? To
- show direction
- describe the flow of a river
- tell routes to a place
- show the highest point in a map.
- Grade 4 learners described physical features as shown below. Which of the following describes a plateau? A
- raised piece of land that is flat at the top
- form where water flows out of the ground from an underground source
- depression between two areas that are high or raised
- large lowland that is generally flat.
- Which one of the following is the main importance of the historic built environments?
- To attract tourist and earn foreign exchange.
- Provide employment opportunities.
- Remind and teach us about our culture.
- Create a sense of belonging.
- Which one of the following is a negative form of interaction? Through
- wedding ceremonies
- hunting activities
- raids and war
- religious activities.
- Henrick mentioned the following benefits of interdependence. Which one is not correct?
- People are able to live in harmony and unity.
- Promotes immorality.
- People get new ideas and knowledge.
- People are able to appreciate each other's culture.
- Belinda matched the industries in the county and their products. Which of the following is correctly matched?
Industry Product A. Creameries Cakes B. Pottery Cheese C. Jua kali Jikos D. Weaving Pots - A learner listed the benefits of trade in the county Which one is correct? It promotes
- bribery
- growth of slums
- pollution of the environment
- the agricultural sector.
- Below are economic activities in the county. Which one is the most common economic activity?
- Mining
- Saw milling
- Agriculture
- Basketry.
CREATIVE ARTS
- A teacher prompted learners to say any word that came in their minds. His aim was to give the words rhythmic names. Whose word was given the name ta-te?
- Lucy - Melon
- Janet-Gate
- Peris-Good morning
- Betty-Farm.
- Grade four learners discovered that a melody is composed by short and long sounds. Which of these is the shortest sound in Music?
- taa
- ta-te
- taa-aa
- taa-te-fe.
- Kiarie had four bottles. He wanted to produce sound with them. Which bottle produced the highest sound? The
- one half filled with water
- one fully filled by water
- empty plastic bottle
- empty metallic bottle.
- Musa sang a melody with these syllables:
mi fa so la. This is called _____________________ singing.- sideways
- upward
- downward.
- round.
- When we combine long and short sounds to form Music, we are creating
- pitch
- dynamics
- rhythm
- pace.
- Njue mentioned the elements of folk dance as shown below. Which one of them is false?
- Tempo
- Volume
- Space
- Energy.
- Participants were to carry musical instruments to accompany their folk songs performance. Who carried an instrument that is different from the others?
- Tom-whistle
- Steve-chivoti.
- Karen-coro
- Liz-isukuti
- Belinda decided to improvise the wind instrument shown below. 'Muturiru'
What is the best material for her to use?- Bamboo stick
- Wooden stick
- Plastic material
- Metal.
- Grade 4 learners were to sing the Kenyan National Anthem during assembly. On which day was it?
- Monday
- Tuesday
- Wednesday
- Thursday
- Grade 5 learners decided to take care of the instrument below.
How best can they do it?- Washing it while in use.
- Sharing with others who don't have.
- Keeping it under direct sunlight.
- Blowing it softly when using it.
A learner displayed the artwork below. Use it to answer questions 26 to 28.
- Which of the following types of lines is not used in the above artwork?
- Straight line
- Curved line
- Zigzag line
- Thick line.
- The learner decided to shade the artwork using the smudge technique. Which of the following materials is he not likely to use?
- Wax Crayons
- Coloured pencil
- Coloured Chalk
- Water colours.
- The above equipment is used to
- apply crayons
- make colours darker
- hold paint during painting
- make colours brighter.
Below is an artwork by a grade 5 learner. Use it to answer questions 29 to 31.
- Which of the following was not likely to have been used by the leaners to create the artwork above?
- Adhesive
- Pencil
- Needle
- Magazines.
- The above artwork was created using a technique called
- cutting and pasting
- collage
- montage
- sticking.
- When making the above artwork, one should consider the following factors except
- choose a particular theme
- ensure proper balance
- utilise the space well
- dry the artwork on a hot surface.
Grade 5 learners made the item below. Use it to answer questions 32 to 35.
- Which of the following materials is not used in making the above item?
- Nails
- Scissors
- Hammer
- Knife.
- The above artwork can be made using
- canvas
- leather
- nylon
- cotton fabric.
- Which of the following correctly matches the parts labeled F, K and P?
F K P A. Membrane
B. Laces
C. Laces
D. TinResonator
Membrane
Membrane
LacesLaces
Tin
Resonator
Membrane - The above item is played by
- tapping
- plucking
- blowing
- shaking
PART 2: Choose a section you have prepared for. Each section is 15 marks
CHRISTIAN RELIGIOUS EDUCATION
- According to the book of Jeremiah 29:11, what is God's purpose for our lives? To make us
- successful
- rich
- poor
- slaves.
- While reading the book of Genesis 1:26, 2:15, we learn that God gave responsibilities to human beings. Which of the following is not one of them? To
- name and take care of animals, fish and birds
- cultivate the land
- take care of the environment
- kill all the animals.
- Which of the following statements shows the way we can demonstrate good stewardship towards God's creation? By
- taking good care of the environment
- cutting down trees
- throwing garbage in the river
- killing wild animals.
- Learners wrote the following as factors that promote family unity. Which one does not promote unity?
- Sharing responsibilities at home.
