SECTION A: BIOLOGY (34 marks)
Answer all the questions in this Section in the spaces provided.
-
- What is meant by the term botany? (1 mark)
- State two rules of binomial nomenclature. (2 marks)
-
- Give one function for each of the following parts of a light microscope: (2 marks)
- mirror;
- rotating nose.
- Distinguish between a tissue and an organ system. (2 marks)
- Give one function for each of the following parts of a light microscope: (2 marks)
-
- What is meant by active transport? (1 mark)
- Give one role of each of the following in plant roots: (2 marks)
- active transport;
- osmosis.
-
- Name the region of the alimentary canal where amino acids are absorbed. (1 mark)
- Other than provision of food, state another importance of photosynthesis to animals.
-
- State two features of the leaf epidermis that allows light to pass through. (2 marks)
- What are the functions of the following minerals in the human body? (2 marks)
- Iron.
- Calcium.
-
- State two environmental conditions that contribute to low rate of transpiration in plants. (2 marks)
- Give one function of each of the following components of blood: (2 marks)
- white blood cells;
- platelets.
-
- Name the causative agent of whooping cough. (1 mark)
- State what happens to the following structures on the chest cavity during inhalation: (2 marks)
- diaphragm;
- rib cage.
-
- Name two products of anaerobic respiration in plants. (2 marks)
- Give two adaptations of blood capillaries to their function. (2 marks)
- The diagram below represents part of a human organ.
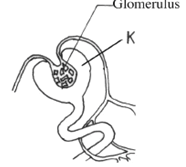
- Name the structure labelled K. (1 mark)
- Explain why contents of K include non excretory substances in a healthy person.(2 marks)
-
- Describe how diabetes mellitus occurs. (2 marks)
- Explain the importance of sweating in regulating human body temperature. (2 marks)
SECTION B: CHEMISTRY (33 Marks)
Answer all the questions in this Section in the spaces provided.
- A mixture contains ammonium chloride, sodium chloride and sand. Describe how one can separate and recover the substances in the mixture. (3 marks)
- The curves below were obtained by a student after heating two solid substances.
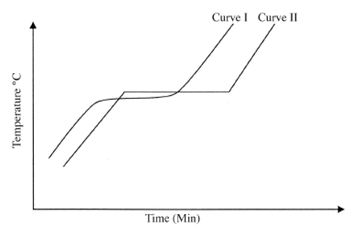
- Which curve represents an impure substance? Explain.
- What property of the substances was used to determine their purity? ( 2 marks)
-
- Write a word equation for the reaction between dilute hydrochloric acid and calcium hydrogen carbonate. (1 mark)
- Name the acid which is commonly used in car batteries. (1 mark)
- The diagram below shows how gas Q is prepared in the laboratory.
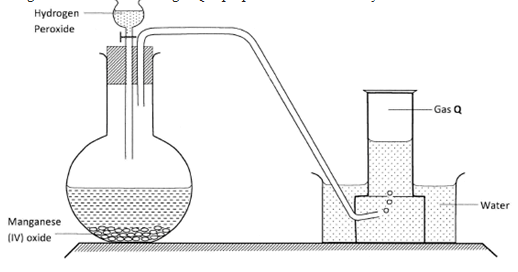
- Identify gas Q. (1 mark)
- If manganese (IV) oxide was removed, what would be the effect on the reaction progress? Explain. (2 marks)
- State one property of gas Q that enables it to be collected as shown in the diagram. (1 mark)
- The diagram below illustrates an experiment where dry hydrogen gas is passed over heated magnesium oxide
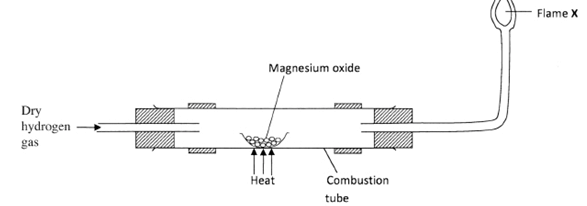
- State the observation that is made in the combustion tube. (1 mark)
- Explain the observation made in (a) above. (1 mark)
- What substance burns at flame X? (1 mark)
-
- Study the table below and fill in the blank spaces. The letters do not represent the actual symbols of the elements. (3 marks)
Atoms of
ElementsNumber of
ProtonsNumber of
ElectronsNumber of
NeutronsAtomic
massX - 12 12 - Y 8 - 8 - Z - 8 - 18 - Which atoms are isotopes of an element? (1 mark)
- Study the table below and fill in the blank spaces. The letters do not represent the actual symbols of the elements. (3 marks)
- Acids and bases are categorised as either strong or weak.
