QUESTIONS
- The scheme below was used to prepare a cleansing agent. Study it and answer the questions that follow
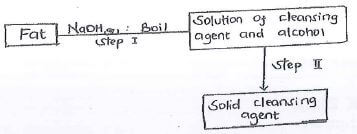
- What name is given to the type of cleansing agent prepared by the method above? (1mk)
-
- Name one chemical substance added in step II (1 mk)
- What is the purpose of adding the chemical substance named in (b) (1) above. (1mk)
- Describe the cleansing action of soap on dirt. (2 mks)
-
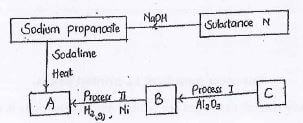
- Identify the following substances. (2mks)
N ...............................................
B ...............................................
A ...............................................
C ............................................... - To which homologous series does substance N belong? (1mks)
- Write the correct name and formula of the organic product formed when compound B reacts with ethanol. (2mks)
- Explain how you would distinguish between C2H5OH and CH3COOH (1mk)
- Identify the following substances. (2mks)
-
- In an experiment to determine the molar heat of neutralization, 50cm of 1M hydrochloric acid was neutralized by adding dilute sodium hydroxide. During the experiment, the data in the table below was obtained.
Volume of NaOH (cm) 0 10 20 30 40 50 60 Temp of the mixture (°C) 25 27 29 31 31 30 29 - On the grid provided, plot a graph of temperature against volume of sodium hydroxide. (3mks)

- Determine from the graph
- Volume of NaOH which completely neutralized the acid. (1mk)
- Change in temperature when complete neutralization occurred. (1mk)
- Calculate the molar heat of neutralization of HCI with NaOH (Shc=4.2J//k, density of solution =1g/cm3) (3mks)
- On the grid provided, plot a graph of temperature against volume of sodium hydroxide. (3mks)
- Study the graph below which shows how the concentration differ in the following dynamic equilibrium.
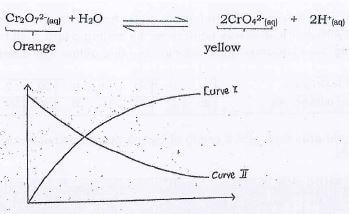
- Define the term dynamic equilibrium (1mk)
- Which of the two curves represents the concentration of Cr2O72-? (2mks)
- State and explain the observation that would be made if 1cm3 of sodium hydroxide was added to the equilibrium mixture represented above. (2mks)
- State and explain how the rate of reaction between zinc granules and steam can be increased. (2mks)
- In an experiment to determine the molar heat of neutralization, 50cm of 1M hydrochloric acid was neutralized by adding dilute sodium hydroxide. During the experiment, the data in the table below was obtained.
-
- Study the standard reduction potentials below and answer the questions that follow; the letters are not the actual symbols of the elements.
Half Cell E volts P2+(aq) + 2e- -> P(s) -0.76 R2+(aq) + 2e- -> R(s) -2.37 S+(aq) + 1e- -> S(s) +0.84 T2+(aq) + 2e- -> T(s) -0.14 - Select the element which is the strongest reducing agent. Explain (2mks)
- Select two half cells when combined would produce the largest e.m.f. (1mk)
- Calculate the e.m.f of the electrochemical cell formed when the two half cells in (II) above are combined. (1mk)
- 1.9g of a metal F was deposited when its aqueous salt was electrolyzed by passing a current of 0.6A for 1.5hours. Determine
- The electrode at which metal F was deposited. (1 mk)
- The oxidation state of F (RAM of F =113; IF=96,500C) (2mks)
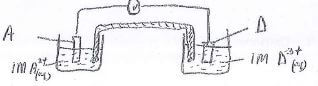
- Draw an electrochemical cell comprising of the following half cells A2+(aq) + 2e- A(s),-0.76V and D3+ + e- D2+(aq) + 0.77V (3ks)
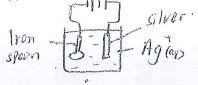
- An iron spoon is to be electroplated using silver. Draw a well labeled diagram to represent the apparatus that could be used to carry out this process. (3mks)
- Study the standard reduction potentials below and answer the questions that follow; the letters are not the actual symbols of the elements.
