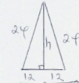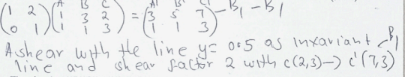Instructions to candidates
- This paper consists of two sections: Section I and Section II.
- Answer all questions in section I and only five questions from section II.
- Show all the steps in your calculations, giving the answers at each stage in the spaces provided below each question.
- Marks may be given for correct working even if the answer is wrong.
- Non-programmable silent electronic calculators and KNEC mathematical tables may be used, except where stated otherwise.
- Candidates should answer the questions in English.
SECTION I (50 Marks)
- Solve the following equations (3mks)
2x + y = 5
− x2 + y + 2x = 1 - Find the percentage error in the volume of a cone whose radius is 7.0 cm and has an exact vertical height of 18cm. (3 mks)
- Solve the equation, 2 cos 2x = 3 sin x for 0 ≤ x ≤ 360 (3mks)
- Simplify without using tables or calculator (3mks)
Sin 480° − Cos 765°
tan 225° − cos (−330°) - Without using mathematical tables or a calculator, solve the equation . (3 marks)
2log10x - 3log102 = 1 − log105 - A businessman invested ksh 1,000,000 in a fixed deposit account that pays 12% per annum compound interest, every 2 month. Calculate the number of years his amount will be Ksh 1,126,162.42 (3marks)
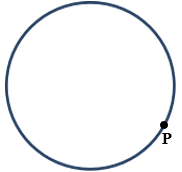
- Using the properties of chords and tangents, construct a tangent touching point P on the circumference of the circle below showing clearly the centre of the circle. (3marks)
- In a soccer competition, the number of goals (G) scored in penalty kicks is partly constant and partly varies as the skill (S) of the player. Given that G = 8 when S = 2 and G = 12 when S = 4, find the value of G when S = 6. (3 marks)
- The position vector of A is OA = i − 3j − 3k and that of B is OB= 3i − j + 2k. A point N divides AB externally in the ratio 3:1. Find the magnitude of ON. (3marks)
-
- Expand (3x − y)5 up to the fourth term. (2marks)
- Use the expansion to evaluate (2marks)
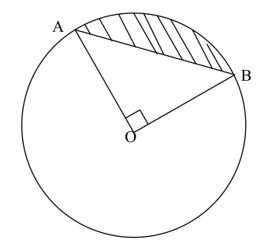
- The figure below shows a circle Centre O, radius 7cm. Angle AOB= . If a point is selected at random inside the circle, find the probability that it lies in the shaded region. (3marks)
- The mass of a mixture P of beans and maize is 72kgs. The ratio of beans to maize is 3:5. A second mixture R of maize and beans of mass 98kg is mixed with P. The final ratio of beans to maize is 8:9 respectively. Find the ratio of beans to maize in R. (3marks)
- A curve has a turning point at the point (1,1). Given that the gradient function of the curve is 6x2 + ax − 12, find the value of a and the equation of the curve. (3 marks)
- Find the area bounded by the curve y = x2 − x − 2 , x =− 3, x = 2 and the x-axis (4marks)
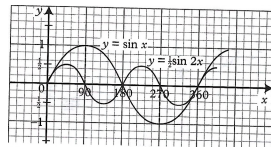
- Study the figure below hence describe transformation mapping the wave y = sin x to y = 1/2 sin 2x (2mks)
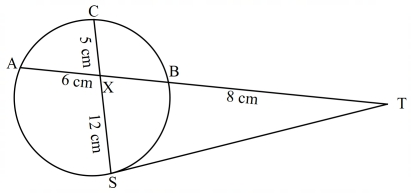
- In the figure below, ST is a tangent to the circle at S. AXBT and CXS are straight lines.
Find;- The length of XB. (2 marks)
- The size of angle STX. (2 marks)
SECTION B – 50MARKS
- X and Yare two points on the earth’s surface and on latitude 30°N. The two points are on the longitude
40 °W and 140°E respectively (Take π = 22/7 and radius of the earth R = 6370km) Calculate:- The distance from X to Y along a parallel of latitude in kilometres. (3marks)
- The shortest distance from X to Y along a great circle in kilometres (4mks)
- If the local time at Y is 8.00am on Wednesday, What is the day and the local time at X in 24 hours system. (3mks)
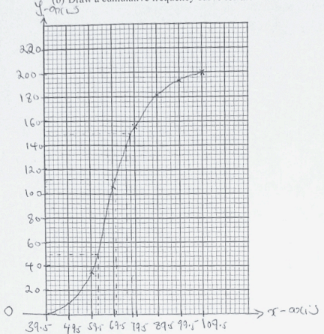
- The table below shows the masses measured to the nearest Kg of 200 people.
