- Give four biotic factors which influence Agriculture positively. (2 marks)
- State two farming practices which enhance organic farming. (1 mark)
- Which chemical are used during water treatment to; (1½ marks)
- Coagulate solid particles _____________________________________________________________
- Soften the water _____________________________________________________________
- Kill pathogens _____________________________________________________________
- Give two reasons that makes phosphatic fertilizers good for use during planting time. (1 mark)
- List down four qualities of a good farm record. (2 marks)
- What do you understand by the following terms? (1½ marks)
- Seed dressing
- Seed inoculation
- Chitting
- State three problems associated with land fragmentation in Kenya? (1½ marks)
- Outline four land Reforms Programmes which have been carried out in Kenya since independence. (2 marks)
- List down four common methods of harvesting water. (2 marks)
- Give three methods of breaking seed dormancy. (1½ marks)
- What do you understand by the following terms as used in pests classification according to mode of action. (2 marks)
- Stomach poisons
- Systemic poisons
- Contact poisons
- Suffocants
- Give two reasons why farmers are encouraged to practice organic farming. (1 mark)
- State three advantages of shifting cultivation. (1½ marks)
- List four methods of farming. (2 marks)
- Outline three effects of soil organisms which benefit crop growth. (1½ marks)
- State two harmful effects of strong wind on crop production. (1 mark)
- State three advantages of adding organic matter to sandy soil. (1½ marks)
- State three ways by which biological agents can enhance the process of soil formation. (1½ marks)
- Outline four main reasons for secondary tillage. (2 marks)
SECTION B (20 MARKS)
Answer ALL the questions in the spaces provides
- Below are two types of soil structures A and B.
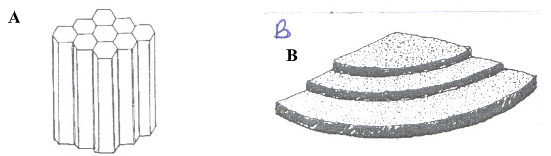
- Identify the two- types of soil structures. (2 marks)
- A ______________________________________
- B ______________________________________
- State where the above soil structures are likely to be found. (1 mark)
- Outline ways which soil structure influences crop production. (3 marks)
- Identify the two- types of soil structures. (2 marks)
-
- Study the diagram below and answer the questions that follow.
- What is layering? (1 mark)
- Identify the type of layering shown below. (1 mark)

- Give two advantages of tissue culture in crop production. (2 marks)
- Study the diagram below and answer the questions that follow.
-
- Maize requires 120kg/ha of phosphorus pentoxide (P2O5). How much of the compound fertilizer 20:20:10 would be applied to 0.4 hectare of land to achieve this rate. (show your working). (3 marks)
- Distinguish between straight fertilizers and compound fertilizers. (2 marks)
- The diagram below shows a cabbage seedling which has been attacked by a certain pest.
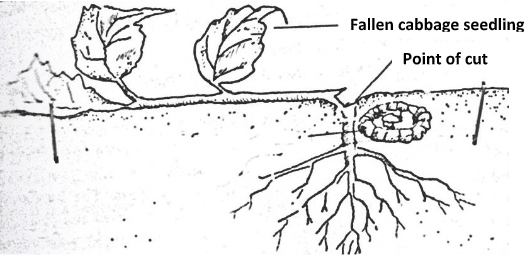
- Identify the pest (1 mark)
- State three methods of controlling the above pest (3 marks)
SECTION C (40MARKS)
Answer any TWO questions in this section in the spaces provided after question 25
-
- Outline the factors affecting rooting of cuttings. (5 marks)
- State and explain human factors that influence Agricultural production. (10 marks)
- Highlight the management practices carried out in a nursery. (5 marks)
-
- State and explain five ways through which soil loses its fertility. (10 marks)
- Describe five characteristics of Nitrogenous fertilizers. (5 marks)
- Outline five methods used in application of inorganic fertilizers. (5 marks)
-
- Explain seven cultural methods of controlling crop diseases. (7 marks)
- Describe precautions taken during the harvesting of coffee. (4 marks)
- Given that a crop of cabbage is planted at a spacing of 60cm × 60cm, calculate the plant population in a plot of land measuring 4m × 3m. (show your working). (4 marks)
- Give five factors that determine spacing of cabbages in the field. (5 marks)
MARKING SCHEME
-
- Pollinators
- Predators
- Decomposers
- Nitrogen fixing Bacteria (4 x ½ = 2 marks)
-
- Mulching
- Crop Rotation (1 x ½ = 1 mark)
-
- Alum ?(Aluminum sulphate
- Soda ash (sodium bicarbonate)
- Chlorine (½ x 3 = 1½ marks)
-
- Have a residual (roots) effects
- Not easily leached (2 x ½ = 1 mark)
-
- Neat
- Concise
- Complete
- Actual (4 x ½ = 2 marks)
-
- Seed dressing is the coating of seed with a fungicide or insecticide or both to protect seedlings from soil borne pests and diseases.
