SECTION A 30 MARKS
- Give four control measures of a liver fluke in livestock. (2mks)
- State two signs that shows that a cow is about to parturate. (2mks)
- State four signs of infestation by external parasites in livestock. (2mks)
- Name two notifiable diseases in Kenya.(1mks)
- State four reasons for feeding colostrums to calves immediately after parturition. (4mks)
- Distinguish between mothering ability and prolificacy as used in livestock breeding. (2mks)
- Name the vegetative part of each of the following crops which is propagated. (2mks)
- Sweet potatoes……………………………………..
- Cassava………………………………………………
- Bananas………………………………………………
- Oranges………………………………………………..
- Name two methods of weed control in pasture.(1mk)
- Name four methods used in identifying farm animals. (2mks)
- State two reason s why it is necessary to have individual calf pens instead of communal calf pen. (1mks)
- State two effects of HIV/AIDS on agricultural production . (1mk)
- State four reasons for maintaining farm tools and equipment in proper condition. (2mks)
- Give four factors which characterise small scale farming. (2mks)
- Give four benefits of conservation of farage. (2mks)
- Name four suitable sites for agroforestry. (2mks)
- Give objectives of land settlement and resettlement in Kenya.(2mks)
SECTION B 20MKS
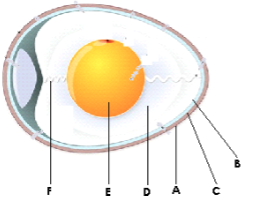
- The diagram below is an illustration of an egg. Study it carefully and answer the questions that follow.
- Name the parts labeled (3mks)
- A…………………………………
- B………………………………..
- C…………………………………..
- D…………………………………….
- E…………………………………
- F…………………………….
- State the qualities of the part labelled A that should be considered when selecting eggs for incubation. (2mks)
- What is the function of the part labeled E in a fertilized egg. (1mks)
- Name the parts labeled (3mks)
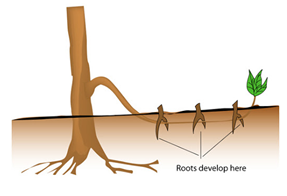
- Study the diagram below and answer the question that follow.
- What is layering?
- Identify the type of layering shown below
- Give two advantages of tissue culture in crop production
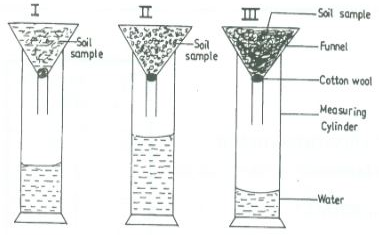
- The diagram below illustrates an experiment on soil. Study it carefully and answer the question that follow.
- State the aim of the experiment. (1mk)
- If the volume of water illustrated in the measuring cylinder was observed after one hour, identify the soil sample labeled I and II and give reasons.
- State two ways in which the soil structure of the soil sample labeled III above can be improved. (2mks)
- State four reasons why docking/tailing is done in wool. (2mks)
- State two management practices that should be carried on a knapsack sprayer. (1mk)
-
- State two reasons why bees swarm. (2mks)
- State two methods of tick control. (1mk)
SECTION C 40MKS
-
- State five difference between ruminants and non-ruminants. (5mks)
- Discuss calf rearing from birth to first calving.
- State five problems that farmers are likely to face when marketing their produce.
-
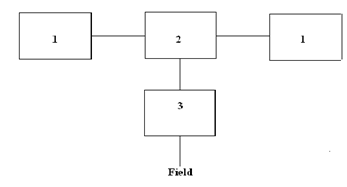
- Illustrated below is a method of turning compost. Study the method and answer the questions that follow.
- Identify the methods. (1mk)
- Using arrows in the diagram show how the turning is done before the manure can be taken to the field. (2mks)
-
- which other methods can be used to prepare the manure.(1mk)
- After how long should the compost be ready for use? (1mk)
-
- state four reasons for maintaining farm tools and equipment in proper condition. (2mks)
- list three factors that makes embryo transplant unpopular with many livestock farmers.(3mks)
- An agriculture student was adviced to apply a complete fertilizer 40:30:10 in a 20m by 10m plot at a rate of 400g per hectare.