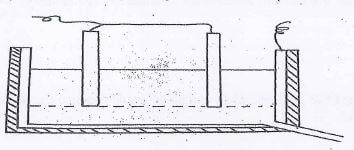
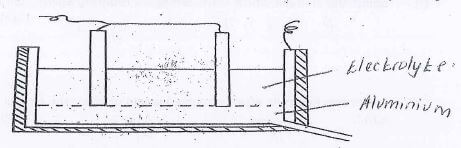
- The extraction of aluminum from its ore takes place in two stages. Purification stage and electrolysis stage. Below is set-up for the electrolysis stage.
-
- Name the chief ore from which aluminium is extracted. (1mk)
- Name one Impurity which is removed at the purification stage. (1mk)
-
- Label on the diagram each of the following
- Region containing electrolyte
- Molten aluminium
- The melting point of aluminium oxide is 2054°C but the electrolysis is carried out between 800°C and 900°C. Explain how this is achieved. (1 mk)
- Label on the diagram each of the following
- Write balanced half lonic equations for the reactions taking place in the electrode (2mks)
- Anode
- Cathode
- A current of 3A was passed through fused aluminium oxide for 10 minutes. Calculate the mass of aluminium obtained at one electrode (Al -27.0, IF: 96500C) (2mks)
-
-
- Aluminium oxide is amphoteric and Insoluble in water.
- What do you understand by the term amphoteric oxide? (1 mk)
- Using equations describe how aluminium oxide is amphoteric (2mks)
- Two different samples of water (I and II) were tested with soap solution. Sample II was further subjected to two other processes before adding soap. 20cm of each sample of water was shaken with soap solution in a boiling tube until a permanent lather was obtained. The results are shown in the table below.
Water sample Volume of soap solution needed (cm3) Before boiling After boiling II 10 5 II 6 6 After filtering 6 6 II after distilling 2 2 - Identify the water sample that had temporary hardness. Explain your answer. (1mk)
- Explain why the results for sample II are different after distilling but remain unchanged after filtering. (1mk)
- Study the information in the table below and answer the questions that follow.
A mixture containing 35g of CuSO, and 78g of Pb(NO3)2 In 100g of water at 60°C was cooled to 40°C.Salt Solubility (g/100g water) At 40ºC At 60ºC CuSO4 28 38 Pb(NO3)2 79 98 - Which salt crystallised out? Give a reason (2mks)
- Calculate the mass of the slat that crystallised out. (1mk)
- Below is a flow chart diagram for the contact process for the manufacture of sulphuric (IV) acid.
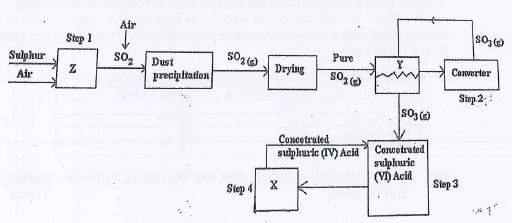
- Other than sulphur state another substance that can be used. (1mk)
- Both platinum and vanadium (V) oxide can be used as catalyst, explain why vanadium (V) oxide is preferred over platinum in the process. (1mk)
- State two precautionary measure taken to prevent pollution by the contact process. (1mk)
- Write the balanced equations for the reaction in (2mks)
- Step 2
- Step 4
- Complete the table below to show the observation made and property when concentrated sulphuric (VI) acid is added to the following substances. (2mks)
Substance Observation Property of acid Sugar Potassium Nitrate crystals
- Aluminium oxide is amphoteric and Insoluble in water.
-
- Define the term half-life. (1mk)
- 50g of a radioisotope 23191 Pa reduced to 6.25g after 45.5 days. Determine the half-life of 23391 Pa (2mks)
- Complete the nuclear equation below.
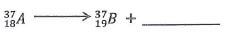
- State one danger associated with radioactivity. (1mk)
-
- Study the information given in the table below and answer the questions that follow.
Element Atomic No. Boiling point (K) Atomic radi J 11 1163 0.158 K 13 2743 0.126 L 16 718 0.104 M 17 238 0.099 N 19 147 0.231 - Write the electron arrangements for the lons formed by K and M. (1mk)
- Which two elements have similar chemical properties? Explain (1mk)
- Select an element which is in gaseous state at room temperature. (1mk)
- In terms of structure and bonding, explain why Khas a very high boiling point. (2mks)
- Explain why the atomic radius of J is greater than that of K. (2mks)
- A carbonate Treacts completely with dilute hydrochloric acid according to the equation below.