- Reading the bible and praying together.
- Working together on chores and other projects.
- Arguing all the time.
- In Mathew 25: 14, we read about the parable of the talents. What lesson do we learn from it?
- God will punish us if we do not use our talents well.
- We should brag about our talents to others.
- We should laugh at those who do not have talents.
- We should not use our talents so that people do not know we have them.
- The Bible tells us about the fall of human beings. What lesson do we learn from it?
- We should obey God's word.
- We should not do anything we are told.
- God is merciless.
- The first humans were foolish.
- Which of the following is not a value we learn from the story of Noah and his sons?
- Honesty
- Empathy
- Obedience
- Carelessness.
- Grade 5 learners were discussing ways of showing respect to the elderly. Which of the following is not among them?
- Talking to them rudely.
- Helping with household chores.
- Obeying them.
- Offering them seats when there are no seats.
- We are taught that family unity is very important. This is because it
- promotes love and respect for one another
- brings chaos
- encourages theft
- brings about nepotism.
- Grade Spupils were learning about humility and pride. Which of the following is not a disadvantage of pride? It makes
- people selfish and self-centered
- a person feel superior and look down upon others
- a person succeed in life
- one be confident in themselves instead of in God.
- Wendy and her friends wrote the effects of child labour on a chart. Which one of the following is not one of the effect they wrote?
- Children become unhappy.
- Children become unhealthy.
- Children earn a lot of money.
- It affects the child's self-esteem.
- Grade 5 learners of were discussing the benefits of reading the Bible. Which of the following is not a benefit? Helps us to
- obey our elders
- know more about God
- know creation stories
- swear.
- Which of the following is not true about Peter and John? They
- told people about the Jesus who had risen from the dead
- healed a lame man in the name of Jesus Christ
- were arrested and put in jail
- earned a lot of money through healing people.
- Who among the following was not a member of the Jewish Council in which John and peter were brought in front of?
- Annas
- Jairus
- Alexander
- Caiaphas.
- Solving disputes is very important because it
- helps to maintain peace and harmony
- brings about pride
- helps one get rich quickly
- brings disagreements.
ISLAMIC RELIGIOUS EDUCATION
- Summar wrote the following prayers on a chart. Which one is NOT a sunnah prayer?
- Dhuha
- Asr
- Baadiya
- Qabliya.
- Grade five learners were asked to search for miracles of prophets on the Internet. Which one did they find out about Nabii Issa?
- Changed walking stick into a snake.
- Thrown into the fire but the fire did not burn him.
- Could understand the language of birds.
- Spoke at infancy.
- Two surahs known as muawidhatein are
- Naas and Maun
- Naas and Falaq
- Ikhlas and Naas
- Falaq and Fatiha.
- Saba'atul mathani must be recited in all prayers. Saba'atul mathani refers to
- Fatiha
- Falaq
- Fatih
- Baqara.
- The teacher narrated to grade 5 learners about the year of elephant. In the story, who wanted to destroy the Holy Kaaba?
- Abu jahal
- Abu Lahab
- Abraham
- Abraha
- In which surah is Ummu jamil mentioned?
- Maun
- Masad
- Ikhlas
- Tiyn.
- The prophet (saw) had the best character. Which one of the following was not among his characters?
- Untrustworthness
- Kindness
- Truthfulness
- Generosity.
- Grade 4 learners were discussing the manners of eating according to the sunnah of the prophet. Who gave the correct manners?
- Zubeir: Eating what is far from you
- Abdos: Eating hot-food.
- Kausy: Eating what is in front of you.
- Khubbayb: Eating with both hands.
- Complete the hadith on brushing our teeth. "Brushing of teeth is a means of purification of the mouths and pleasing
- Allah
- Angels
- parents
- iblis.
- Which one of the following pillars of Islam does not require physical fitness?
- Swalah
- Jum
- Zakat
- Hajj.
- Allah SWT sees everything. Which attribute of Allah describes Him as the all-seeing?
- AL samiu
- AL basir
- As salaam
- AL malik.
- Angels of Allah are created from
- nur
- clay
- fire
- smoke.
- Grade 5 learners were asked to write down the angels mentioned in the Holy Qur'an. How many prophets did they write down?
- 35.
- 15
- 20
- 25
- Angels have special duties. Which angel is incharge of rain?
- Mikail
- Malik
- Israfeel
- Raqib
- Who among the following prophets is referred to as ulul azm?
- Yunus
- Yusuf
- Yahya
- Musa.
MARKING SCHEME
- C
- C
- B
- D
- A
- C
- D
- D
- A
- A
- C
- B
- C
- D
- C
- A
- B
- D
- B
- C
- B
- D
- A
- A
- D
- A
- D
- C
- C
- A
- D
- A
- B
- C
- A
CRE
- A
- D
- A
- D
- A
- A
- D
- A
- A
- C
- C
- D
- D
- B
- A
IRE
- C
- D
- B
- A
- D
- B
- A
- C
- A
- C
- B
- A
- D
- A
- D
Integrated Science Questions and Answers - Grade 5 Mid Term 2 Exam 2023 Set 2
QUESTIONS
- John was asked by his teacher to list down examples of waterborne diseases. Which one of the following is not an example he listed?
