INSTRUCTIONS TO CANDIADATES
- Answer all question in section A and B
- In section C answer any two questions
- Candidates should check the question paper to ascertain that all pages are printed as indicated and that no questions is missing
- Candidates must answer all the questions in English
For examiner’s use only
|
Section |
Questions |
Maximum score |
Candidate score |
|
A |
1 -19 |
30
|
|
|
B |
20 -23 |
20
|
|
|
C |
|
20
|
|
|
|
|
20
|
|
|
Total score |
90
|
|
|

QUESTIONS
SECTION A (30MARKS)
INSTRUCTIONS: ANSWER ALL THE QUESTIONS IN THIS SECTION
- Name two camel species reared in arid and semi-arid areas (1mark)
- Give one reason why fresian’s milk is more whitish while jersey milk is yellowish (1mark)
- State two roles of a drone in a bee hive (2maks)
- What do you understand by the term raddling as used in sheep management (1mark)
- List four conditions that an animal structure should meet in order to help in controlling livestock diseases (2marks)
- List four physical characteristics of a dairy cow (2marks)
- Distinguish between stress and vices as used in poultry production (1mark)
- State two circumstances that would lead a farmer to cull a high producing cow (1mark)
- List four factors that may inhibit milk let down in dairy cattle (2marks)
- Name the other tool used together with each of the following
- Canula (1mark)
- Hypodermic needle
- Name four mineral deficiency livestock disorders (2marks)
- Give four ways in which a farmer can restrain a bull on the farm (2marks)
- Name four components of milk (2marks)
- List four factors that affect the digestibility of a feed (2marks)
- Give two symptoms of brucellosis in a cow (1mark)
- Differentiate between drift and pen lambing (1mark)
- State four abnormalities observed during egg candling (2marks)
- State four characteristics of succulent roughages (2marks)
- List four features on the animal which may predispose it to livestock disease (2marks)
SECTION B (20 MARKS)
ANSWER ALL THE QUESTIONS IN THIS SECTION
- The diagram below illustrate the stages of life cycle of a tick Study it and answer the questions that follow
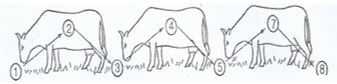
- Describe the life cycle of the tick above (4marks)
- Classify the tick on the basis of the life cycle (1mark)
- The diagram labelled A and B below show the teeth arrangements in workshop tools
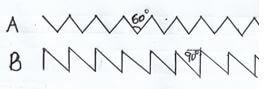
- Identify the tools represented by the teeth arrangement A and B (2marks)
A -
B - - State one functional difference between tools represented by the teeth arrangement A and B (1marks)
- Give two maintenance practices for the tools represented by the teeth arrangement shown above (2marks)
- Identify the tools represented by the teeth arrangement A and B (2marks)
- Study the illustration of fences below and answer the questions that follow
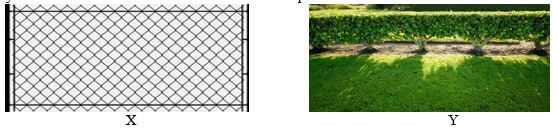
- Name the type of fences illustrated above (2mark)
X -
Y - - Name the correct tool used in maintenance of the fence Y (1mark)
- State two advantages that fence Y may have over fence X (2mark)
- Name the type of fences illustrated above (2mark)
- The diagram below shows a method of incubation in poultry rearing
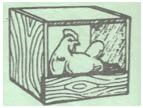
- Identify the method of incubation shown above (1mark)
- State four advantages of the method of incubation identified in (a) above (4marks)
SECTION C (40 MARKS)
ANSWER ANY TWO QUESTIONS IN THIS SECTION
-
- Describe ten routine management practices carried out during calf rearing (10marks)
- Explain five functions of water in livestock nutrition (5marks)
- Outline any five advantages of a battery cage system (5marks)
-
- Outline ten differences between a spray race and a cattle dip (10marks)
- State five structural requirement for a good grain store (5marks)
- Describe foot and mouth under the following sub – headings
- Casual organism (1mark)
- Symptoms of attack (4marks)
-
- Describe ten characteristics of a poor layer (10marks)
- State five differences between ruminants and non- ruminants digestive systems (5marks)
- Describe five management practices carried out in a fish pond (5marks)

MARKING SCHEME
- Name two camel species reared in arid and semi-arid areas. (1mark)
- Bactrian rej bacterian
- Dromedary
- Give one reason why fresian’s milk is more whitish while jersey milk is yellowish (1mark)
- Jersey milk has a higher butter fat content hence the yellowish colour/freshian milk has less butter content hence whitish in colour
- State two roles of drone in a bee hive (2marks)
- To control temperature in the hive/to cool the hive.