- Seed inoculation is the coating of legume seeds with the right strain of ;Rhizobia bacteria to enable fix free atmospheric Nitrogen into the soil
- Chitting – putting potato sets in a partially dark room to break their dormancy (3 x ½ = 1½ marks)
-
- Time wasting while travelling from one holding to another
- proper and effective control of weeds and pest became difficult
- difficulties in supervision of the scattered plots
- difficulties in caring out various soil conservation measures
- difficulties of offering agricultural extension advise (3 x ½ = 1½ marks)
-
- Land tenure reform
- land consolidation
- Land adjudication and registration
- Settlement and resettlement (4 x ½ = 2 marks)
-
- Weirs
- Dams
- Ponds
- Roof catchment (4 x ½ = 2 marks)
-
- mechanical method
- heat treatment
- chemical treatment
- soaking in water (3 x ½ = 1½ marks)
-
- Stomach poisons – This is the pesticide which kills the part of the pest sprayed or dressed.
- Systemic poison – The chemical circulates to all parts of the pest once eaten, killing the pest
- Contact poisons is chemical kills the pests when it is absorbed into the body through the skin or cuticles
- Suffocates the chemical which interferes with the breathing system of the pest (4 x ½ = 2 marks)
- Reasons why farmers practices organic farming
- Environmental friendly / no pollution
- It is sustainable/ conserve soil
- It is easily carried out
- Materials used are easily available/ cheaper
- Produce healthy product
- The produce fetch higher prices in the international market of the produce 2 x ½ = 1 mark
- Advantages of shifting cultivation
- Land is allowed to rest and regain fertility
- Low incidences of pests and diseases
- Economies of use of fertilizers 3 x ½ = (11/2mks)
- Method of farming
- Shifting cultivation
- Nomadic pastoralism
- Organic farming
- Mixed farming
- Agro-forestry 4 x ½ = 2 marks
- Effects of soil organisms
- Decompose organic matter
- Help to create the soil
- Atmospheric Nitrogen to nitrates
- Upon death and decay release plant nutrient 3 x ½ = (11/2mks)
- Harmful effects of strong wind on crop production
- Increase rate of evaporation
- Increase spread of diseases pests
- Causing lodging in cereals and damage to crops
- Acting as agent of soil erosion
- Advantages of adding organic matter to sandy soil
- Improve soil structure
- Reduce leaching
- Improves water holding capacity
- Increase cation exchange capacity
- Improve nutrient status upon decomposition
- Moderate soil temperature
- Ways by which biological agents can enhance the process of soil formation
- Movements of animals in large numbers
- Decomposition of plants and animals remains by soil micro-organism
- Physical breaking of rocks by roots of higher plants
- Man’s activities e.g. cultivating, mining and road
- Mixing up of soil burrowing animals e.g. earth worms and termites.