- Bilharzia
- Cholera
- Pneumonia
- Dysentery
- Grade five learners were discussing about causes of external parasites. Four learners listed the following causes
- Shaquel-Dirty hair and clothing.
- Trevor-Walking bare foot.
- Maureen - Dirty and muddy floor.
- Sandra - Fleas found on animals.
Who among the learners listed the causes of lice?- Shaquel
- Trevor
- Maureen
- Sandra
- Grade five learners listed down the signs and symptoms of internal parasites. Which of the following parasites did they correctly match with its symptoms?
- Round worms - Vomiting.
- Hookworms - Breathing difficulties.
- Pinworms-Vomiting.
- Tapeworms - Wheezing.
- Njuguna wore gumboots when walking in stagnant water. Which of the following waterborne diseases was he likely to prevent?
- Bilharzia
- Cholera
- Dysentery
- Typhoid
- Which one of following is not a preventive measure of waterborne diseases?
- Washing hands with clean water after visiting the toilet.
- Avoid walking in stagnant water.
- Washing fruits and vegetables properly before eating.
- Avoid crowded places.
The figure below shows an internal parasite. Use it to answer questions 6-8.
- The internal parasite above is called
- tapeworm
- round worm
- pinworm
- hookworm.
- Which one of the following practices can cause the above parasite?
- Avoiding congested rooms.
- Eating undercooked food.
- Walking barefoot.
- Bathing with warm water.
- Which one of the following is not a sign and symptom of the parasite above?
- Diarrhoea.
- Stomach pains
- Persistent cough.
- Loss of weight
- Ellis bought a bottled water on his way home. Which one of the following is the best way to manage the bottle waste after drinking the water?
- Buming.
- Re-using.
- Throwing into the river.
- Burying in the soil.
- Which of the following plants is correctly classified?
Flowering Non flowering A. Moss Maize B. Peas Fern C. Cedar Passion D. Beans Bananas - Grade five learners were asked to list diseases that affect the breathing system. Which one of the following was not in their list?
- Influenza
- Tuberculosis
- Asthma
- Cholera.
- Grade five learners collected materials that they would use to model the breathing system. Which one of the following materials was not part of their collection?
- Nail
- Clear plastic bottles.
- Cello tape
- Balloon
- The following are characteristics of a certain vertebrate.
- Breaths through gills.
- Body covered with scales
- Lays eggs.
Which of the following animals has the characteristics above?- Frog
- Fish
- Crocodile
- Toad
- Which of the following fungi is used as food?
- Mould
- Toadstool
- Mushroom
- Dandruff.
- Which one of the following is not a non-flowering plant?
- Lichen
- Moss
- Pawpaw
- Fern
- Which one of the following is an importance of athletics? It
- destroys our breathing system.
- helps reduce stress
- increases weight.
- increases mental difficulties.
- Which one of the following is not a material use to make a relay baton?
- Manilla
- Newspapers
- Plastic bottles
- Sisal.
- A standing discus throw involves the use of a discus and phases when playing the game. Which one of the following is not a phase in the sport
- Stance
- Grip
- Discus
- Swing
- Njeri was skipping the rope using the technique shown below.
The technique is known as- the straddle technique
- rope game technique
- straddle cross technique
- jumping rope technique.
- Which one of the following equipment is used in softball?
- Catcher's mitts
- Discus
- Baton
- Stance.
- Hurdling is a sport that involves the use of hurdles. Below are the stages of hurdling.
- Landing.
- Approach.
- Flight.
- Hurdle clearance.
Which one of the above phases takes place last?- Flight
- Hurdle clearance
- Approach
- Landing.
- A long jump facility has various parts.
What is the name of the part marked X?- Take off board
- Run way
- Landing pit
- Facility
- Ochieng was officiating an elongated sprint race. Which one of the following is not a command in an elongated sprint race?
- Run-away
- On your mark
- Set
- Go
- A softball game is played by two teams. How many players does each team have?
- 12
- 4
- 10
- 9
- Batting is a game played by batters. What is the batting technique used by the batter below?
- Overhand throw technique.
- Swing technique.
- Batting technique.
- Soft balling technique.
- Mrs Ondimu taught grade 5 learners on the speed training drills used in a medium sprint start. Which one of the following is not a speed training drill in a medium sprint start?
- Box drill.
- Elongating drill.
- Single leg box drill.
- Reaction drill.
- During the interschool competitions, one of the teams used the technique below in the relay baton race:
Which relay baton technique is shown above? A- Relay racing change.
- Non visual baton change.
- Visual baton change.
- Swing technique.
- Kimani is a good outfielder in softball game. Which one of the following characteristics is false about Kamau as a softball outfielder? He should
- be accurate in throwing the ball
- position hiniself well for batting
- do doping
- be quick in making judgements.
- Which one of the following is an equipment used in standing discus?
- Which one of the following is not a way of taking care of recreation community facilities?
- Drawing graffiti on their walls.
- Putting trash in the litter bin.
- Littering the compound.
- Planting trees.
- We can finish a race by use of the run through finish technique. Which one of the following is not a strategy to use when using the finishing technique?
- Maintain high speed when approaching the finish line.
- Lift the knees.
- Celebrate as you approach the finish line.
- Drive your arms harder.
- The following are the importance of organic waste material in the soil except that they
- provide nutrients required by the crops to grow healthy
- improve the movement of air in the soil
- improve the water retention ability of the soil
- give the soil a different colour.