TCO3(s) + 2HCl(aq) TCL2(aq) + CO2(g) + H2O(l)
If 1g of the carbonate reacts completely with 20cm of 1MHCI, calculate the relative atomic mass of T. (C=12, 0=16) (3mks) - Two miscibles liquids S and T whose boiling points are 60°C and 84°C respectively got mixed together accidentally.
- Suggest a method you would use to separate the two liquids. (1mk)
- Which liquid will be collected first? Give a reason. (1mk)
- Give one industrial application of the method in (a) above. (1mk)
- Study the information given in the table below and answer the questions that follow.
MARKING SCHEME
- The scheme below was used to prepare a cleansing agent. Study it and answer the questions that follow

- What name is given to the type of cleansing agent prepared by the method above? (1mk)
soapy detergent -
- Name one chemical substance added in step II (1 mk)
sodium chloride - What is the purpose of adding the chemical substance named in (b) (1) above. (1mk)
to precipitate soap
- Name one chemical substance added in step II (1 mk)
- Describe the cleansing action of soap on dirt. (2 mks)
The soap has a polar head and non-polar tail. The polar head is attracted to the water and the non-polar tail to the grease dirt. After aggitation the dirt/grease is removed from the cloth. -

- Identify the following substances. (2mks)
N propanoic acid
B ethene
A ethane
C ethene - To which homologous series does substance N belong? (1mks)
alkanoic acids - Write the correct name and formula of the organic product formed when compound B reacts with ethanol. (2mks)
CH3CH3COOH(aq) + C2H5OH(aq) → CH3CH3COOC2H5(aq) + H2O(l) - Explain how you would distinguish between C2H5OH and CH3COOH (1mk)
Add Mg/Na2CO3. in C2H5OH; no effervescence in CH3COOH there is effervescence
- Identify the following substances. (2mks)
- What name is given to the type of cleansing agent prepared by the method above? (1mk)
-
- In an experiment to determine the molar heat of neutralization, 50cm of 1M hydrochloric acid was neutralized by adding dilute sodium hydroxide. During the experiment, the data in the table below was obtained.
Volume of NaOH (cm) 0 10 20 30 40 50 60 Temp of the mixture (°C) 25 27 29 31 31 30 29 - On the grid provided, plot a graph of temperature against volume of sodium hydroxide. (3mks)

- Determine from the graph
- Volume of NaOH which completely neutralized the acid. (1mk)
35cm3 - Change in temperature when complete neutralization occurred. (1mk)
35 - 25 = 10ºC - Calculate the molar heat of neutralization of HCI with NaOH (Shc=4.2J//k, density of solution =1g/cm3) (3mks)
ΔH = mcΔT
= 0.085 kg x 4.2 x 10
= 3.5700J
50 + 35 = 85
moles = 1 x 0.05
= 0.05
3.570 -> 0.05
? = 1
3570 x 1
0.05
= 714 KJ/mol
- Volume of NaOH which completely neutralized the acid. (1mk)
- On the grid provided, plot a graph of temperature against volume of sodium hydroxide. (3mks)
- Study the graph below which shows how the concentration differ in the following dynamic equilibrium.

- Define the term dynamic equilibrium (1mk)
The state at which the foward and the backward reactions are taking place at the same rate - Which of the two curves represents the concentration of Cr2O72-? (2mks)
Curve II - State and explain the observation that would be made if 1cm3 of sodium hydroxide was added to the equilibrium mixture represented above. (2mks)
the yellow colour intensifies; equilibrium shifts to the right. This is to replace the H+ ions that reacted with NaOH - State and explain how the rate of reaction between zinc granules and steam can be increased. (2mks)
increasing the temperature
this increases the kinetic energy of the reacting particles , increasing the reaction rate
- Define the term dynamic equilibrium (1mk)
- In an experiment to determine the molar heat of neutralization, 50cm of 1M hydrochloric acid was neutralized by adding dilute sodium hydroxide. During the experiment, the data in the table below was obtained.