- To fertilise the queen.
- What do you understand by the term raddling as used in sheep management (1mark)
- This the practice of fitting the rams with breeding chutes which are painted in different colours during breeding to identify the ewes that have been served and by which ram.
- List four conditions that an animal structure should meet in order to help in controlling livestock diseases (4x½ =2marks)
- Be well ventilated but free from cold winds
- Provide adequate space
- Allow for proper drainage
- Be leak proof
- Be well lit
- Be easy to clean
- Free from draught
- List four physical characteristics of a dairy cow (4x½ =2marks)
- Has a straight top line
- Has a well set apart hindquarter to allow room for the big udder
- Has large and well developed udders with large teats that are well spaced.
- Has prominent milk veins
- Has a lean body that carry little flesh
- Has a large stomach capacity
- Distinguish between stress and vices as used in poultry production (1mark)
- Stress is any cause of discomfort to the birds while vices are abnormal behaviour shown by the birds.
- State two circumstances that would lead a farmer to cull a high producing cow
(2x½ =1marks) mark as whole- Poor health
- Old age
- Has physical deformities
- Has a poor mothering ability
- Has a bad temperament
- Not adapted to the prevailing climatic conditions in the area
- Has a low prolificacy
- List four factors that may inhibit milk let down in dairy cattle (4x½ =2marks)
- Change of milkman
- Change of routine
- Presence of strangers
- Inflicting Pain on the animal
- Name the other tool used together with each of the following (2x½ =1mark)
- Cannula - trocar
- Hypodermic needle - Syringe
- Name four mineral deficiency livestock disorders (4x½ =2marks)
- Anaemia
- Milk fever
- Curled toe paralysis
- Goitre
- Enzootic ataxia
- Bovine ketosis
- Osteomalacia
- Give four ways in which a farmer can restrain a bull on the farm (4x½ =2marks)
- Use of head yoke
- Use of rope/ casting
- Use of crush
- Use of halters
- Bull ring and a lead stick
- Name four components of milk (4x½ =2marks)
- Proteins
- Fats/ Butter fat
- Lactose/ Carbohydrates
- Water
- Vitamins
- Minerals/ Ash
- List four factors that affect the digestibility of a feed (4x½ =2marks)
- Chemical composition of the feed
- Form in which the feed is offered to the animal
- Species of the animal
- Ratio of energy to protein
- Quantity of feed already present in the digestive system of the animal
- Give two symptoms of brucellosis in a cow (2x½ =1marks)
- Spontaneous abortion/ premature birth
- Retained afterbirth/ placenta
- Barrenness
- A yellowish, brown, slimy odourless discharge from the vulva after abortion
- Differentiate between drift and pen lambing (1mark) mark as whole
- Drift lambing is where all the pregnant ewes are put together in one paddock and separated as they lamb down while pen lambing is where the ewes are only separated from the others after showing signs of lambing
- State four abnormalities observed during egg candling (4x½ =2marks)
- Yolk have blood spots
- Shell has hair cracks
- Egg shell is broken
- Egg shell very porous
- Double yolk
- Has meat spot
- State four characteristics of succulent roughages (4x½ =2marks)
- Has high fibre content
- Has high moisture content
- Has low protein content
- Has high carbohydrate content
- List four features on the animal which may predispose it to livestock disease (4x½ =2marks)
- Species of the animal
- Breed of the animal
- Age of the animal
- Sex of the animal
- Colour of the animal
- The diagram below illustrate the stage of life cycle of a tick. Study the diagram and answer the questions that follow.