- Which of the following is not a water conservation practice in farming?
- Mulching
- Shading
- Cover cropping
- Sprinkler irrigation.
- Wakanda has a problem with wild animals destroying her crops. Which of the following is the most suitable method to control them? Using
- poison
- sound devices like rattles
- shooting them with guns
- throwing stones at them.
- The picture below shows one of the plants used as a repellant. What is its name?
- Euphorbia
- Daffodil
- Rosemary
- Hot pepper.
- Grade five learners were discussing about soil erosion. Which of the following is not a type of soil erosion?
- Trench erosion.
- Gulley erosion.
- Sheet erosion.
- splash erosion.
- Jabain noticed that soil arried by runoff in his farm is deposited in the river bank. Where else can it be deposited?
- In a pond.
- At the farm.
- An the latrine.
- By the roadside.
- In a discussion, Grade 5 learners mentioned the crops below. Which one is not an indigenous crop?
- Sorghum
- Pumpkin
- Spider weed
- Wheat.
- The following tools are used to take care of vegetable crops except
- wheelbarrow
- rake
- watering can
- hammer.
- The picture below shows a vegetable crop. What is its name?
- Courgette
- Bulb onions
- Cabbage
- Carrots.
- All animals have both male and female animals. What is the name given to a male goat?
- Nanny
- Billy
- Bull
- Ox.
- Which of the following shows positive use of digital devices?
- Communicating with other people.
- Watching movies all night.
- Pranking our friends on the internet.
- Posting nasty photographs of people we don't like.
- A student asked the teacher to explain what leisure means. What was the teacher's response? It is the time
- time when we are most busy
- when we are free after finishing work
- time just before bed
- we spend after lunch.
- Which of the following materials is used for making most floors of buildings in urban centres?
- Wood
- Glass
- Tiles
- Clay
- Which are the most appropriate materials to use to clean the windows of your classroom?
- Warm soapy water, clean cloth, duster and old newspaper.
- Cold soapy water, rug and duster.
- Soapy water and scrubbing brush.
- Broom, detergent and mop.
- The following is a procedure for cleaning wooden surfaces. Which should come first? A
- Rinse using a clean cloth wrung out of warm water to remove soap and dirt.
- Dust the surface from top to bottom using dry cloth to remove loose dirt.
- Collect the cleaning materials or tools.
- Dry the surface with clean dry cloth to remove excess water.
- The following can cause accidents at home and school except
- sharp pointed nails on wood
- slippery floors
- open wells and pits
- flat football pitch.
- The government body responsible for approving packed food before it is sold is called
- Kenya Beureal of Statistics (KEBS)
- Kenya Business Services (KBS)
- Kenya Institute of Business Studies (KIBS)
- Kenya Cereal and Produce Board (KCPB)
- The following are positive leisure activities except
- swimming and playing football
- playing in restricted areas
- dancing and singing
- playing video games.
- Which of the following is an importance of a clean home?
- A clean home makes a family comfortable.
- It ensures that we can eat on the floor.
- A clean home is hard to maintain.
- Cleaning a lot destroys surfaces.
MARKING SCHEME
- C
- A
- A
- A
- D
- A
- B
- C
- B
- B
- D
- A
- B
- C
- C
- B
- D
- C
- A
- A
- D
- B
- A
- D
- B
- B
- C
- C
- B
- C
- C
- D
- D
- B
- D
- A
- D
- D
- D
- A
- B
- A
- C
- A
- A
- C
- D
- A
- B
- A
Shughuli za Kiswahili Questions and Answers - Grade 5 Mid Term 2 Exam 2023 Set 2
Soma taarifa hii kisha ujibu maswali 1-5.
Sisi watoto wa nchi hii hatuna ubaguzi. Tunapendana. Tunasoma pamoja, tunacheza pamoja, tunaishi pamoja na tunakaa pamoja. Hatuna ubaguzi wa ukabila, dini, rangi wala cheo. Kwetu, kila mtu ni sawa, wasichana kwa wavulana,wake kwa waume na wazee kwa vijana. Tunaamini kwamba tukiishi pamoja kwa kupendana tutakuwa na amani, upendo na ushirikiano katika nchi yetu. Tukumbuke kwamba
nchi yetu ni moja. Na ndipo mahali petu pa kuishi hadi mwisho wa maisha yetu. Hivyo ni lazima sisi pia tuwe na umoja na ushirikiano.
Tunawaomba viongozi, wazazi, walimu wetu na kila mtu kwa jumla, huu ni wakati wa kuwajulisha vijana wote na watoto wa nchi hii kuwa umoja ni nguvu na utengano ni udhaifu.Tuache ukabila ili tujiite kuwa sisi ni watu wa kabila moja linaloitwa 'Wakenya'.Tuanze leo hii kutumia lugha yetu moja ya taifa, ambayo ni Kiswahili. Wanaotubagua na kututenganisha, tuwakatae katakata na tuwaambie "Ng'o!"
- Sauti ya watoto wa nchi hii
- haina ubaguzi
- imejaa ukabila
- haitaki ukabila
- ina chuki.
- Vijana ni watu gani?
- Wavulana
- Wanaume wadogo
- Watoto kwa kiume
- Wasichana kwa wavulana.
