INSTRUCTIONS TO CANDIDATES
- Answer all the questions in this question paper.
SECTION A
- Answer all the questions in this section:
-
- Define the term environment (2 mks)
- Name two branches of Geography (2 mks)
-
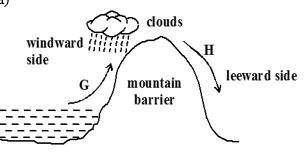
- Identify the type of rainfall shown in the diagram above (1 mk)
- State the difference in characteristics of the winds marked G and (2 mks)
- State three factors that determine the amount of solar radiation reaching the earth’s surface (3 mks)
-
- Differentiate between weather and climate (2 mks)
- Explain how the following factors influence climate
- Distance from the sea (3 mks)
- Altitude (3 mks)
-
- Differentiate between epicenter and seismic focus (2 mks)
- State any two major earthquake seismic zones of the world (2 mks)
- Give two ways in which minerals occur (2 mks)
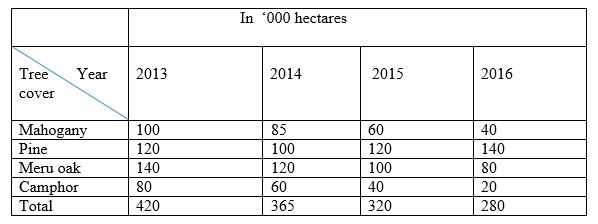
SECTION B (Answer all the questions in this section) - The table below shows the area under different species of trees in forest cover in Kenya. Study the table and answer the questions that follow.
-
- Using a scale of 1 cm to represent 20,000 hectares, draw a comparative line graph to represent the data shown (7 mks)
- Explain the difference between forestry in Kenya and Canada on:
- Transporting of logs (2 mks)
- Distribution of softwood forests (2 mks)
- Harvesting (2 mks)
-
-
- Name three types of faults (3 mks)
-
- With the aid of a well labeled diagram, describe how rift valley is formed by tensional forces (6 mks)
- Explain three ways in which faulting may influence drainage system (6 mks)
- Explain three ways in which faulting is of significance to human activities (6 mks)
-
- What is a natural vegetation (2 mks)
- Describe any three characteristics of equatorial vegetation (3 mks)
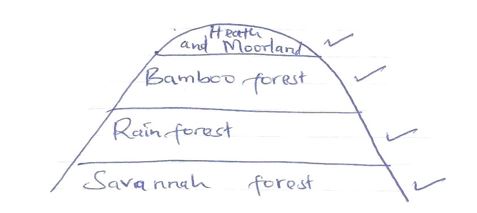
- Draw a diagram to show the vegetation zones on a mountain in Africa (4 mks)
- Student from a local secondary school carried out a field study on vegetation around their school.
- State two follow-up activities after the field study (2 mks)
-
- State two methods of representing relief on Topographical maps (2 mks)
- Convert the following scales into statement scale
- 1:50,000 (1 mks)
- 1:250,000 (1 mks)
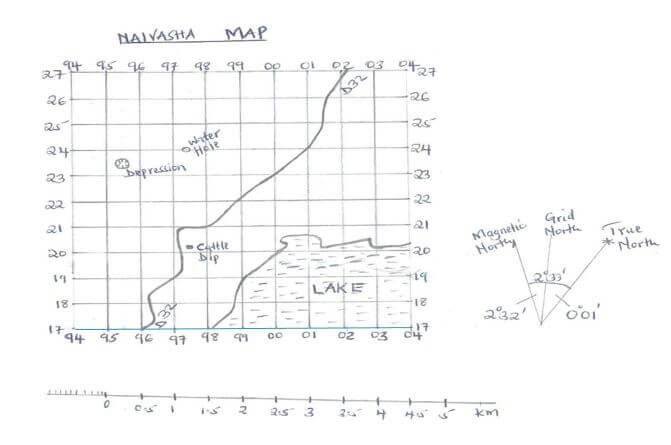
- Study the map of Naivasha below and answer the questions that follow.