- Describe the life cycle of the tick above (4marks)
- Eggs on the ground hatch to larvae, the larvae climbs the first host, sucks blood and becomes engorged
- Engorged larvae drop to the ground, moult into nymph which climbs onto the second host.
- The nymph suck blood on the second host and becomes engorged.
- Engorged nymph drops to the ground, moults into adult which climbs onto the third host.
- The adult suck blood, engorges, male & female mate and the female drops to the ground to lay eggs.
- Classify the tick on the basis of the life cycle (1mark)
- Three host tick.
- Describe the life cycle of the tick above (4marks)
-
- The diagram labelled A and B below show the teeth arrangements in workshop tools.
Identify the tool represented by the teeth arrangement. A and B (2marks)- A - Cross cut saw
- B - Rip saw
- State one functional difference between tools represented by the teeth arrangement A and B (1mark)
- A – Used for cutting across the grain.
- B – Used for cutting along the grain.
- Give two maintenance practices for the tools represented by the teeth arrangement shown above. (2marks)
- Clean the blade after use.
- Straighten the bent blade
- Sharpen the cutting edge
- Tighten loose screws
- Repair/ replace worn out handles
- Oil the metallic parts
- Teeth setting
- The diagram labelled A and B below show the teeth arrangements in workshop tools.
- Study the illustration of fences below and answer the questions that follow
- Name the type of fences illustrated (2 mark)
- X – Dead fence/ Chain link
- Y -- Live fence
- Name the correct tool used in maintenance of the fence Y. 1mark
- Pruning shears
- State two advantages that fence Y may have over fence X (2marks)
- Thorny species keep off intruders
- Tall varieties act as wind breakers
- Some species act as livestock feed
- They provide shade to livestock.
- Legumes increase soil fertility by fixing nitrogen
- Roots bind soil particle together controlling soil erosion
- Name the type of fences illustrated (2 mark)
- The diagram below shows a method of incubation in poultry rearing.
- Identify the method of incubation shown above. (1mark)
- Natural incubation
- State four advantages of the method of incubation identified in (a) above (4marks)
- Less laborious
- Requires little skills
- Margin of risk is reduced
- Small scale farmers who cannot afford an incubator can multiply flocks using this method.
- Identify the method of incubation shown above. (1mark)
-
- Describe ten routine management practices carried out during calf rearing. (10x1=10marks)
- Allow the calf to suck the colostrum/ practice bucket feeding
- Feed the calf on milk up to the tenth week before weaning
- Introduce calf pellets and soft forage from 8 weeks (early weaning) or from third week to sixteenth week (late weaning).
- Spray the calf with correct concentration of acaricides to control external parasites.
- Drench the calf with correct antihelmintics to control internal parasites.
- Vaccinate the calf against infectious diseases e.g. foot and mouth disease, black quarter disease, brucellosis.
- Castrate male calves at the age of 2 to 3 months to control breeding.
- Identify the calves by carrying out ear notching, ear tagging, tattooing etc.
- Remove extra teats using sterilised scissors, sharp knife or teat clippers and disinfect the wound.
- Dehorn or disbud the calf using disbudding iron.
- Maintain proper hygiene by cleaning the calf’s pen regularly.
- Provide adequate water.
- Cull susceptible calves
- Carry out single housing.
- Provide clean feed.
- Isolate sick calves
- Use clean water troughs and feed troughs.
- Provide adequate feed
- Explain five functions of water in livestock nutrition (5marks)
- A component of body cells and many body fluids e.g. blood
- Responsible for the transportation of nutrients
- Makes cells turgid, maintaining the shape of the body cells.
- Used in Biochemical reactions
- Regulates body temperature.
- Helps in excretion of waste products
- Forms part of animal products.
- Outline any five advantages of a battery cage system (5marks)
- High egg production
- Accurate egg records are kept
- Cannibalism and egg eating are controlled
- Eggs are clean
- The system can easily be mechanised
- Birds do not contaminate food and water.