- Calculate the percentage of p2o5 in the complete fertilizer. (3mks0
- Calculate the amount of fertilizer the student would require for the plot. (3mks)
- Calculate the amount of k2o that would be contained in 600kg of a compound fertilizer. 30:20:10 (NP2O2:K2O) respectively.
- Illustrated below is a method of turning compost. Study the method and answer the questions that follow.
- Describe the production of tomateos under the following sub-heading:
- Nursery production (12mks)
- Transplanting
- Field management practices. (3mks)
MARKING SCHEME
SECTION A 30 MARKS
- State the four control measures of a liver fluke in livestock. (2mks)
- Controlling fresh water snail which is the intermediate host of liver fluke.
- Chemically control by use of copper sulphate solution added to stagnant water to kill the snail.
- Draining of swampy areas.
- Burning of pastures during dry seasons.
- Not grazing of animals near marshy or water logged areas.
- Routine drenching of animals with ant helminthes.
- State two signs that shows that a cow is about to parturate. (2mks)
- Restlessness.
- Loss of appetite.
- Clear discharge from vulva
- Vulva enlargers/swells.
- State four signs of infestation by external parasites in livestock. (2mks)
- Anaemia
- Irritation/scratching
- Loss of hair
- Wounds on skin
- Presence of parasites on the body.
- Name two notifiable diseases in Kenya.(1mks)
- Foot and mouth
- Newcastle
- Anthrax
- African swine fever
- State four reasons for feeding colostrums to calves immediately after parturition. (4mks)
- It is highly digestable
- It is highly nutritious and contains for growth and disease resistance.
- It has antibodies that enable calf to resist early diseases infection.
- It is good in cleaning the bowel of the calf(has a laxative effect)
- It is highly palatable.
- Distinguish between mothering ability and prolificacy as used in livestock breeding. (2mks)
- Mothering ability- caring for young ones(kindness)
- Prolificacy- ability to give birth to more than one young ones (production of many offspring e.g in sheep, pigs in one parturition)
- Name the vegetative part of each of the following crops which is propagated. (2mks)
- Sweet potatoes…………………….stem cutting/vine/tuber
- Cassava……………………………stem cutting
- Bananas……………………………suckers
- Oranges……………………………bud/bud wood
- Name two methods of weed control in pasture.(1mk)
- Timely land preparation
- Slashing
- Application
- Application of selective herbicides
- Uprooting of weeds
- Name four methods used in identifying farm animals. (2mks)
- Ear tagging
- Branding
- Ear notching
- State two reasons why it is necessary to have individual calf pens instead of communal calf pen. (1mks)
- To avoid licking each other I leading to hair balls in rumen.
- Reduce the spread of parasite e.g worms.
- Provide individual care by farmer/attendant.
- State two effects of HIV/AIDS on agricultural production. (1mk)
- Leads to shortage of labour
- A lot of money is spent on treatment and hospitalization of people with HIV/AIDS.
- Leads to low food supply and poverty due to loss of market for agricultural products.
- Resources use in treatment of HIV/AIDS could be used in agricultural production.
- Less time is spent on farming activities because a lot of time is spent looking after people with HIV/AIDS.
- State four reasons for maintaining farm tools and equipment in proper condition. (2mks)
- Increases durability.
- To reduce the replacement cost.
- Increased efficiency.
- To avoid injury to the farmer.
- To avoid damage to the tool.
- Give four factors which characterize small scale farming. (2mks)
- Small size of land.
- Limited capital.
- Limited tools/equipment
- Less labour is required.
- Maximum use of available labour.
- Give four benefits of conservation of forage. (2mks)
- Provide feed during period of scarcity.
- Ensure proper utilization of land.
- Can be sold.
- Future anticipation of weather changes.
- Name four suitable sites for agro forestry. (2mks)
- Farm boundaries
- Homestead
- Terraces
- Riverbanks/water catchment areas
- Steep slopes/slopes
- Within pasture land.
- Give objectives of land settlement and resettlement in Kenya.(2mks)
- Settle landless citizens.
- To ease population pressure
- To increase agricultural productivity.