- Main reasons for secondary tillage
- Control weeds
- Control pests and diseases
- Incorporate organic matter in the soil
- Improves physical condition/form required tilt
- Make appropriate tilt for planting certain crops, e.g. ridging, rolling prevailing 4 x ½ = 2 marks
SECTION B 20MKS
-
-
- A- Prismatic
- B - Platy (2 × 1= 2 marks)
-
- A- In arid and semi-arid soils
- B- Top horizon of forest and clay soils (1 x 1 = 1 mark)
-
- Determining the type of crop to be grown
- Determine the water holding capacity
- Determines aviation and drainage of the soil (3 x 1 = 3 marks)
-
-
-
- Inducing part of a stem to produce root while still attached to the mother plant (1mk)
- Trench layering (1mk)
-
- Produces pathogen free plants
- Mass production of propagules
- Its fast
- Requires less space (4x ½=2mks)
-
- 20kg of P2OS is contained in 100kgs of 20,20, 0
Therefore 120kg of P2OS will be contained in 120×100 = 600kg of 20,20,10
20
1 acre of maize requires 600kg of 20, 20, 10.
Therefore , 0.4 × 600 = 240kg of 20, 20, 10
1 -
- Cut worm. (1mark)
-
- Use of appropriate insecticides.
- Physically by picking and killing.
- Crop rotation Any 2x1=2marks
SECTION C
-
- Factors affection rooting of cutting
- temperature
- relative humidity
- light intensity
- oxygen supply
- chemical treatment
- leaf area (5 x 1 = 5 marks)
- State and explain human factors influencing Agricultural production
- level of education and technology
- health HIV/AIDS and health in general
- economy (level of economic development
- government policy
- transport and communication
- cultural practices and religion beliefs
- market forces
- Stating (1mk)
- Explaining briefly (1mk) (2 x 5=10 marks)
- Management practices carried out in a nursery
- mulching
- watering
- weed control
- pricking out
- shading
- pests and diseases control
- hardening off
- Factors affection rooting of cutting
-
-
- Leaching
- Soil erosion
- Monocropping
- Continuous cropping
- Change in soil PH
- Burning of vegetation
- Accumulation of salts
NB State any five ( 1 mark) , correct explanations (1 mark) (Total 10 marks)
-
- Highly soluble in soil water
- Highly leached
- Have a short residual effect
- Has a scorching / Burning effect
- Highly volatile
- Hygroscopic
- Highly corrosive
Correct explanation (1 mark) In total (5 marks)
-
- Broad casting
- Placement method
- Side dressing
- Foliar spraying
- Drip
Correct explanation (1 x 5 = 5 marks)
-
-
- cultural methods of controlling crop diseases
- using healthy planting materials does not spread diseases
- using field hygiene like burning diseased crop residues/ rouging/ clean diseases
- weeding reduces spread of diseases
- proper spacing controls damping off and resettle diseases in groundnuts
- heat treatment in control of rations stunting diseases of sugarcane
- proper drying of grains and pulses to- avoid afflation
- use of diseases resistant varieties like Ruiru for coffee that is resistant to coffee berry diseases and leaf rust 7x1=(7mks)
- precautions taken during the harvesting of coffee
- both grade one and two berries are taken to the factory on the same day
- sorting of cherry at the factory has to- be done well
- only the red ripe berries are picked
- the barriers are taken to the factory at the end of the harvesting seasons 4x1=(4mks)
- plant population = Area of land
Spacing of crop
= 4m x 3m = 12m2
0.6 x 0.6m = 0.36m2 ✔2
= 33 plants ✔2 Total = 4 marks) - Factors that determine spacing of cabbage
- Pest and disease incidences
- Variety of the cabbage
- Soil moisture status
- Type of soil
- Soil fertility 5x1= 5marks
- cultural methods of controlling crop diseases
Download Agriculture Paper 1 Questions and Answers - Form 3 Term 2 Opener Exams 2023.
Tap Here to Download for 50/-
Get on WhatsApp for 50/-
Why download?
- ✔ To read offline at any time.
- ✔ To Print at your convenience
- ✔ Share Easily with Friends / Students