Mass kg 40-49 50-59 60-69 70-79 80-89 90-99 100-109 No. of people 9 27 70 50 26 12 6 - Draw a cumulative frequency curve for the data above. (4 marks
- Use your graph to estimate
- The median mass. (1mark)
- The number of people whose mass lies between 70.5 kg and 75.5 kg (1 mark)
- From your graph find
- The lower quartile (1 mark)
- The upper quartile (1 mark)
- The interquartile range (2 marks)
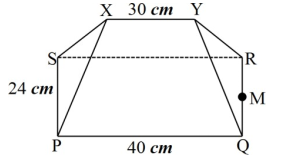
The figure above shows the model of a roof with rectangular base PQRS. PQ= 40 cm and PS= 24 cm. The ridge XY = 30 cm and is centrally placed. The faces PSX and QRY are equilateral triangles. M is the midpoint of QR.
Calculate correct to 2 decimal places the:- Perpendicular distance of XY from the plane PQRS (3 marks)
- Angle between SX and PQRS (4 marks)
- Angle between planes RSXY and QPXY (4 marks)
- The principal of mazuri high school intends to spend not more than ksh 18,000 to transport minimum of 70 students to the county games using two matatus A and B. Matatu A has a passenger capacity of 10 and B a capacity of 30.The cost per trip for matatu A is ksh 2000 and that of matatu B is ksh 3000. Given that A makes less than 5 trips.Taking trips made by matatu A be x while trips made by matatu B be y
- Write down all the inequalities to represent the above information. (4marks)
- Use the grid below to represent the above information. (4mks)
- Find the number of trips that each matatu should make to minimize the amount of money the school will spend. (2mks)
-
- A quantity p varies directly as the square of q and inversely as the square root of r. If q increases by 20% and r decreases by 36%, find the percentage change in p. (3 marks)
- The velocity of water flowing through a pipe is inversely proportional to the square of the radius of the pipe. If the velocity of the water is 30cm/s when the radius of the pipe is 2cm. Find the velocity of water when the radius of the pipe is 4cm. (3 marks)
- Three quantities X and Y and Z are such that X varies partly as Y and partly as the inverse of the square of Z. When X= 6, Y= 3 and Z = 2.When X = 8,Y=5 and Z = 1.Find the value of X when Y = 10 and Z = 8 (4mks)
-
- Complete the table below for the function y = x3 − 3x2 − 5x + 7 . (2 marks)
x −3 −2 −1 0 1 2 3 4 5 y - On the grid provided, draw the graph of y = x3 − 3x2 − 5x + 7 for −3 ≤ x ≤ 5 . (3 marks)
- Use your graph to solve the equation x3 − 3x2 − 5x + 7 = 0 (2 mks)
- By drawing a suitable line, use the graph in (b) to solve the equation x3 − 3x2 − 10x + 17 = 0
(3 marks)
- Complete the table below for the function y = x3 − 3x2 − 5x + 7 . (2 marks)
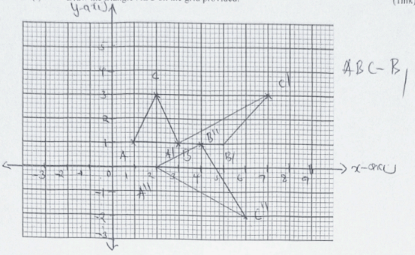
- A triangle with vertices A(1,1),B(3,1) and C(2,3) undergoes a transformation represented by the matrix
to A’B’C’.
- Draw the triangle ABC on the grid provided. (1mk)
- Calculate the coordinates of A’B’C’ and draw it on the grid hence describe the transformation that maps ABC to A’B’C’. (3mks)
- The triangle A’’B’’C’’ A’’(2,0) ,B’’(6,−2) and C’’(4,1) is the image of triangle ABC.