- To improve people’s standards of living.
- To create employment.
SECTION B 20MKS
- The diagram below is an illustration of an egg. Study it carefully and answer the questions that follow.
- Name the parts labeled (3mks)
- A.......shell
- B……inner shell membrane
- C……outer membrane
- D……albumen/egg white
- E……chalazae
- State the qualities of the part labelled A that should be considered when selecting eggs for incubation. (2mks)
- Text/smoothness of the cell
- Absence of cracks on the shell
- Cleanliness/absence of blood stains
- Oval in shape
- What is the function of the part labeled E in a fertilized egg. (1mks)
- Provide nutrients for the developing embryo/chick
- Name the parts labeled (3mks)
- Study the diagram below and answer the question that follows.
- What is layering?
- Inducing part of a stem to produce root while still attached to the mother plant.
- Identify the type of layering shown below
- Trench layering
- Give two advantages of tissue culture in crop production
- Produces pathogen free plants.
- Mass production of propagules.
- Its fast
- Requires less space
- What is layering?
- The diagram below illustrates an experiment on soil. Study it carefully and anwser the question that follow.
- State the aim of the experiment. (1mk)
- to compare soil porosity/drainage/water holding capacity of different soils.
- If the volume of water illustrated in the measuring cylinder was observed after one hour, identify the soil sample labeled I and II and give reasons.
- Soil sample
- I…sandy soil
- Reasons
- Large air space does not hold water
- Soil sample
- II……loam soil
- Reason.
- Higher water holding capacity compared to A
- Soil sample
- State two ways in which the soil structure of the soil sample labeled III above can be improved. (2mks)
- State the aim of the experiment. (1mk)
- State four reasons why docking/tailing is done in wool. (2mks)
- To facilitate even distribution of fat .
- Easy trypping
- Prevent blow fly infestation.
- Prevent dirtying wool.
- State two management practices that should be carried on a knapsack sprayer. (1mk)
- Wash thoroughly and dry after use.
- Unblock nozzle that are blocked
- Tighten any loose parts.
- Grease morable parts e.g trigger valve
- Replace or repair worn out parts e.g.
- Nozzle and washers.
-
- State two reasons why bees swarm. (2mks)
- Shortageof food and water in their surrounding
- Outbreak of pest and disieses.
- Damage of broad combs
- Lack of adequate ventilation.
- Dampness and bad smell.
- Overcrowding e.t.c
- State two methods of tick control. (1mk)
- Natural or biological method
- Self-licking by animals
- Interfering with or altering tick environment
- Spraying
- Fencing
- Dipping
- Hand dressing
- Hand picking e.t.c
- State two reasons why bees swarm. (2mks)
SECTION C 40MKS
-
- State five differences between ruminants and non-ruminants. (5mks)
- ruminants chew the cud while non-remnant do not ched cud.
- Ruminants have four stomach chamber thus polygastric while non-rumminants have one stomach chamber
- Rumnants regurgitate food while non-ruminants do not regurgitate once swallowed.
- Ruminants can digest cellulose while non-ruminants cannot digest cellulose.
- Ruminants have no ptyalin in saliva hence no enzymatic digestion in the mouth while non-rumunants digestion starts from mouth.
- In ruminants most digestion and absorption takes place in the rumen while non-ruminants take place in small intestines.
- Ruminants have alkaline saliva due to presence on ammonia while non-ruminants have neutral.P.H
- Discuss calf rearing from birth to first calving.
- Ensure the calf is breathing or perform artificial respiration.
- Ensure the calve is licked by the mother or wipe it with dry cloth.
- Disinfect the umbilical cord to prevent infection.
- Keep the calf in a warm pen.ensure the calf gets colostrums to satisfaction.\
- Ensure the calf gets millk upto the 10th week for early weaning.
- Ensure the calf gets early weaning concentrates e.g calf pellets.
- Introduce green fodder
- Control parasites i.e. ticks by sparaying weekly or dipping.
- Control diseases by vaccination againt infectious diseases and treatment.
- Identification of male calfes e.g ear tagging/ear nitching, branding e.t.c
- Castration of masle not selected for breeding.
