INSTRUCTIONS TO CANDIDATES
- This paper consists of two sectons: a and b
- Answer all questions in section a
- In section b, answer question 6 and any other two
SECTION A: 25 MARKS
-
- Name two areas where gold is mined in South Africa (2mks)
- State three ways in which mining create employment in Kenya (3mks)
-
- Distinguish between a forest and forestry (2mks)
- List three hard wood tree species in Kenya (3mks)
-
- Differentiate between statistics and statistical methods (2mks)
- List three sources of secondary data (3mks)
-
- Name two oil producing countries in Middle East (2mks)
- Give three by-products obtained when crude oil is refined (3mks)
-
- Explain why mining is regarded as a robber industry (2mks)
- Explain why petroleum, oil and natural gas are not regarded as minerals 2mk)
- Name one area in Kenya where gold is mined (1mk)
SECTION B: 75 MARKS
ANSWER QUESTION SIX AND ANY OTHER TWO
- The table below represents the rainfall and temperature data of station Y for one year. Study it and answer the questions that follow:
Month Jan Feb Mar April May June July Aug Sept Oct Nov Dec Rainfall (mm) 5 10 33 40 60 100 75 40 30 15 5 5 Temp 23 24 25 27 27 29 28 27 26 25 24 24 - Calculate the following:
- Annual temperature range (2mks)
- Mean monthly temperature (2mks)
- Annual Rainfall (2mks)
- Draw a combined line and bar graph to represent the data (8mks)
- Describe the characteristics of the polygraph in b above (6mks)
- Apart from choosing and labeling the vertical scales for rainfall and temperature, state four other steps to be followed in constructing a polygraph (4mks)
- Give one disadvantage of this type of graph (1mk)
- Calculate the following:
-
- Define the term mineral (2mks)
-
- Name two areas in South Africa where diamond is mined (2mks)
- Give four ways in which minerals occur (4mks)
-
- Explain Three negative effects of mining on the environment (6mks)
- Identify any two methods of mining (2mks)
- Name a port through which minerals in East Africa are exported (1mk)
- Explain four ways in which soda ash contributes to the economy of Kenya (8mks)
-
-
- Name two provinces where forests are found in Canada 2mks)
- Give three tree species that are found in Canada (3mks)
- Explain three ways in which the transportation of logs in Canada differ from Kenya (6mks)
- Explain four problems that face forestry in Canada (8mks)
- A form four class conducted a field study in a forested region in the area around their school
- Identify two main categories of hypothesis that the students would have formulated (2mks)
- Identify four activities the students could have been involved in during the study (4mks)
-
-
-
- Identify the two types of photographs (2mks)
- State three advantages of using photographs as a technique of recording data (3mks)
- With reference to ground photographs explain the meaning of
- Dead ground (2mks)
- Fore ground (2mks)
- Back ground (2mks)
- Study the photograph below and use it to answer the questions that follow

- Name the type of photograph shown (1mk)
- Describe the appearance of the forest shown on the photographs (7mks)
- Name the kind of farming activity in the photograph (1mk)
- Name the type of trees shown in the photograph (1mk)
- Compare tree harvesting in Kenya and Canada (4mks)
-
-
- State 3 factors influencing distribution and types of natural forests in Kenya . (3mks)
- List 4 characteristics of coniferous forest. (4mks)
- Explain 4 importance of forests in kenya . (8mks)
- Students of your school decided to carry out a field study in nearby forest.
- Give 3 importance of the previsit. (3mks)
- State 3 reasons why they needed a route map. (3mks)
- State 2 follow-up activities the students will have after the field study. (2mks)
- Give 2 reasons why students required a working schedule. (2mks)
MARKING SCHEME
SECTION A 25 MARKS
-
- Name two areas where gold is mined in South Africa (2mks)
- Witwatersrand
- Lydenburg
- ogendaalrus
- State three ways in which mining create employment in Kenya (3mks)
- some people are employed as miners
- some people are employed indirectly as managers in factories that make use of minerals
- some people are employed to transport the minerals from the site to the factories
- some people are employed to work as security officers in the mining industries
- Name two areas where gold is mined in South Africa (2mks)
-
- Distinguish between a forest and forestry (2mks)
- forest is a continuous and extensive land covered with a closed stand of tall trees usually of commercial value, while forestry is the science of developing or cultivating forests.