-
- Measure the distance of the road D32 and give your answer in kilometres (2 mks)
- Give the six figure grid reference of the cattle dip (1 mk)
- Calculate the area of the lake using the Grid Square method (2 mks)
- Give any two uses of maps (2mks)
- Give the magnetic variation/declination of Naivasha map (1 mk)
- Study the diagram below
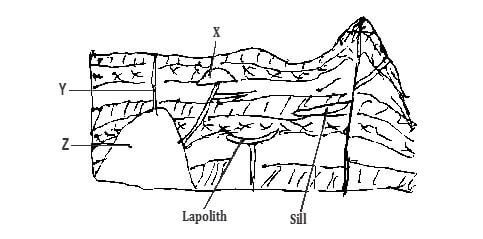
-
- Name the features marked X,Y and Z (3 mks)
X……………………………………………………………………………………
Y………………………………………………………………………………………….
Z…………………………………………………………………………………………… - Explain how a sill is formed (4 mks)
- Name the features marked X,Y and Z (3 mks)
- Explain four ways in which volcanic mountain positively influence human activities (8 mks)
- Students carried out a field study on volcanic rocks
- State two problems they are likely to encounter (2 mks)
- State two objectives for the study (2 mks)
-
MARKING SCHEME
-
- Is the external conditions surrounding an organism/plants/animals
- Physical
- Human
- Practical
-
- Relief/Orographic rainfall
- G is warm and moist while H is cold and dry
- The intensity of sun’s radiation
- The transparency of the atmosphere
- The earth’s average distance from the sun
- The position of the earth on its orbit
- The inclination/angle of the surface on which the sun’s rays fall
-
- Weather is the daily atmospheric conditions of a place over a short period of time while climate is the average weather conditions of a place over a long period of time.
- Altitude
- Temperature decreases with increasing to height hence high altitude areas have lower temperatures than low altitude areas which are warmer
- High altitude areas have a low atmospheric pressure than low altitude areas which have higher atmospheric pressure
- A rise in altitude causes a fall in temperature and a cooling effect which cause condensation and rainfall on the windward side
- Altitude causes Anabatic and Katabatic winds/temperature inversion in mountainous areas
Distance from the school - Areas closer to the sea are wetter than those for the sea due to maritime influence
- During summer land surfaces are warmer than sea surfaces so that inland areas are warmer than those nearer to the sea in winter land are warmer
- Winds blowing over the sea pick moisture which later fall as rainfall in the coastal areas. They blow as dry winds further inland causing aridity
-
Epicenter Seismic focus Is a point on the earth's surface vertically above the seismic focus Is the point where the seismic waves originate -
- Mid-ocean ridges
- Ocean deeps and volcanic islands
- Regions of crustal compressions
- Within the Rift Valleys
- In areas of volcanic activities
-
- Beds and seams
- Lodes and veins
- Alluvial deposits
- Weathering products
- A COMPARATIVE LINE GRAPH SHOWING FOREST COVERAGE IN “000 HACTARES BETWEEN 2013 AND 2016

-
- Kenya transport logs through tracks and lorries/road while Canada transport logs through melt ice/rivers
- In Kenya softwood forests occupy the highland regions while in Canada softwood forests occupy both lowland and highland regions.