- What is meant by the term weak acid? (1 mark)
- Give one example of each of the following:
- strong alkali; (1 mark)
- strong acid. (1 mark)
- The electronic configurations of P and U (not actual symbols of elements) are shown below.
Use the information to answer the questions that follow.
P 2.8.2
U 2.6- What type of bond would be formed between P and U? (1 mark)
- Identify the type of bonds found in ammonium ion(NH) (2 marks)
- The diagram below represents a set-up that was used to electrolyse molten lead (II) iodide.
Use the diagram to answer the question that follows.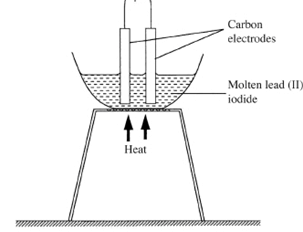
Why was molten lead (II) iodide used instead of solid lead (II) iodide. (2 marks) - The table below is a section of the periodic table. Use it to answer the questions that follow.
The letters do not represent the actual symbols of the elements.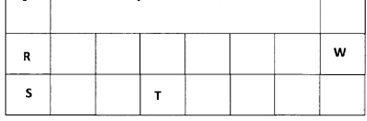
- How do the ionisation energies of R and S compare? Explain. (2 marks)
- Write the electronic configuration of W. (1 mark)
- To which group and period does element T belong?
- Group
- Period
-
- A student put lead (II) carbonate and lead (II) nitrate in separate test tubes and performed the tests as shown in the table below. Complete the table by giving the expected observations. (2 marks)
Salt Adding water Heating Lead(II) carbonate Lead(II) nitrate - State one use of calcium hydroxide. (1 mark)
- A student put lead (II) carbonate and lead (II) nitrate in separate test tubes and performed the tests as shown in the table below. Complete the table by giving the expected observations. (2 marks)
SECTION C: PHYSICS (33 marks)
Answer all the questions in this Section in the spaces provided.
- Figure 1 shows a burette containing some liquid after 8 g of the liquid was drained out. If the level of the liquid was initially at the 10 cm3 mark, determine the density of the liquid. (3 marks)
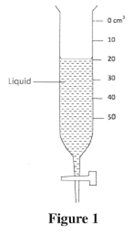
- When a drop of water is placed on a clean metal surface, it wets the surface. Explain this observation in terms of the forces involved. (3 marks)
- Figure 2 shows a simple mercury barometer set up in a physics laboratory.
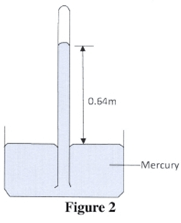
The height of the mercury column is 0.64 m. Given that the density of mercury is 13600 kgm-3 (3 marks) - A student in a room observed a beam of sunlight entering into the room from a hole on the roof. The student noted that dust particles illuminated by the beam were moving in random motion. Explain how this motion was caused. (2 marks)
- Figure 3 shows a glass container being used to heat a liquid. The wire gauze is placed between the container and the flame.
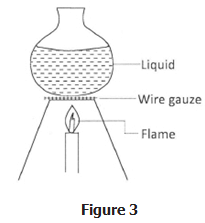
Explain how the wire gauze prevents the glass container from cracking. - State two properties of mercury that make it a suitable liquid for use in thermometers.
- Figure 4 shows a uniform plank of length 4 m and of weight 50 N. It is pivoted at a distance x from one end and balanced horizontally by a weight of 30 N.
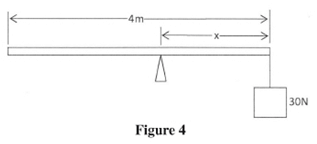
Determine the value of x. (3 marks) - Figure 5 shows a block of wood with a hollow part. The block is resting on a horizontal bench.