- List three hard wood tree species in Kenya (3mks)
- Meru oak - mangrove
- Camphor - Elgon Olive
- Elgon teak -mvule
- Distinguish between a forest and forestry (2mks)
-
- Differentiate between statistics and statistical methods (2mks)
- Statistics are facts and figures collected and analyzed in a systematic manner while Statistical methods are the techniques of collecting, recording, analyzing and presenting statistical data
- List three sources of secondary data (3mks)
- Textbooks
- Newspaper
- Journals
- Reports
- periodicals
- Differentiate between statistics and statistical methods (2mks)
-
- Name two oil producing countries in Middle East (2mks)
- Saudi Arabia
- kuwait
- Iran
- united Arabs emirates
- Iraq
- Give three by-products obtained when crude oil is refined (3mks)
- Tar - bitumen/ peat/ asphalt
- Grease/ lubricants
- Resin/ petrol chemicals
- Name two oil producing countries in Middle East (2mks)
-
- Explain why mining is regarded as a robber industry (2mks)
- This is because once the mineral resource have been exploited, it cannot replenish unlike forests
- Explain why petroleum ,oil and natural gas are not regarded as minerals (2mk)
- gas and oil are not solids and do not have crystal structures.
- Name one area in Kenya where gold is mined (1mk)
- kakamega
- Explain why mining is regarded as a robber industry (2mks)
SECTION B: 75 MARKS
ANSWER QUESTION SIX AND ANY OTHER TWO
- The table below represents the rainfall and temperature data of station Y for one year. Study it and answer the questions that follow:
- Calculate the following:
- Annual temperature range (2mks)
Maximum temp − minimum temp
29°c − 23°c = 6°c - Mean monthly temperature (2mks)
Maximum temp + minimum temp
29°c + 23°c = 26°c - Annual Rainfall (2mks)
5 + 10 + 33 + 40 + 60 + 100 + 75 + 40 + 30 + 15 + 5 + 5
= 418mm
- Annual temperature range (2mks)
- Draw a polygraph to represent the data (8mks)
Combine line and bar graph for station Y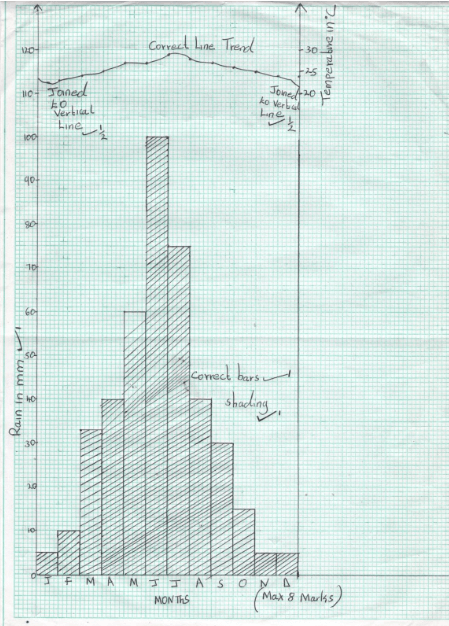
- Describe the characteristics of the polygraph in b above (6mks
- There is rainfall throughout the year
- There is one rainfall maxima: from March to September
- Temperatures are high throughout the year
- Mean annual rainfall is low about (418mm)
- Mean annual range of temperature is small about 6oc
- The amount of rainfall increases with the increase of temperature
- The wettest month is June
- Apart from choosing and labeling the vertical scales for rainfall and temperature, state four other steps to be followed in constructing a polygraph (4mks)
- Choosing and labeling the horizontal scale
- Plotting the values for rainfall and drawing the bar graph
- Plotting the values for temperature and drawing the line graph
- Writing an appropriate title above the graph
- Give one disadvantage of this type of graph (1mk)
- It is difficult to choose a suitable vertical scale when values for valuables have a great difference
- Calculate the following:
-
- Define the term mineral (2mks)
- A mineral is a naturally crystalline inorganic substance with a definite chemical composition and physical properties
-
- Name two areas in South Africa where diamond is mined (2mks)
- Kimberly
- Orange free state
- pretoria
- Give four ways in which minerals occur (4mks)