- Draw triangle A’’B’’C’’ on the grid provided. (1mark)
- Find the matrix of transformation that maps A’’B’’C’’ to ABC. (3marks)
- Triangle DEF area 60cm2 undergoes transformation represented by the transformation matrix
. Find area of the image of triangle DEF. (2marks)
-
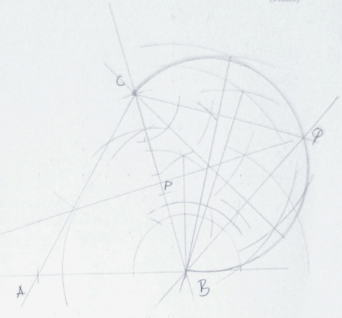
- Using a ruler and a pair of compass only, construct a triangle ABC in which AB=6cm, BC = 7cm and angle ABC = 75° (3mks)
Measure:- Length of AC (1mark)
- Angle ACB (1mark)
- Locus of P is such that BP = PC. Construct P (2marks)
- Construct the locus of Q such that Q is on one side of BC, opposite A and angle BQC = 60° (3mks)
- Using a ruler and a pair of compass only, construct a triangle ABC in which AB=6cm, BC = 7cm and angle ABC = 75° (3mks)
MARKING SCHEME
- Y = 5 − 2X
− x2 + 5 − 2x + 2x = 1
−x2 = −4
x = ± 2
x = −2
y = 5 − 2x − 2
= 9
x = 2
y = 5 − 2 × 2
= 1
x = 2, y = 1, x = −2, y = 9 - Actual = 7.0 × 7.0 × 18
= 882
Max = 7.05 × 7.05 × 18
= 894.645
Min = 6.95 × 6.95 × 18
=869.445
Absolute Error = 894.645 − 869.445
2
= 12.6
%Error = 12.6 × 100
882
= 1.429% or 13/7% - 2(1 − Sin2x) = 3 sin x
2y2 + 3y − 2 = 0
2y(y+2) − 1(y+2) = 0
(y+2) (2y−1) = 0
y = 1/2 or −2
⇒ Sin x = 1/2
x = 30,150 -
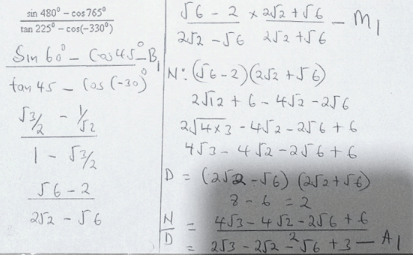
- log10 (5x2) = 1
8
5x2 = 10
8
80 = 5x2
16 = x2
x = ±4 - 1, 126, 162.42 = 1,000,000 (1 + 2/100)n
1.12616242 = (1.02)n
n = log 1.12616242
log 1.02
n = 6
= 1 year - 8 = k + 2m .....(i)
12 = k + 4m ....(ii)
−4 = −2m
m = 2
k = 8 − 2m
= 8 − 2 × 2
k = 4
G = 4 + 25
S = 6
G = 4 + 2 × 6
= 4 + 12
G = 16 -
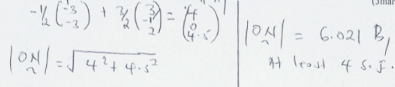
-
- (3x)5 − (3x)4(y) + (3x)3(y)2 − (3x)2(y)3
243x5 − 405x4y + 270x3y2 − 90x2y3 - (3 − 0.02)5 = 3x − y)5
3 = 3x
x = 1
− 0.02 = − y
y = 0.02
243 × 1 − 405 × 0.02 + 270 × (0.02)2 + 90(0.02)3
243 − 8.1 + 0.108 − 0.00072
= 235.000728 At least 4s.f
- (3x)5 − (3x)4(y) + (3x)3(y)2 − (3x)2(y)3
- AC = 22/7 × 72 = 154
1/4 × 22/7 × 72 = 38.5
1/2 × 7 × 7 = 24.5
14.0
p(s) = 14/154 = 1/11 - In P
maize = 5/9 × 72 = 45kg
beans = 3/8 × 72 = 27kg
72 + 98 = 170 − P & R
beans = 8/17 × 170 = 80kg
maize = 9/17 × 170 = 90kg
80 − 27 = 53
90 − 45 = 45
53 : 45 - 6x2 + ax − 12 = 0
x = 1
6 + a − 12 = 0
a = 6
y = 2x3 + 3x2 − 12x + C
1 = 2 + 3 − 12 + C
C = 8
y = 2x3 + 3x2 − 12x + 8 -
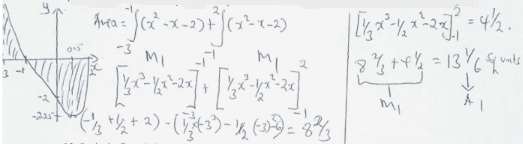