- Tunahitaji umoja kwa sababu nchi yetu ni
- kubwa
- nzuri
- moja
- changa.
- Sisi sote wananchi tunafanana yaani tu
- pamoja
- umoja
- wamoja.
- kumoja
- Wanaotubagua tuwaambie ng'o kisha tuanze kutumia lugha ya
- kimombo
- mama
- Kiswahili
- ung'eng'e.
Soma kifungu hiki kisha ujibu maswali 6 - 10.
Siku moja nilikuwa nimebaki nyumbani peke yangu. Wazazi wangu walikuwa wameenda kwenye matanga ya mjomba wangu. Nilikuwa mtoto wao wa kipekee. Wazazi wangu walinikanya na kunionya kuwa nisimkaribishe mtu yeyote nyumbani ikiwa wao hawakuwepo. Hakika sikutarajia kumruhusu mtu au kumkaribisha mtu yeyote aje akae nami kwetu. Lakini ilipofika jioni, akaja rafiki yangu wa chanda na pete Kichwachuma alijidai kuja kunisalimia. Nilishangaa kuhusu hizo salamu zake za jioni. Alipoketi tu hata kabla hatujaanza kuulizana za hujambo- sijambo, mvua ilianza kunyesha huku ngurumo kama za simba zikiandamana na radi. Hakika niliduwaa kushuhudia mvua ya miujiza isiyokuwa na dalili yoyote ya mawingu.
Sikuwa na jingine la kufanya. Nilimruhusu Kichwachuma kulala kwetu. Ajabu ni kwamba, kesho yake sikuamka mapema nilivyozoea. Nililala hadi saa tano asubuhi. Nilipoamka nilijikuta nimelala sakafuni.
Sikumpata rafiki yangu. Pia kila kitu nyumbani kwetu kilikuwa kimechukuliwa hadi kitanda tulichokuwa tumekilalia. Kila kitu! Vitu vyote havikuwepo. Nilibaki mimi tu nikishangaa jinsi ya kuwaambia wazazi wangu.
- Mwadishi anasema kuwa alibaki nyumbani peke yake. Hivyo alikuwa
- peke
- upweke
- pweke
- pekee
- Aliyekuwa ameaga dunia ni
- dada wa mama
- kaka wa baba
- kaka wa mama
- dada wa baba.
- Wazazi wake walitoa onyo kwamba
- asikaribishe watu nyumbani milele
- amkaribishe mtu yeyote nyumbani
- mtu akaribishwe bila wao kuwapo
- asimkaribishe yeyote nyumbani wasipokuwepo.
- Mvua ilikuwa ya miujiza kwa sababu
- ilikuwa na radi
- ilileta wezi
- haikuonyesha dalili kabla ya kunyesha
- ilikuwa na ngurumo za simba.
- Alipoamka aligundua kuwa vitu vyote nyumbani vilikuwa
- vimeuzwa
- vimeibiwa
- vimepotea
- vimetoroka
Soma kisa kifuatacho kisha ujibu swali la 11 - 15.
Siku hiyo ya Alhamisi, Kalume alikataa katakata kwenda shuleni. Siku hiyo ilikuwa ya kufanya mtihani wa Kiswahili. Alikataa kwenda shule kwa sababu mama yake alikataa kumnunuli vibanzi vya kula wakati wa mtihani. Mama alimwacha nyumbani asubuhi na mapema baada ya kumwamsha. Akamwambia kuwa akimaliza kufungua kinywa aende upesi shuleni asichelewe. Naye akaenda zake kazini.
Kalume alijua kimoyomoyo kuwa hangeenda shuleni. Alitaka vibanzi kwanza. Aliona kuwa vibanzi vilikuwa vitamu kuliko masomo au hata mtihani wa Kiswahili. Mama yake aliporudi saa saba adhuhuri alimkuta akiwa amejikunja akilia. Alipoulizwa alichokuwa akililia alisema: "Umekataa kuninunulia vibanzi"
Kesho yake mama alimpeleka shuleni. Akawaeleza walimu sababu za kukosa shule. Walimu walishangaa. Wanafunzi waliposikia habari hizo walimcheka Kalume sana, wakamwita Bwana Vibanzi. Wengine wakambatiza Kalume banzi! Hadi wa leo wanamwita hivyo. Je, wewe ni Kalume nani? Au Kalume nini?
- Kalume alikataa kwenda shuleni siku ya
- Alhamisi
- Jumatano
- Ijumaa
- Jumanne.
- Ni kwa nini Kalume alikataa kwenda shuleni?
- Alichukia shule.
- Alikuwa na njaa.
- Aliogopa mtihani.
- Alitaka vibanzi.
- Kufungua kinywa ni
- kulia
- kupanua mdomo.
- kusugua meno
- kula asubuhi.
- Neno jingine lenye maana sawa na vibanzi ni
- mahamri
- viazi
- chipsi
- viazi karai,
- Mama alipotoka nyumbani asubuhi alijua kuwa Kalume
- haendi shule
- atachelewa shule
- alikataa chipsi
- angeenda shule
Jaza mapengo kwa jibu mwafaka.