- Handling is easy as hens are restricted to a small place.
- Broodiness is discouraged.
- A large number of birds can be kept in a small space.
- Sick birds can be detected readily and isolated for treatment.
- Wire floors prevent re-infestation of parasitic worms and coccidian.
- There are no bullying during feeding.
- There is low labour requirement.
- Describe ten routine management practices carried out during calf rearing. (10x1=10marks)
-
- Outline the differences between a spray race and a cattle dip (10x1=10marks)
Spray race
Cattle dip
Uses chemical solution in a reservoir.
Chemical solution in a dip tank
Chemical sprayed with nozzles.
Animals immersed in dip wash
Chemical sprayed relative to the number of animal/per animal
Chemical put depend on volume of dip tank
Open walk in entry
Jump in entry to dip tank
Uses motorized pump
No motorized pump
Faster spraying
Slow dipping
Less labour is required
Labour intensive
Require skill maintenance labour
No skilled maintenance labour
Safe for pregnant and sick animal
Not safe for pregnant and sick animal
Acaracide not easily contaminated
Acaracide easily contaminated
Concentration of acaricide cannot altered
Concentration of acaricide can be easily altered by evaporation and rain from leaking roof
Animal don’t swallow acaricide
Animal can easily swallow acaricide
Less wastage of chemical
More wastage of chemical
- State five structural requirement for a good grain store (5marks)
- Should be vermin proof to keep away rodents
- Should be water/leak proof to prevent dampness
- Free from cracks and crevices.
- Constructed above the ground/raised to prevent dampness.
- Well secured to prevent theft.
- Easy to load and offload.
- Describe foot and mouth under the following sub – headings.
- Casual organism 1mark
- Virus
- Symptoms of attack (4marks)
- Fever/high temperature
- Dullness
- Loss of appetite/anorexia
- blisters or wounds in the mouth and feet
- Profuse and continuous salivation
- Lameness due to wounds in the coronet on all legs.
- Emaciation and drop in production.
- Smacking of mouth.
- Casual organism 1mark
- Outline the differences between a spray race and a cattle dip (10x1=10marks)
-
- Describe ten characteristics of a poor layer. (10 marks)
- Combs and wattles appear small, shrunken, dry, scaly and pale.
- Eyes appear dull and pale yellow.
- Beaks appear yellowish in colour
- Have hard and full breast/abdomen
- Have round, dry and less active vent.
- Space between keel and pelvic bone is small and fits only one or two fingers.
- Feet/shanks appear yellowish in colour
- Broodiness is common.
- Early moulting.
- Plumage appear preened and glossy (smooth).
- State five differences between ruminants and non- ruminants digestive systems. (5marks)
Ruminant Non - ruminant chew the cud Do not chew the cud have 4 stomach chambers have one stomatch chamber regurgitatae food swallowed cannot regurgitate food once swallowed can digest cellulose / have micro - organism in the rumen that digest cellulose cannot digest cellulose / Have no micro - organisms in the stomatch except animals with caecum. Have no ptyalin in saliva / no enzymatic digestion takes place in the mouth Have ptyalin in the salive Most digestion and absorption takes place in the rumen Digestion starts in the mouth Have alkaline saliva due to the presence of ammonia Most digestion and absorption takes place in the small intestine The saliva is neutral in pH - Describe five management practices carried out in a fish pond. (5marks)
- Maintaining a good water level in the pond
- Cleaning the pond to remove foreign particles
- Removing weeds found growing around the pond.
- Planting grass on the wall tops to prevent soil erosion.
- Proper fencing to keep off predators and avoid water pollution.
- Removal of silt from the pond.
- Describe ten characteristics of a poor layer. (10 marks)
Download Agriculture Paper 2 Questions and Answers - MECS Pre Mock Exams 2023.
Tap Here to Download for 50/-
Get on WhatsApp for 50/-
Why download?
- ✔ To read offline at any time.
- ✔ To Print at your convenience
- ✔ Share Easily with Friends / Students