-
- Study the standard reduction potentials below and answer the questions that follow; the letters are not the actual symbols of the elements.
Half Cell E volts P2+(aq) + 2e- -> P(s) -0.76 R2+(aq) + 2e- -> R(s) -2.37 S+(aq) + 1e- -> S(s) +0.84 T2+(aq) + 2e- -> T(s) -0.14 - Select the element which is the strongest reducing agent. Explain (2mks)
p it is the most negative - Select two half cells when combined would produce the largest e.m.f. (1mk)
p/p2+ and s/s+ - Calculate the e.m.f of the electrochemical cell formed when the two half cells in (II) above are combined. (1mk)
0.84 + 0.76 = 1.60v
- Select the element which is the strongest reducing agent. Explain (2mks)
- 1.9g of a metal F was deposited when its aqueous salt was electrolyzed by passing a current of 0.6A for 1.5hours. Determine
- The electrode at which metal F was deposited. (1 mk)
cathode - The oxidation state of F (RAM of F =113; IF=96,500C) (2mks)
0.6 x 60 x 60 x 15 = 3.240c
1.5g -> 3240c
113 -> ?
113 x 3240
1.5
= 244.080c
If = 96,500c
? = 244,080
244080
96500
2.5 = 3
+ 3
- The electrode at which metal F was deposited. (1 mk)
- Draw an electrochemical cell comprising of the following half cells A2+(aq) + 2e- A(s),-0.76V and D3+ + e- D2+(aq) + 0.77V (3ks)
- An iron spoon is to be electroplated using silver. Draw a well labeled diagram to represent the apparatus that could be used to carry out this process. (3mks)
- Study the standard reduction potentials below and answer the questions that follow; the letters are not the actual symbols of the elements.
- The extraction of aluminum from its ore takes place in two stages. Purification stage and electrolysis stage. Below is set-up for the electrolysis stage.
-
- Name the chief ore from which aluminium is extracted. (1mk)
bauxite - Name one Impurity which is removed at the purification stage. (1mk)
iron(iv) oxide
silicon (iv) oxide
- Name the chief ore from which aluminium is extracted. (1mk)
-
- Label on the diagram each of the following
- Region containing electrolyte
- Molten aluminium
- The melting point of aluminium oxide is 2054°C but the electrolysis is carried out between 800°C and 900°C. Explain how this is achieved. (1 mk)
adding an impurity ; cryolite
- Label on the diagram each of the following
- Write balanced half lonic equations for the reactions taking place in the electrode (2mks)
- Anode
- Cathode
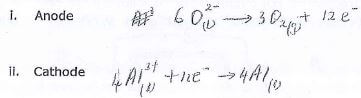
- A current of 3A was passed through fused aluminium oxide for 10 minutes. Calculate the mass of aluminium obtained at one electrode (Al -27.0, IF: 96500C) (2mks)
3 x 10 x 60 = 1800c
3f -> mole of A1
1 mole -> 3 x 96500
27 -> 289,500c
? -> 1800c
27 x 1800
289500
= 0.168 g
-
-
- Aluminium oxide is amphoteric and Insoluble in water.
- What do you understand by the term amphoteric oxide? (1 mk)
has both acidic and basic nature/properties - Using equations describe how aluminium oxide is amphoteric (2mks)
Al2O3(s) + 6HCl(aq) -> 2AlCl3(aq) + 3H2O(l)
2NaOH + Al2O3 -> 2Na. AlO2 + H2O - Two different samples of water (I and II) were tested with soap solution. Sample II was further subjected to two other processes before adding soap. 20cm of each sample of water was shaken with soap solution in a boiling tube until a permanent lather was obtained. The results are shown in the table below.
Water sample Volume of soap solution needed (cm3) Before boiling After boiling II 10 5 II 6 6 After filtering 6 6 II after distilling 2 2 - Identify the water sample that had temporary hardness. Explain your answer. (1mk)
- Explain why the results for sample II are different after distilling but remain unchanged after filtering. (1mk)
the ions causing water hardness were removed
- Study the information in the table below and answer the questions that follow.