- veins and lodes
- beds and seams
- weathering products
- Alluvial deposits
- Name two areas in South Africa where diamond is mined (2mks)
-
- Explain Three negative effects of mining on the environment (6mks)
- Waste of agricultural land- mines and their associated tip-heaps may occupy land otherwise suitable for farming
- Waste of industrial land – where derelict land is in or near towns it may occupy industrial land which could be used for industries
- Open cast mines may be filled with water and create deep pools thus accidents are likely to occur. Such pools are also breeding grounds for mosquitoes and other water borne diseases
- Pollution- during mining toxic gases may be emitted from the mimes leading to air pollution
- Identify any two methods of mining (2mks)
- Open cast mining
- Underground mining
- Alluvial mining/ placer method
- Name a port through which minerals in East Africa are exported (1mk)
- mombasa
- Explain Three negative effects of mining on the environment (6mks)
- Explain four ways in which soda ash contributes to the economy of Kenya (8mks)
- it has led to the growth of magadi township
- it has led to the development of social amenities such as hospitals, schools, social clubs, electricity that have benefited the local maasai community
- it has stimulated the development of infrastructure. For example the 110km tarmac road and railway line from konza to magadi in an otherwise remote region.
- The company provides employment to many Kenyans improving their living standards
- Through exports of soda ash the country earns a substantial amount of foreign exchange.
- Define the term mineral (2mks)
-
-
- Name two provinces where forests are found in Canada (2mks)
- British Columbia
- North Eastern provinces up to new found land
- Give three tree species that are found in Canada (3mks)
- Spruces
- Douglas fir
- White pine
- Name two provinces where forests are found in Canada (2mks)
- Explain three ways in which the transportation of logs in Canada differ from Kenya (6mks)
- Transportation of logs in Kenya is by tractors and lorries/trucks while in Canada Rivers are widely used to float the logs on the water
- Canada uses tractors to transport the logs where the rivers are too small or far away from the logging sites while in Kenya tractors are used throughout the year
- Kenya rivers are never used to transport the logs at all while in Canada rivers are used most of the times.
- In Kenya workers are transported daily to the logging sites while in Canada workers live in the logging sites and so the cost of transportation is reduced
- Explain four problems that face forestry in Canada (8mks)
- In Canada large tracts of land is faced by fires that are caused by smokers, bush burning fires, campers and industrial operations like logging
- Some sections of the forest in the northern part of Canada are in accessible due to rugged terrain and so it becomes hard to exploit the trees.
- The forest in the northern part of Canada is in accessible in winter due to snow.
- The replanted young seedlings take a lot of time to mature usually 50-60 years of tree growing in Canada after harvesting or even after cutting them down in case they have been attacked by aphids like in the case of Kenya.
