INSTRUCTIONS TO CANDIDATES
- Write your name, class and admission number in the spaces provided above.
- Answer all questions in the spaces provided.
- This paper consists of Question 1 to 8
- Answer all questions in section A. Question 6 is compulsory, then choose either question 7 or 8.
- Students should check the question paper to ascertain that all the pages are printed as indicated and no questions are missing.
FOR EXAMINER’S USE ONLY
|
Question |
Maximum Score |
Candidate’s score |
|
1 |
8 |
|
|
2 |
8 |
|
|
3 |
8 |
|
|
4 |
8 |
|
|
5 |
8 |
|
|
6 |
8 |
|
|
7 |
20 |
|
|
8 |
20 |
|
QUESTIONS
SECTION A - 40 MARKS
-
- What is meant by the term Genetics. (1mk)
- State two examples of discontinuous variation in human beings. (2mks)
- A female with sickle cell trait marries a normal man. The allele for Sickle cell is Hbs and the normal allele HbA. Determine the probability that their first born will have sickle cell trait. Show your working. (5mks)
- Study the diagram below of the mammalian ear and answer the questions that follow.
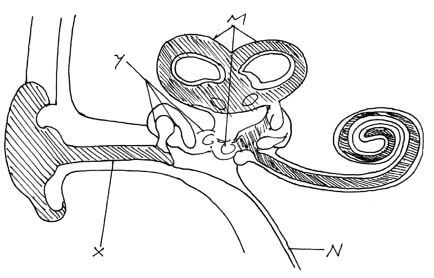
- Name the parts labeled X,Y and N. (3mks)
X
Y
N - State how the parts labeled Y are adapted to their functions. (2mks)
-
- Besides hearing, state one other function of the ear. (1mk)
- Which of the labeled parts is responsible for the function you have stated in c(i) above. (1mk)
- What would happen if the auditory nerve is completely damaged? (1mk)
- Name the parts labeled X,Y and N. (3mks)
- The diagram below represents a stage of growth in a seed during germination.
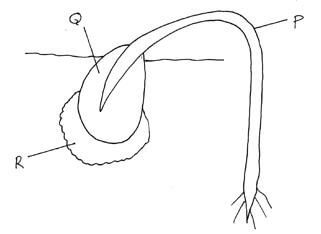
-
- Name the type of germination illustrated above. (1mk)
- Give a reason for your answer in a(i) above. (1mk)
- Name the part labeled R. (1mk)
- Give two functions of the part labeled Q. (2mks)
- Explain how part labeled P straightens. (3mks)
-
- Below is a diagram of structure found in Eukoryotic cells. Study it and answer the questions that follows.
- Identify the structure. (1mk)
- State two functions of the structure. (2mks)
-
- Name one organelle found in animal cells but absent in plant cell. (1mk)
- State one function of the organelle you have named in c(i) above. (1mk)
- State 3 properties of structure you have identified in (a) above. (3mks)
- The diagrams below represents a set up to investigate the conditions necessary for seed germination.