- A stretch parallel to y-axis x-axis invariant, stretch factor 1/2, followed by a stretch parallel to x-axis, y-axis invariant scale factorv(stretch factor)1/2
-
- XB × 6 = 5 × 12
XB = 5 × 12
6
= 10cm - 24 × 8 = 572
ST = √192
122 = 82 + (√192)2 − 2 × 8 × √192 Cos T
144 = 64 + 192 − 2 × 8 × √192 Cos T
−112 = −16√192 Cos T
Cos T = −112
−16√192
T = 59.66°
- XB × 6 = 5 × 12
-
- 40 + 140 = 180
180/360 × 22/7 × 2 × 6370 Cos 30
= 17,337.82858km
At least 1d.p - 17337.8kkm - 180 − (30×2) = 120
120/360 × 2 × 22/7 × 6370
133462/3 or 13346.66667
At least 1d.p or 133462/3 - 1° = 4min
180
180 × 4 = 720
1 60
= 12 hours
8 + 12 = 2000hrs tuesday
- 40 + 140 = 180
-
Mass kg 40-49 50-59 60-69 70-79 80-89 90-99 100-109 No. of people 9 27 70 50 26 12 6 9 36 106 156 182 `194 200 -
-
- 68.5
- 70.5kg -112
70.5kg - 140
140 − 112 = 28
-
- 62.5kg
- 77.5kg
- 77.5 - 62.5 = 15
-
-
√(242 − 122) = 20.7846
H = √ 20.78492 − 52
= 20.17cm
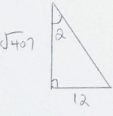
Sin Q = √407
24
G = Sin−1(√407)
24
= 57.20°
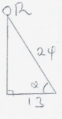
Cos Q = 13/24
Q = COs−1(13/24)
= 57.20°
tan Q = 12
(√407)
Q = tan−1 (12)
(√407)
= 30.74494004
<btn RSXY & QPXY = 2(30.74494004)
= 61.49°
-
-
- x + 3y ≥ 7......(i)
2x + 3y ≤ 18 ......(ii)
x < 5 ...........(iii)
x < 0 .....(iv)
y < 0 '' -
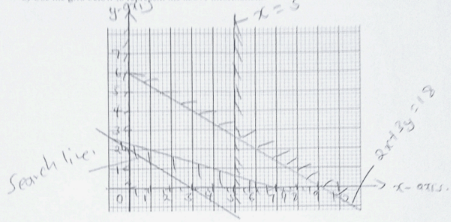
- 2000x + 3000y = k
2000x + 3000y = 6000
A - 1 trip
B - 2 trips
- x + 3y ≥ 7......(i)
-
- P = kq2
√r
P1 = (1.2q)2k = 1.44q2k
√0.648 0.85r
P1 = 1.8kq2
√r
%Δ = (1.8 − 1) 100
1
= 80% - V= k
r2
30 = k/4
k = 120
V = 120
r2
V = 120
42
= 7.5cm/s - x = kY + m
Z2
6 = 3k + m/4 ......(i)
8 = 5k + m ........(ii)
24 = 12k + m
8 = 5k + m
16 = 7k
k = 16/7
m = 24 − 12k
= 24 − 12 × 16/7 = −33/7
= −24/7
x = 16/7 × 10 − 24
7×64
= 2245/56 or 22.80
- P = kq2
-
-
x −3 −2 −1 0 1 2 3 4 5 y −32 −3 8 7 0 −7 −8 3 32 -
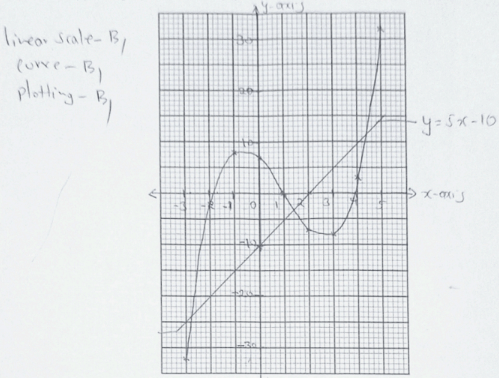
- x = −1.8 or 1 or 4 ± 0.1
- x = − 2.8 or 1.4 or 4.2 ± 0.1
drawing line y = 5x − 10
-
-
-
-
-
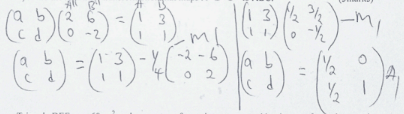
- Def = A.S.F
l3.8l = 5
5 = A.I
90
A.I = 300cm2
-
-
-
- 8cm ± 0.1
- 47°
-
Join our whatsapp group for latest updates
Tap Here to Download for 50/-
Get on WhatsApp for 50/-
Download Mathematics Paper 2 Questions and Answers - Mokasa II Joint Mock Exams 2023.
Tap Here to Download for 50/-
Get on WhatsApp for 50/-
Why download?
- ✔ To read offline at any time.
- ✔ To Print at your convenience
- ✔ Share Easily with Friends / Students