Kitabu __16__ kilianguka chini __17__ vipandevipande. Kipande __18__ kikachukuliwa na upepo lakini kipande __19__ kiliingia ndani __20__ maji.
| A | B | C | D | |
| 16. | yangu | changu | zangu | langu |
| 17. | ikararuka | akararuka | kikararuka | kikararua |
| 18. | kimoja | moja | mmoja | kamoja |
| 19. | ingine | mwingine | nyingine | kingine |
| 20. | ya | cha | mwa | wa |
Kutoka swali la 21 hadi 30 jibu kulingana na maagizo.
- Ipi si jozi ya vitate vyenye sauti zinazokaribiana kimatamshi?
- Sima- Zima
- Fuka- Vuka
- Fora-Fola
- Cheka-Choka.
- Mwalimu akitusalimu masalkheri. Salamu hii inatumika wakati gani?
- Mchana
- Jioni
- Asubuhi
- Usiku
- Neno la mwisho kupatikana kwenye kamusi kati ya haya ni
- mbio
- mbuzi
- mbili
- mbuni.
- Ni aina ipi ya nomino iliyo katika sentensi ifuatayo?
Maji mengi yamemwagika chini.- Idadi
- Mahali
- Wingi
- Pekee
- Chagua wingi wa sentensi ifuatayo.
Kula kwake huko kunaudhi.- Kula kwao huko kunaudhi.
- Kula kwake huko kunaudhi.
- Kukula kwake huko kunaudhi.
- Vyakula vyake hivyo vinaudhi.
- Tegua kitendawili kifuatacho.
Ananitazama, hasemi, hasikii- Kivuli
- Kioo
- Picha
- Mtoto
- Kamilisha. ___________________________ ya ndizi.
- Mkungu
- Tita
- Bunda
- Chane
- Chagua nomino zinazoweza kuunda nomino ambata sahihi.
- Mwana + maji
- mwana + muke.
- mwana + mbe.
- mwana + inchi
- Neno lipi lisilo la heshima kati ya haya?
- Endesha
- Choo
- Kinyesi
- Mjamzito
- Chagua sentensi sahihi kisarufi.
- Mbuzi zimeshiba.
- Ndege limeanguka chini.
- Daktari wamegoma.
- Choo kinaoshwa.
INSHA
Umepewa dakika 40 kuandika insha yako.
Andika insha ya kusisimua kuhusu;
JINSI YA KUKABILIANA NA UMASKINI
MARKING SCHEME
- A
- D
- B
- D
- C
- B
- C
- D
- C
- B
- A
- D
- D
- C
- D
- B
- C
- A
- D
- A
- D
- B
- B
- C
- A
- C
- D
- A
- B
- D
English Questions and Answers - Grade 5 Mid Term 2 Exam 2023 Set 2
Read the following passage and answer the questions that follow.
Kimeno was woken up by the sounds of gunshots. He was very scared and was afraid to make any sound. When he looked around the hut for his grandmother, he did not see her. Though it was pitch dark, he knew she was not inside the hut. Kimeno had always slept with his grandmother in her hut for as long as he could remember. His younger brothers slept in their mother's hut.
When he got used to the darkness, Kimeno slowly got out of bed and crept to the door. He looked out through the crack that had always been at the side of the door but he couldn't see anything. Everywhere was so quiet that he could hear his heartbeat. It sounded so loud he was afraid the intruders could hear him. He stood by the door for a long time trying to make sense of what was happening and why his grandmother was not in her hut.
After what felt like forever, he opened the door and slowly walked outside. By then the moonlight had appeared and it was quite bright. What he saw outside almost made him faint. He could not believe his eyes. He fell on his knees and vomited right there. All over his compound, there were bodies everywhere. He saw, his mother and two brothers just outside their hut. The sight was so horrible that he felt like his heart was being torn into two. "Who was horrible enough to do something like that?" Kimeno cried out loudly but he already knew the answer. The rival tribe from the other side of the hill. They had always been rivals for as long as he could remember but he did not know why. "I swear that when I grow up, I will make sure that this rivalry is resolved." Kimeno promised himself. Indeed, we need peace in the interior parts of our beloved country Kenya.
- What was it that woke Kimeno?
- Cries
- Gunshots
- Earthquake
- Thunder.
- Kimeno slept in his grandmother's hut. Where did his brothers sleep? In
- his grandfather's hut
- the granary
- their mother's hut
- their bedroom.
- What did Kimeno do immediately he got outside? He
- fainted
- vomited
- laughed
- cried.
- What did Kimeno see on his compound?
- Bodies everywhere.
- Nothing.
- His parents.
- His classmates.
- Who was responsible for the sight that Kimeno saw at his compound?
- His father.
- Pirates.
- The rival tribe.
- The vigilantes.
Read the following passage and answer questions 6 to 10.
Utamaduni day is one of the National holidays in Kenya. The holiday is marked on the tenth of December every year. The holiday is used to celebrate the diversity of Kenyan cultures. In Kenya, there are over forty tribes and each tribe has its own unique culture.
The purpose of celebrating Utamaduni day is to bring together Kenyans from all over to showcase some of their cultural aspects and help other Kenyans to appreciate each culture. This is very important because it brings unity.
Different cultural aspects displayed on this unique day include food, dress code and other artifacts like decorations. There are also songs and dances to showcase each tribe's unique dances and costumes. The Maasai have their special dance by the Morans where they jump high in the air. We have the Kikuyus with their 'mokimo', the kambas with their 'muthokoi', and the Kalenjins with their 'mursik'. All these and more are showcased during this special day. Since the event began a couple years ago, many Kenyans have learned to appreciate each other's culture.