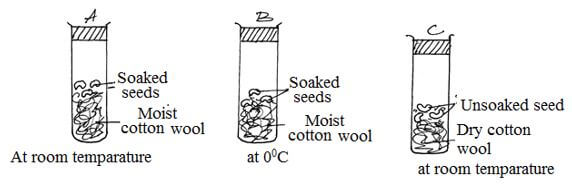
The set up was left for 7 days.- What conditions were being investigated in the experiment? (2mks)
- State three reasons for soaking seeds in set up A and B. (3mks)
- What were the expected results after seven days. (3mks)
- Set up A
- Set up B
- Set up C
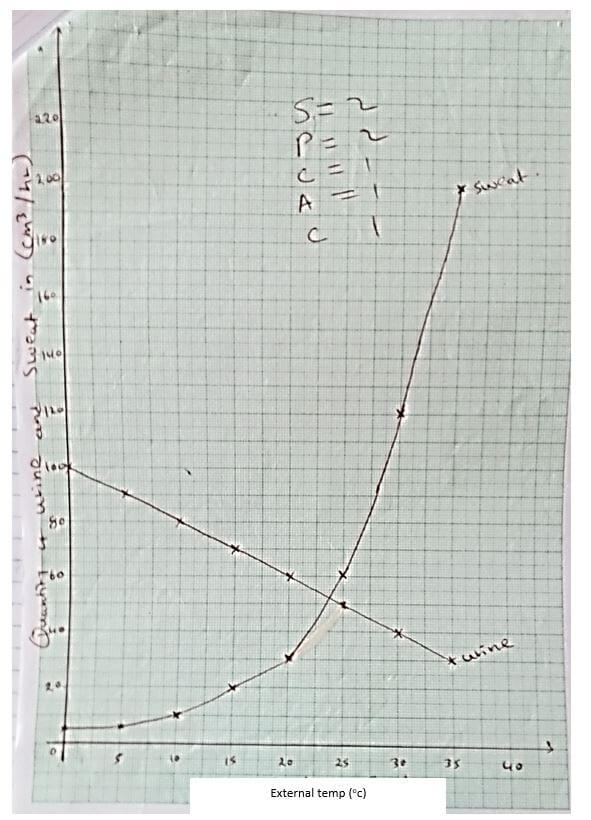
- The table below shows how quantities of sweat and urine vary with external temperatures.
External Temperature oC
Urine (cm3/hr)
Sweat cm3/hr
0
100
5
5
90
6
10
80
10
15
70
20
20
60
30
25
50
60
30
40
120
35
30
200
- Using the same axis, draw a graph of quantity of urine and sweat against the external temperature. (7mks)
-
- State the quantity of urine and sweat produced when external temperature was 12.5ºC. (2mks)
- State the physical process through which the body was cooled by sweating as temperature was rising. (1mk)
- Account for the quantity of urine produced as the temperature increased. (4mks)
- State the nitrogenous waste that could be eliminated in urine or sweat in human beings. (3mks)
- State three behavioural mechanism that poikilotherms use to regulate their body temperature under hot conditions. (3mks)
-
- Describe the process of double fertilization in flowering plants. (14mks)
- State the changes that occur in a flower after fertilization. (6mks)
-
- State the importance of locomotion in animals. (4mks)
- Describe the adaptations of the finned fish to locomotion. (16mks)
MARKING SCHEME
-
- Genetics – Branch of biology that deals with the study of inheritance and variation. (1mk)
-
- sex
- ABO blood group
- Toungue rolling
- free or attached earlobe
- Hairs in ear pinna / nose (2mks)
-
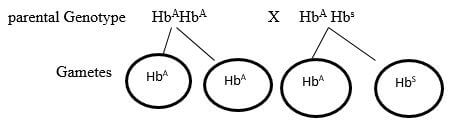
Probability of sickle cell trait (HbAHbs)Male / Female
HbA
HbA
HbA
HbAHbA
HbAHbA
Hbs
HbAHbs
HbAHbs
2⁄4 = ½; 0.5; 50%; (5mks)
-
- X – External auditory meatus;
Y – Ear ossicles;
N – Eustachian tube; - They are bony/solid and small forming a lever system that amplifies and transmits vibrations to the fenestra ovalis.
They are loosely held by suspensory ligaments which enables them to transmit vibrations;
NB: Mark any one. -
- Maintaining body balance / posture;
- M; NB: (ii) is tied to (i)
- Permanent deafness; rej. Deafness alone
lack of balance Mark any one
- X – External auditory meatus;
-
-
- Epigeal germination; (1mk)
- Hypocotyl grows faster pulling the cotyledons above the ground; (1mk)
- Seed coat; (1mk)
-
- protect the embryo; (1mk)
- food storage; (1mk)
- Exposure of the curved part to light stimulates migration of auxin to the lower side; higher concentration of auxin on the lower side stimulates faster cell elongation; on the lower side than on the upper side; and this causes P to straighten. (3mks)
-
-
- Cell membrane;
-
- It encloses cell contents;
- It selectively allows materials in and out of the cell;
-
- Centriole;
- Take part in formation of cilia and flagella.