A mixture containing 35g of CuSO, and 78g of Pb(NO3)2 In 100g of water at 60°C was cooled to 40°C.Salt Solubility (g/100g water) At 40ºC At 60ºC CuSO4 28 38 Pb(NO3)2 79 98 - Which salt crystallised out? Give a reason (2mks)
CuSO4
Its solubility at 40ºC is 28g/100g of water - Calculate the mass of the slat that crystallised out. (1mk)
35 - 28 = 7g
- Which salt crystallised out? Give a reason (2mks)
- What do you understand by the term amphoteric oxide? (1 mk)
- Below is a flow chart diagram for the contact process for the manufacture of sulphuric (IV) acid.

- Other than sulphur state another substance that can be used. (1mk)
iron (ii) sulphide - Both platinum and vanadium (V) oxide can be used as catalyst, explain why vanadium (V) oxide is preferred over platinum in the process. (1mk)
it is not easily poisoned by impurities
it is cheap - State two precautionary measure taken to prevent pollution by the contact process. (1mk)
building / constructing long chimneys lines with Ca(OH)2
Recycling SO2 - Write the balanced equations for the reaction in (2mks)
- Step 2
2SO2(g) + O2(g) → 2SO3(g) - Step 4
H2S2O7(l) + H2O(l) → 2H2SO4(l)
- Step 2
- Complete the table below to show the observation made and property when concentrated sulphuric (VI) acid is added to the following substances. (2mks)
Substance Observation Property of acid Sugar change from white to black dehydrating Potassium Nitrate crystals from crystals to powder dehydration
- Other than sulphur state another substance that can be used. (1mk)
- Aluminium oxide is amphoteric and Insoluble in water.
-
- Define the term half-life. (1mk)
this is the time taken for a given mass of or number of nuclides to decay to half its original mass - 50g of a radioisotope 23191 Pa reduced to 6.25g after 45.5 days. Determine the half-life of 23391 Pa (2mks)
50g ______________ 25g_____________12.5g_______________________6.25
45.5 days ÷ 3
= 15.167
= 15.2 days - Complete the nuclear equation below.
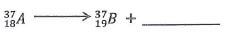
- State one danger associated with radioactivity. (1mk)
causes death
- Define the term half-life. (1mk)
-
- Study the information given in the table below and answer the questions that follow.
Element Atomic No. Boiling point (K) Atomic radi J 11 2,8,1 1163 0.158 K 13 2,8,3 2743 0.126 L 16 2,8,6 718 0.104 M 17 2,8,7 238 0.099 N 19 2,8,8,1 147 0.231 - Write the electron arrangements for the lons formed by K and M. (1mk)
k 2,8
m 2,8,8 - Which two elements have similar chemical properties? Explain (1mk)
J & N - Select an element which is in gaseous state at room temperature. (1mk)
M - In terms of structure and bonding, explain why K has a very high boiling point. (2mks)
strong metallic bonds and giant mettalic structure - Explain why the atomic radius of J is greater than that of K. (2mks)
J has less protons than k, hence weaker nuclear attraction than k
- Write the electron arrangements for the lons formed by K and M. (1mk)
- A carbonate Treacts completely with dilute hydrochloric acid according to the equation below.
TCO3(s) + 2HCl(aq) TCL2(aq) + CO2(g) + H2O(l)
If 1g of the carbonate reacts completely with 20cm of 1MHCI, calculate the relative atomic mass of T. (C=12, 0=16) (3mks)
= 0.01 moles - Two miscibles liquids S and T whose boiling points are 60°C and 84°C respectively got mixed together accidentally.
- Suggest a method you would use to separate the two liquids. (1mk)
fractional distillation - Which liquid will be collected first? Give a reason. (1mk)
s lower boiling point than T - Give one industrial application of the method in (a) above. (1mk)
separation of crude oil
obtaining oxygen from air
- Suggest a method you would use to separate the two liquids. (1mk)
- Study the information given in the table below and answer the questions that follow.
Join our whatsapp group for latest updates
Tap Here to Download for 50/-
Get on WhatsApp for 50/-
Download Chemistry Paper 2 Questions and Answers - Mangu High School Mock Exams 2022.
Tap Here to Download for 50/-
Get on WhatsApp for 50/-
Why download?
- ✔ To read offline at any time.
- ✔ To Print at your convenience
- ✔ Share Easily with Friends / Students