- A form four class conducted a field study in a forested region in the area around their school
- identify two main categories of hypothesis that the students would have formulated (2mks)
- Null hypothesis/negative hypothesis
- Alternative hypothesis / substantive hypothesis/positive hypothesis
- Identify four activities the students could have been involved in during the study (4mks)
- Identifying the trees by their local or botanical names
- Finding out the trees that are hard wood and those that are soft wood
- Finding out the uses of trees
- Identifying the trees that are indigenous and those that are exotic
- Finding out the problems facing the trees in the region
- identify two main categories of hypothesis that the students would have formulated (2mks)
-
-
-
- Identify the two types of photographs (2mks)
- Ground photographs
- Aerial photographs
- State three advantages of using photographs as a technique of recording data (3mks)
- Photographs are easy to take
- Photographs are less time consuming in that one only needs to focus on the object being photographed
- Photographs shows physical features such as the appearance of a landscape or economic activities taking place
- Photographs are easily accessible
- With reference to ground photographs explain the meaning of
- Dead ground (2mks)
- The area hidden or blocked from the lens of the camera by other objects
- Fore ground (2mks)
- The part of the photograph nearest to the camera
- Back ground (2mks)
- It’s the part of photograph furthest from the camera
- Dead ground (2mks)
- Identify the two types of photographs (2mks)
-
- Name the type of photograph shown (1mk)
- Ground general view photograph
- Describe the appearance of the forest shown on the photographs (7mks)
- The trees are thin
- The trees have straight stems
- The forest has tall trees
- The trees are conical shaped
- The trees are composed of the same species
- The trees are almost of the same height
- The trees are close to each other
- The undergrowth is composed of crops
- Name the type of photograph shown (1mk)
- Name the kind of farming activity in the photograph (1mk)
- Agro forestry
- Name the type of trees shown in the photograph (1mk)
- cypress
- Compare tree harvesting in Kenya and Canada (4mks)
- In Kenya there is less mechanization while in Canada lumbering is more mechanized.
- In Kenya logging takes place throughout the year while in Canada it is done in winter
- In Kenya cutting of trees is selective while in Canada harvesting is done through clear cutting.
-
-
- State 3 factors influencing distribution and types of natural forests in Kenya.
- Climate
- Altitude
- Soils
- Human activities
- list 4 characteristics of coniferous forests.
- Trees are light in weight and easy to cut
- Trees are ever green
- Trees occur in pure stands , same species
- Trees cover a large area
- Trees have tall about 30m with straight trunks
- Trees have conical shape
- Trees have thick barks
- Explain 4 importances of forests in Kenya.
- Trees regulate the climate of a place
- Trees conserve and preserve the environment
- Forests are a major source of income
- Forests are suitable habitats for wild animals
- Forests provide raw materials for industrial use
- Forests provide beautiful scenery which attract tourists
- Forests are source of fuel – firewood and charcoal
- students of your school decided to carry a field study in nearby forest
- Give 3 importance of the previsit
- Helps to estimate the cost of study and plan accordingly
- Helps the researcher to familiarize with the area of study
- Helps one to know the tools to carry
- Introduces the researcher to the authorities and the respondents in the area of study
- Helps to determine the appropriate route to follow during the study.
- Helps to identify the problems likely to be encountered
- Guides the researcher to prepare a working schedule
- State 3 reasons why they needed a route map.
- Helps to identify the direction to follow
- Helps to prepare a working schedule
- Helps to locate feat areas for the study
- Helps to estimate the distance to be covered
- Helps to estimate the time for field study is likely to takes
- state 2 follow up activities the students will have after the field study
- Writing reports
- Drawing diagrams
- Discussing with the rest of the class
- Displaying photographs / items collected
- Assessing the information collected against the hypothesis
- give 2 reasons why students required a working schedule.
- Helps to estimate time required for the study
- Gives ample time to each activity so that no activity is forgotten
- Reduces tendering to waste time as an activity is confined to specific time.
- Ensures one remains in the scope of study
- Provides a basis for evaluating the fieldwork while still in progress.
- Give 3 importance of the previsit
- State 3 factors influencing distribution and types of natural forests in Kenya.
Download Geography Paper 2 Questions and Answers - Form 3 Term 2 Opener Exams 2023.
Tap Here to Download for 50/-
Get on WhatsApp for 50/-
Why download?
- ✔ To read offline at any time.
- ✔ To Print at your convenience
- ✔ Share Easily with Friends / Students