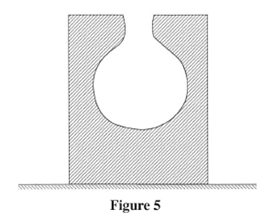
Explain the effect on the stability of the block when sand is used to fill the hollow section. (2 marks) - An object of weight 25 N extends a spring by 0.4 cm. Determine the weight of an object that would extend the spring by 0.96 cm. (3 marks)
- A car starts from rest and accelerates uniformly for 4 seconds. It attains a velocity of 15 ms-1 and maintains it for 3 seconds. Sketch a velocity time graph for the motion of the car within the 7 seconds. (3 marks)
- A body is pulled along a horizontal surface at a constant velocity. State two factors that affect friction between the body and the surface. (2 marks)
- State the energy changes that take place as a building block drops from the top of a building to the ground. (2 marks)
- Two copper spheres A and B of the same size are placed in a container. Sphere A is hollow while B is solid. When the container is filled with water, it is observed that A floats while B sinks. Explain this observation.

MARKING SCHEME
SECTION A : BIOLOGY
-
- The study of plants; (1 mark)
- It gives two names to an organism, generic and specific names; The generic name starts with a capital letter while the specific name starts with a small letter; the names should be underlined / or italicized; (2 marks)
-
-
- Directs/reflect light onto the specimen;
- Places desired objective lens into position; (2 marks)
- Tissue - a group of similar cells performing a function;
Organ system - a group of (connected) organs functioning as a unit; (2 marks)
-
-
- Movement of substances against concentration gradient across cell membranes using energy; (1 mark)
-
- Absorption of ions/mineral salts; (1 mark)
- Absorption of water; (1 mark)
-
- Small intestines/ileum; (1 mark)
- Provision of oxygen; (1 mark)
-
- Transparent / have no chlorophyll;
Thin/one cell thick; (2 marks) -
- Formation of blood; (1 mark)
- Formation of teeth and bones;
Participates in blood clotting. (1 mark)
- Transparent / have no chlorophyll;
-
- Low temperature; high humidity/high soil water;
Low wind velocity; low light intensity;
First two correct. (2 marks) -
- Defence; (1 mark)
- Participates in blood clotting; (1 mark)
- Low temperature; high humidity/high soil water;
-
- Bordetella pertussis; (1 mark)
-
- Diaphragm flattens;
- Rib cage is lifted upwards and outwards. (2 marks)
-
- Carbon dioxide; alcohol; energy;
First two correct. (2 marks) - Thin walled to reduce diffusion distance;
Numerous to increase surface area;
Moist to dissolve diffusing substances;
First two correct. (2 marks)
- Carbon dioxide; alcohol; energy;
-
- K - Bowman's capsule; (1 mark)
- Ultrafiltration; forces all small molecules into the Bowman's capsule; before useful ones can be re-absorbed back again. (2 marks)
-
- Failure of the pancreas to secret enough insulin/
Failure of the liver to convert glucose into glycogen;
leading to excess sugar in the blood; (2 marks) - When it is hot, sweat is produced on the skin;
The sweat uses heat from the body to evaporate thereby cooling the body;
(Latent heat of vaporisation)
- Failure of the pancreas to secret enough insulin/
SECTION B : CHEMISTRY (33 marks)
- Heat the mixture : ( 2) for ammonium chloride to sublime and collect the sublimate;: ( 2)
Add water to dissolve sodium chloride and decant / filter to obtain sand as the residue and sodium chloride solution; Evaporate sodium chloride solution to dryness : ( 2) to obtain sodium chloride crystals. : ( 2) (2 marks)
OR
Add water, filter off sand, carry out fractional crystallization, to obtain NaCl(s) filter off NaCl(s) (3 marks) -
- Curve I :
Curve I does not have definite temperature change / constant temperature change. : (1) - Melting point. : \ ( 1 2 mark)
- Curve I :
-
- Calcium hydrogen carbonate + Dilute hydrochloric acid → Calcium chloride + Carbon (IV) oxide + Water;: (1) (1 mark)
- Sulphuric (VI) acid. : (1) or sulphuric acid (1 mark)
-
- Oxygen / O2 : (1) (1 mark)
- Reaction slows down / less production of gas Q : (1)