- In Kenya only mature trees are harvested while in Canada clear cutting is done
-
-
-
- Normal
- Reverse
- Tear/shear/slip/strike
- Thrust fault
- Anticlinal
- Layers are subjected to tensional forces
Two normal faults develop parallel to each other
The middle block subsides/sinks/downloads
The sunken middle part forms a depression called Rift Valley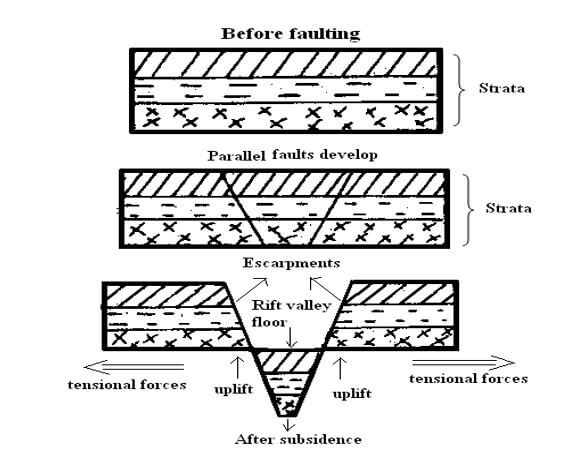
- Some rivers may end up flowing along faults lines, thus forming a fault guided drainage pattern
- Uplifting of land which follows faulting may block a river. This may cause it to reverse/change its direction of flow
- When faulting occurs across a river valley, it may cause the river to disappear into the ground through a fault line
- Faulting may lead to the formation of escarpments with springs forming at the forming at the base due to exposure of the water table
- When faulting occurs across a river valley, vertical displacement of land may occur. The river forms a waterfall where it descends the newly formed escarp
- If rift valley occurs in an enclosed area, a basin may be formed when rivers flow into the basin a lake may be formed. This basin may become an area of inland drainage.
- Faulting leads to formation of features that form beautiful scenery which attracts tourists
- Faulting leads to formation of lakes that are important fishing grounds/tourist sites/provide water for irrigation/ for domestic use
- Faulting causes displacement of rocks which exposes minerals that are mined
- Faulting may lead to the formation of mountains/horst which experiences rainfall on the windward side that give rise to rivers which provide water for industrial/domestic/agricultural use
- Block mountains leads to formation of relief rainfall on the windward side which favours agriculture
- Faulting may cause subsidence of land which may lead to loss of life/property
- Faulting creates deep faults which are passage of steam jets which may be utilized for geothermal power, production
- When faulting occurs a ridge it may provide a dip which could form a mountain pass where transport/communication lines can be constructed/may hinder development of transport
-
-
- Is a type of plant life that develops naturally and is the most suited to that particular environment.
-
- Trees are tall
- Trees have straight and smooth trunks
- Trees have formed canopies
- Vegetation has little or no undergrowth
- The trees are mainly hardwood
- Trees have buttressed roots for support
-
- To identify the type of vegetation around
- To investigate factors favouring the growth of vegetation (any two)
- Holding group discussion in class
- Group presentation (any two)
-
-
- Spot heights
Trigonometrical points
Contours
Form lines
Pictorials
Hachures -
- 1 cm rep 0.5 km
- 1 cm rep 2.5 km
- 6.9 7.0 7.1
- 977202
- Full squares
13+8/2
13+4
17 km2 -
- To understand roads and subways at new places.
- To calculate distance between two places.
- To know whether there are two or more paths to the same place and which is the shortest.
- We can get information about mountains, rivers, valleys or any other thing, which may come on the way, and we can prepare for that.
- 1350
20 33'
- Spot heights
-
- x – laccolith
y – batholith - Rocks beneath the crust are in a semi-solid state due to high temperature and high pressure
When pressure decreases the rocks become semi liquid and are known as magma.
Earth movement cause vertical or horizontal cracks in the rocks
The molten magma force itself through the cracks when magma cools and solidifies in a horizontal crack or bedding plan it forms a feature called sill.
- x – laccolith
- Volcanic moutains are sources of rivers which provide water for irrigation, domestic and industrial
- Influence formation of relief rainfall
- Volcanic soils are suitable for agriculture
- Volcanic mountains encourage the growth of forests on windward side which provide timber for construction
- Volcanic mountains form beautiful sceneries which attract tourists
- Host springs/geysers are used to generate geothermal
- Crater lakes are good for fishing
- Volcanic rocks provide materials for construction
-
-
- Bad weather eg it may rain
- Accidents may occur
- A researcher may fall sick
- To identify the main type of rocks
To find out the uses of rocks (any two )
-
-
Join our whatsapp group for latest updates
Tap Here to Download for 50/-
Get on WhatsApp for 50/-
Download Geography Form 2 Questions and Answers - Term 3 Opener Exams 2021.
Tap Here to Download for 50/-
Get on WhatsApp for 50/-
Why download?
- ✔ To read offline at any time.
- ✔ To Print at your convenience
- ✔ Share Easily with Friends / Students