Take part in formation of spindle fibres during cell division
-
- Sensitive to changes in temperature and pH
- Posses electric charges / polarized
- Semi-permeability
-
- Water; acc moisture
Temperature; acc warmth (2mks) - Mobilise / Activate enzymes / hydrolyse stored food / breaking of dormancy;
softens the testa / seed coat;
acts as a solvent / medium of transport; (3mks) -
- Those in set up A will geminate; (1mk)
- Those in set up B will not geminate; (1mk)
- Those in set up C will not germinate; (1mk)
- Water; acc moisture
-
- On graph paper. (7mks)
-
- Urine 74 cm3 / hr ± 1
Sweat 14cm3 / hr ±1 (2mks) - Evaporation (1mk)
- An increase in external temperature decreases the amount of urine produced; this is due to increased sweating; which increases osmotic pressure of blood; hence more water is reabsorbed back into the blood stream at the kidney tubules. (4mks)
- Urine 74 cm3 / hr ± 1
- Urea
- Uric acid (3mks)
- Ammonia
-
- Aestivation
- Staying under shaded places. (3mks)
- Borrowing underground.
-
-
- pollen grains land and stick onto the stigma; stigma secretes / produces a sticky fluid; that causes pollen grains to adhere onto it.
- Sticky secretion also stimulates the pollen grain to germinate; into a pollen tube;
- The pollen tube grows into the stigma and protrudes down the style tissues;
- The pollen tube denies its nutrition from style tissues
- As the tube grows downwards, the tube nucleus occupies the position just behind the tip;
- The generative nucleus then enters the tube and divides mitotically; to give a pair of male gamete nuclei; which follow the tube nucleus and the pollen tube grows further doen the style.
- On reaching the ovary, the pollen tube enters the ovule through the microphle;
- It bursts open;
- The vegetative (tube) nucleus disintegrates; leaving a clear passage for the two male gamete nuclei.
- One male gamete fuses with the functional egg cell; to form a diploid zygote;
- The other fuses with the two polar nuclei; to form a triploid nucleus; called primary endosperm nucleus;
-
- Zygote (divides mitotically) and forms the embryo; Embryo differentiates into plumule and radicle; primary endosperm nucleus (divides mitotically) and becomes the endosperm (for food storage);
- integuments become the seed coat;
- antipodal nuclei and synergids disintegrate;
- ovules become seeds;
- ovary wall becomes the pericarp;
- stigma and style dry up leaving a scar;
- corolla dries up;
- calyx may dry up or persist;
-
-
-
- Searching for food / mates / shelter, (4mks)
- Migration away from unfavourable conditions/ environments;
- Escape from predators / enemies;
- Colonization of new areas;
-
- Vertebral column consists of a series of vertebrae; held together loosely so that its flexible;
- Myotomes / muscles; associated with vertebral column contract and relax to produce movement;
- The sideways and backwards thrust of the tail and body against water, result in resistance of the water pushing the fish sideways;
- Head is inflexible; to maintain the forward thrust;
- Body streamlined; to reduce resistance;
- Presence of fins; for forward movement / balance in water;
- Presence of swim bladder; make fish buoyant;
- Scales tip towards the back; provide smooth surface to reduce resistance (friction);
- Body covered with mucus making it slippery; hence reducing friction during movement in water.
18 marks, max 16 marks
-
Download Biology Paper 2 Questions and Answers - Mincks Group of Schools Mock Examinations 2022.
Tap Here to Download for 50/-
Get on WhatsApp for 50/-
Why download?
- ✔ To read offline at any time.
- ✔ To Print at your convenience
- ✔ Share Easily with Friends / Students