Manganese (IV) oxide is a catalyst or increases rate of decomposition of hydrogen peroxide. : (1) (2 marks) - Gas Q slightly soluble in water. : (1)(1 mark)
-
- White magnesium oxide remains white. : (1) (1 mark)
Hydrogen is below magnesium in the reactivity series hence it can not reduce its oxide. : (1)
OR
Hydrogen is less reactive than magnesium, so it cannot reduce magnesium oxide. (1 mark) - Hydrogen gas/H2. : (1) (1 mark)
- White magnesium oxide remains white. : (1) (1 mark)
-
- (3 marks)
Atoms of
ElementsNumber of
ProtonsNumber of
ElectronsNumber of
NeutronsAtomic
massX 12 12 12 24 Y 8 8 8 16 Z 8 8 10 18 - Y and Z are isotopes : (1)(1 mark)
- (3 marks)
-
- Weak acid is one that does not ionize/dissociate completely in aqueous solution. : (1) (1 mark)
-
- Sodium hydroxide or potassium hydroxide. : (1) (1 mark)
- Sulphuric (VI) acid : (1) or Hydrochloric acid / Nitric (V) acid/Nitric acid or
Sulphuric acid. (Accept correct formulae) (1 mark)
-
- Ionic bond / Electrovalent : (1). (1 mark)
- Covalent bonds : (1)
Co-ordinate / Dative bond : (1) (2 marks)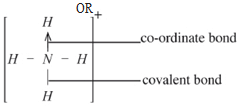
- In the molten lead (II) iodide, the ions are mobile : ( 2) hence conducts electricity : ( 2)while in solid lead (II) iodide, the ions are at fixed : (1 2) positions hence does not conduct electricity.: (1 2) (2 marks)
-
- Ionisation energy for R is higher than that of S : (1). R is smaller in size than S : (1 2) making outer electron in R more difficult to remove since nuclear attraction on outermost electrons in R is higher : ( 2). (2 marks)
- 2.8 : (1)
-
- Group 4
- Period 3 : (1 2)
-
- (2 marks)
Salt Adding water Heating Lead(II) carbonate Does not dissolve Forms yellow solid when hot turns reddish-brown solid on cooling Lead(II) nitrate Dissolves to form colourless solution Brown fumes produced
Yellow when hot, turns reddish-brown solid on cooling (any one observation) -
- Making builder's mortar and plaster : (1)
- In agriculture to reduce/prevent too much acidity
- Making bleaching powder
- For detecting Carbon (IV) oxide gas in laboratory
- In softening hard water
- In scrubbing in contact process (Any 1 correct)
- (2 marks)
SECTION C : PHYSICS
- Volume = 20 - 10 (1 mark)
= 10 cm3
Density = Mass
Volume
= 8
10
= 0.8 gcm-3 - The forces involved : are cohesive and adhesive forces :.
The adhesive forces between the water molecules and the metal surface is greater :
than the cohesive forces between water molecules.: - Pressure = h t g
= 640 # 1.36 x 104 x 10
1000
= 87040 Nm-2 - The large dust particles are being bombarded by the tiny air particles : , which are in continuous random motion. :
-
- The wire gauze prevents the glass from being heated at one point, :
- Since the wire gauze is a good conductor : it conducts the heat evenly : to a large area of the glass container.
-
- It is a good conductor of heat.
- It is visible (opaque).
- It has a wide range of temperature (high boiling point and low freezing point).
- It expands / contracts uniformly. (any two correct)
- Clockwise moment = Anticlockwise moment
30 × x = 50(2 - x)
30x = 100 - 50x
80x = 100
x = 1.25m - The Center of gravity is raised : thus reducing the stability : of the block.
- F = Kx K = 25
0.4
F = 25 # 0.96
0.4
= 60N -
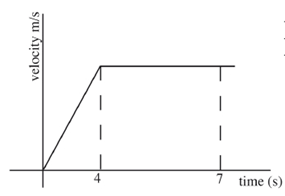
- labelled axis ✓
- accelerating for first 4 seconds
- uniform velocity between 4 seconds and 7 seconds
-
- The reaction force from the supporting surface. ✓
- Nature of the surfaces in contact. ✓
- Potential V → kinetic → sound/heat
-
- The sphere that floated was hollow while the other one was a solid sphere.
- The floating sphere experienced an upthrust equal to its own weight. ✓ The sinking sphere experienced an upthrust lower than its own weight. ✓
Download Kenya Certificate Of Secondary Education(KCSE 2013) General Science Paper 1 with Marking Scheme.
Tap Here to Download for 50/-
Get on WhatsApp for 50/-
Why download?
- ✔ To read offline at any time.
- ✔ To Print at your convenience
- ✔ Share Easily with Friends / Students