- On which date is Utamadumi day celebrated in Kenya?
- First May.
- Twelfth December.
- First June.
- Tenth December.
- Which unique aspect of their culture do the Maasai showcase on Utamaduni day?
- Jumping high in the air.
- Their unique food.
- Their fighting tactics.
- Their language.
- Which tribe has "Muthokoi" as their unique food of choice?
- Kalenjins
- Maasai
- Kikuyu
- Kamba.
- What is the benefit of celebrating Utamaduni day? It
- brings unity
- brings revenue
- gives Kenyans an excuse not to go to work
- gives Kenya a good name around the world.
- What is the purpose of Utamaduni day? It
- brings Kenyans together to showcase their cultures
- is a day of rest
- gives people an excuse to celebrate
- is written in the constitution.
Read the following story and answer the questions that follow.
Once there lived a beautiful girl called Malaika. She lived with her parents in a village called Moto Moto. In the forest just beyond the village, there lived ogres. Malaika was the most beautiful girl in the village. Other girls were jealous of her beauty and avo -d her. As a result, Malaika was lonely because she had no friends to play with and do things together.
As Malaika grew older, she seemed to get even more beautiful. She got a lot of attention from all the young men who wanted to court her. Since the other girls were angered by this, they made a plan to get rid of Malaika forever.
One day, Malaika was surprised when four girls, Uzembe, Wivu, Chuki and Ushoga, approached her and said that they wanted her to accompany them into the forest to gather wild fruits. Malaika was so happy to finally be included in their group. She ran into the house and took her basket. She and the other girls walked to the forest and when they reached one particular tree, they decided to gather fruits from it. They had been warned not to stay in the forest till dark. Chuki suggested they close their eyes. The one who gathered many ripe fruits would be the winner. They counted one to three and closed their eyes. After some minutes, one said they had gathered enough and they should open their eyes.
Malaika opened her eyes and behold, only her basket was filled with unripe fruits. It turned out that the other girls opened their eyes and picked only the ripe fruits. They told Malaika that she would have to be left behind to gather ripe fruits. They left her there and went home. Malaika was scared but she was determined to fill her basket with ripe fruits. So, she worked fast, but as she was nearly finishing an ogre came and took her away. Malaika was never seen again and her parents and the other villagers were devastated.
- What was the name of the village in which Malaika lived?
- Wivu.
- Moto Moto.
- Uzembe.
- Chuki.
- The other girls in the village wanted to get rid of Malaika because she
- was smarter than them
- was a bad person
- got the attention of all the young men in the village
- stole their things.
- Who suggested that they close their eyes?
- Uzembe
- Chuki
- Wivu
- Ushoga.
- How comes Malaika's basket was filled with unripe fruits while all the other girls' were filled with ripe ones? Because they
- were experts
- were lucky
- did not close their eyes
- knew which ones were ripe without looking.
- What happened to Malaika in the end? She
- was taken by an ogre and was never seen again
- finished picking her fruits and went home
- abandoned her basket and went home
- became good friends with the other girls.
CLOZE TEST
Fill in the blank space numbered 16-20 with the most suitable word.
Eating a __16__ diet is important, __17__ it gives the body all the important nutrients to function. A balanced diet __18__ of carbohydrates, proteins, vitamins and minerals. Lack __19__ one of these nutrients can lead __20__ deficiencies and diseases.
| A | B | C | D | |
| 16. | good | balanced | great | variety |
| 17. | for | and | but | plus |
| 18. | is | made | consists | entails |
| 19. | of | by | in | at |
| 20. | with | on | at | to |
In this section, choose the correct answer to fill the blanks in the given questions.
- ___________________________ are celebrated during Mashujaa Day.
- Heros
- Heroes
- Hero
- Hiroes
- I hurt _____________________________ when I was cutting firewood.
- myself
- ourself
- yourself
- himself
- We were told that we _____________________________ brush our teeth twice daily.
- should
- may
- might
- would
- The people said their chief was as greedy as a
- lion
- leopard
- king
- hyena
- The two girls said that ________________________ cat had disappeared.
- there
- their
- her
- theirs
- Thomas said that _________________________wants to be a doctor when he grows up.
- she
- he
- they
- I
- The mangoes from Mutua's farm are the ________________________ in the region.
- sweet
- sweeter
- more sweet
- sweetest
- My father bought an _________________________ car.
- ugly, old, red
- old, red, ugly
- ugly, red, old
- red, ugly, old
- We ___________________________ deal with the issue tomorrow.
- will
- shall
- can
- could
- The rat was found dead ___________________________ the sofa.
- in
- along
- under
- at
COMPOSITION
You have 40 minutes to write your composition.
Write and complete an interesting story about;
HOW TO PREVENT ROAD ACCIDENT
MARKING SCHEME
- B
- C
- B
- A
- C
- D
- A
- D
- A
- A
- B
- C
- B
- C
- A
- B
- A
- B
- A
- D
- B
- A
- A
- D
- B
- B
- D
- A
- B
- C
Mathematics Questions and Answers - Grade 5 Mid Term 2 Exam 2023 Set 2
QUESTIONS
- There are eight hundred and eight thousand eight hundred and eight books in a county library. What is the number of books in words?