- Removal of extra teats especially for females born with vestigial teats.
- Dehorning, desbuddling of all calves with horns.
- Steaming uop at 2 months to parturition.
- Incase of malpresentation, a veterinarian office is called to assist.
- State five problems that farmers are likely to face when marketing their produce.
- Perishability
- Limited elasticity of demand
- Seasonality
- Lack of market information
- Bulkiness
- Changes of supply
- Storage
- Lack of efficiency innmarketing
- Poor transport system
- Changes in market demand.
- State five differences between ruminants and non-ruminants. (5mks)
-
- Illustrated below is a method of turning compost. Study the method and answer the questions that follow.
- Identify the methods. (1mk)
- Four heap system
- Using arrows in the diagram show how the turning is done before the manure can be taken to the field. (2mks)
-
- which other methods can be used to prepare the manure.(1mk)
- Seven heap method
- After how long should the compost be ready for use? (1mk)
- Three months
- which other methods can be used to prepare the manure.(1mk)
- Identify the methods. (1mk)
-
- state four reasons for maintaining farm tools and equipment in proper condition. (2mks)
- Increase durability
- To reduce replacement cost
- Increase efficiency
- To avoid injury to the farmer
- To avoid damage to the tool.
- list three factors that makes embryo transplant unpopular with many livestock farmers.(3mks)
- Its expensive
- Labour demanding
- Requires a lot of skills
- Requires special equipment for fertilization and storage of embryo.
- An agriculture student was adviced to apply a complete fertilizer 40:30:10 in a 20m by 10m plot at a rate of 400g per hectare.
- Calculate the percentage of p2o5 in the cmlete fertizer. (3mks)
40:30:10 represents n:p2o:k2o respectively
Total ratio=40+30+10=80
P2O5 as a percentage of the total is
30/80 x 100 = 37.5% - Calculate the amount of fertilizer the student would require for the plot. (3mks
Iha=10,000m2
Area of the plot
=20 x10 = 200m2
10,000m2 would require 400 kg of
Fertile
1m2 = 400 kg
10000
200m2 will require
400 x 200 = 8kg
10000
The plot therefore requires complete 8kg fertilizer - Calculate the amount of k2o that would be contained in 600kg of a compound fertilizer.
30:20:10 (NP2O2:K2O) respectively.
30:20:10 is contained in 100 kg
10kg k20 is contained in 100kg fertilizer
600kg fertilizer contains
600 x10 k2o
100
60kg k2o
- Calculate the percentage of p2o5 in the cmlete fertizer. (3mks)
- state four reasons for maintaining farm tools and equipment in proper condition. (2mks)
- Illustrated below is a method of turning compost. Study the method and answer the questions that follow.
- Describe the production oftomateos under the following sub-heading:
- Nursery production (12mks)
- Clear land/pangas/slashes
- Mark corners with pegs/sisal twine
- Dig to a depth of 15cm/forked jembe
- Break the clod/spade/hoe/fine tilth
- Rake out the debris
- Level top using rake/wood board
- Raise the side to about 15cm
- Make drills using a hand fork 2-3cm deep of a spacing of 15 to 20cm (inter row spacing)
- Apply a thin layer of organic mulch*dry grass free from weeds seed.
- Transplanting
- Uplift watered seedilng from the nursery using a trowel in the evening at the onset of long rains.
- Place them in the planting toles
- Cover the root zone/ root base with soil rich in organic manure and phosphatic fertilizers.
- Mulch the roof base/dryfree rass.
- Water thoroughly with a watering can
- Field management practices. (3mks)
- Gapping/spacing seedlings which have not picked up
- Top dressing/nitrogenous fertilizer/calcium CAN.
- Pruning/removing roots from the main stem
- Clean weeding
- Staking/ ensure no lodging.
- Pest control through spraying with fungicides.
- Nursery production (12mks)
Download Agriculture Paper 2 Questions and Answers - Form 3 Term 2 Opener Exams 2023.
Tap Here to Download for 50/-
Get on WhatsApp for 50/-
Why download?
- ✔ To read offline at any time.
- ✔ To Print at your convenience
- ✔ Share Easily with Friends / Students