- 808808
- 8808
- 880808
- 8080808
- A farmer harvested 109929 kilograms of yellow beans. What is the place value of digit 0 in the number?
- Thousands
- Hundreds
- Ten thousands
- Hundred thousand.
- Mzalendo bought 36 goats and 48 sheep. He shared the animals among some of his relatives. Find the highest possible number of relatives who shared the animals equally.
- 12
- 6
- 72
- 8
- Tea was packed into 10 kg packets. Which of the following amount of tea was packed into exact number of packets?
- 90385
- 26150
- 12088
- 24004
- What is the next number in the sequence? 2, 3, 5, 6, ________________________
- 9
- 11
- 8
- 10
- The number of stationeries sold by Tusome bookshop in four months was; 20203, 22300, 20023 and 23020. Arrange the number of stationeries in discending order.
- 20023, 20203, 22300, 23020
- 23,020, 20023, 20203, 22300
- 20023, 20203, 23020, 22300
- 23020, 22300, 20203, 20023
- Mangoes are arranged in piles of 12 mangoes. How many mangoes will be there in 42 piles?
- 54
- 504
- 30
- 484
- Some correctly converted 42/3 into an improper fraction. What answer did he get?
- 42/31
- 14/3
- 14/2
- 43/2
- Pupils from two schools planted 45838 and 47362 Un tree seedlings. What is the total value of digit 2 after finding the sum of the number of seedlings?
- 200000
- 2000
- 200
- Twenty thousand.
- Three ladies contributed sh. 905 each for a charity work. How much money did they contribute in total?
- Sh. 4550
- Sh. 2705
- Sh. 2715
- Sh. 908
- Mzee Juma divided his piece of land into the following fractions;
1/10, 2/5, 1/2 . Arrange the fractions in descending order.- 1/2, 2/5, 1/10
- 1/10, 2/5, 1/2
- 2/5, 1/10 ,1/2
- 1/2, 1/10, 2/5
- In a school, there are 894 pupils. The girls are 432. How many boys are in the school?
- 462
- 1326
- 1236
- 362
- A school received a piece of land that was 73.584 acres. What is the place value of digit 8 in the number 73.584?
- Tens
- Hundreds
- Hundredths
- Tenths
- The distance from Nderitu's home to school is 7 km 21 m. What is the distance in metres?
- 7000 m
- 7021 m
- 7500 m
- 721 m
- A rectangular table measures 35 cm by 17 cm. What is the area of the table?
- 214cm2
- 52cm2
- 495cm2
- 595cm2
- Keziah walked around the figure below. What distance did she cover altogether?
- 94m
- 146m
- 188m
- 100m
- A jug contained 2 litres of porridge. Mwema took 0.95 litres of the porridge. How much porridge remained in the jug?
- 2. 075 litres
- 1.05 litres
- 1.025 litres
- 0.73 litres
- Halima borrowed x books while Judy borrowed y books. How many books did they borrow altogether?
- x + y
- x − y
- y − x
- xy
- Mkenya had 4/5L of juice. He drunk 1/10L from it. How much juice remained?
- 3/10L
- 3/5L
- 7/10L
- 10/7L
- A tailor had a piece of cloth of length 488 cm. He cut the clothe into smaller pieces each 42 cm long. What length of clothes remained if he used the pieces to make a table cloth?
- 16cm
- 11cm
- 446cm
- 26cm
- A school holiday lasted for 20 days. How many hours were these?
- 480 hours
- 4800 hours
- 20 hours
- 240 hours
- A piece of cloth was bought at sh.145 30 cts. How much will be spent in buying 8 such pieces of cloth?
- Sh. 1160 240cts
- Sh. 1162 40cts
- Sh. 1160 40cts
- Sh. 1162 240cts
- Otieno had 4-two hundred shilling notes. He changed them into 50 shilling notes. How many 50 shilling notes did he get?
- Five
- Sixteen
- Eight
- Ten
- A square has a perimeter of 56 cm. What is the length of one side?
- 14 cm
- 224 cm
- 28 cm
- 14 m
- A tile was in the shape of a cube. The length of the sides of the tile was 12 cm. What was the volume of the tile?
- 144cm3
- 36cm3
- 1728cm3
- 1584cm3
- A tap takes 20 minutes 55 seconds to fill a tank. How long will the tap take to fill four such tanks?
- 82mins 40seconds
- 83mins 20 seconds
- 83mins 40 seconds
- 82mins 20 seconds
- What is; 300 x 14?
- 4200
- 420
- 440
- 210
- What is 1/3 × 18?
- 18
- 6
- 3
- 15
- Kamau started working on his farm at 7:45 am. If he spent 4h 15 min, at what time did he stop working?
- 12:00 noon
- 12:30 pm
- 3:30 am
- 1:00 pm
- Okoth is 7 years older than his brother. What is the age of his brother if Okoth is x years old?
- X
- X + 7
- 7 − X
- X − 7
MARKING SCHEME
- A
- C
- A
- B
- C
- D
- B
- B
- C
- C
- A
- A
- C
- B
- D
- B
- B
- A
- C
- D
- A
- B
- B
- A
- C
- C
- A
- B
- A
- D