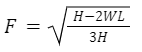- This paper consists of two sections: Section I and Section II.
- Answer all questions in section I and any five questions in Section II.
- Show all the steps in your calculations, giving your answers at each stage in the spaces below each question.
- Marks may be given for correct working even if the answer is wrong.
- KNEC Mathematical tables may be used.
SECTION I (50 marks)
- Without using a calculator evaluate (3 marks)
21/3 − 12/3 ÷ 5/9
4/7 of 21/3 − 22/7 - Simplify the expression. (3 marks)
18xy−18xr
9xr−9xy - Solve the equation sin (5/2x) = −½ for 0°≤x≤360° (3 marks)
- The sum of the interior angles of a regular polygon is 1800°. Find the size of each exterior angle (3 marks)
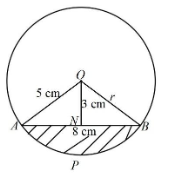
- In the figure below the shaded region is a segment of the circle with Centre O and radius r. AB=8 cm, ON = 3 cm, angle AOB =106.3°.
Find the area of the shaded part. (4 marks) - Simplify the expression √48 leaving your answer in the form a+b√c where a, b and c are integers. (3 marks)
√5 + √3 - By use of a quadratic formula solve the equation (3 marks)
2P(P+1)=4 - Solve for x in the equation (3 marks)
32(x−3) ÷ 8(x−4) = 64 ÷ 2x - Use logarithms correct to 4 decimal places to evaluate; (4 marks)
- Make H the subject of the formula (3 marks)
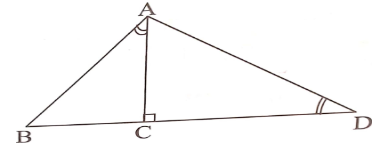
- In the figure below angle BAC and ADC are equal. Angle ACD is a right angle. The ratio of the sides AC:BC =4:3. Given that area of triangle ABC is 24 cm2, find the area of triangle ACD. (3 marks)
- Evaluate without using a calculator or a mathematical table, (3 marks)
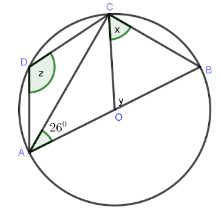
log (3x+8) − 2 = log (x − 4) - In the figure below O is the centre .Calculate the angles marked x ,y and z (3 marks)
- The exchange rate in January 2000 was US $ 1 = Ksh 75.60 and UK £1 = Ksh 115.80. A tourist came to Kenya with US $ 5000 and out of it spent ksh.189,000. He changed the balance in UK£. How many pounds did he receive? (3 marks)
- The length and width of a rectangle are given to the nearest 0.1 cm as 18.5 cm and 12.4 cm respectively. Calculate the percentage error in the area of the rectangle. (3 marks)
- Solve the following inequalities and hence state the integral values that satisfy the inequalities. (3 marks)
x + 1 ≤ 4x −5 < 3x+2
SECTION II (50 Marks)
-
- L1 is a line which passes through (2, 5), (5, 16) and (−4, h). Find the equation of the line and the value of h. (3 marks)
- Equation of L2 is 3y + x =23 and it intersects line L1 at point A. Find the co-ordinates of A. (2 marks)
- B (−1, p) is on line L1. Find p hence find the length of AB. (2 marks)
- C(t, 9) is on the line L2. Find t. It is given that the line L3 passes through C and parallel to L1. Find the equation of L3 (3 marks)
- The table below shows the rates of taxation in a certain year.
In that year, Juma was earning a basic salary of Ksh. 41 000 per month. In addition he was entitled to a house allowance of Ksh. 13 000 p.m. and a personal relief of Ksh. 1056 p.m.Income in K£ p.a Rates in Ksh per K£ 1 - 3900 2 3901- 7800 3 7801 - 11700 4 11701 - 15600 5 15601 - 19500 7 19501 and above 9 - Calculate Juma’s taxable income in K£ per annum. (2 marks)
- How much tax did he pay per month? (5 marks)
- His other deductions per month included: Sacco contribution of Ksh 4000 and loan repayment of Ksh 5 500. Calculate Juma’s net salary. (3 marks)
- The distance between towns A and B is 360km .A minibus left town A at 8.15a.m and travelled towards town B at an average speed of 90km/hr .A matatu left town B two and a third hours later on the same day and travelled towards town A at an average speed of 110km/hr.
-
- At what time did the two vehicles meet (4 marks)
- How far from town A did the two vehicles meet (2 marks)
- A motorist started from his home at 10.30 a.m. on the same day as the matatu and travelled at an average speed of 100km/hr .He arrived at B at the same time as the minibus .Calculate the distance from A to his house. (4 marks)
-
- A triangle ABC with vertices A(−4,2), B(−6,6) and C(-−6,2) undergoes enlargement scale factor −1 and centre (−2,6) to produce triangle A'B'C'.
- On the grid provided draw triangle ABC and its image A'B'C', state the co-ordinates of ∆A'B'C' (4 marks)
- Triangle ∆A'B'C' is the reflected in the line y+x=0 to give ∆A''B''C''. Draw triangle ∆A''B''C'' and state the co-ordinates of its vertices. (3 marks)
- If triangle A'B'C' is mapped onto a triangle whose co-ordinates are '''(−4,−2) , B'''(−6,−6) and C'''(−6,−2) by a rotation, find the centre and angle of rotation. (3 marks)
- Three quantities R, S and T are such that R varies directly as S and inversely as the square root of T.
- R = 480 when S = 150 and T = 25.Write an equation connecting R, S and T. (4 marks)
- Find;
- The value of R when S = 360 and T = 2.25. (2 marks)
- The percentage change in R if S is increased by 5% and T decreased by 15.36%. (4 marks)
- The diagram below represents a lampshade in the form of an open-ended frustum of a cone. Its bottom and the top diameters are 14cm and 7cm respectively. Its height is 10cm. Use (π=3.142)
- Find
- The height of the cone from which the frustum was cut. (2 marks)
- The area of the curved surface of the frustum (5 marks)
- The material used for making the lampshade is sold at Shs.800 per square metre. Find the cost of 10 lampshades if a lampshade is sold at twice the cost of the material. (3 marks)
- Find
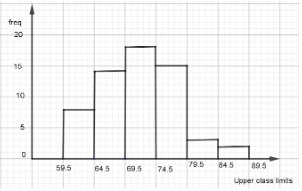
- The table below shows the mass of 60 women working in hotels
Mass (Kg) 60 - 64 65 - 69 70 - 74 75 - 79 80 - 84 85 - 89 No. of women 8 14 18 15 3 2 - State:
- The modal class (1 mark)
- The median class (1 mark)
- Estimate the mean mark (4 marks)
- Draw a histogram for the data (2 marks)
- State:
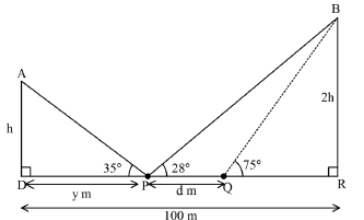
- Two vertical walls of height h and 2h respectively stand on a level ground and the walls are 100m apart. From a point P which is y m from the shorter wall, the angles of elevation of the top of the walls are 35° and 28° respectively. From another point Q, d metres from P, the angle of elevation of the top of the taller building is 75° as shown.
Calculate;- The vertical heights of the two walls. (6 marks)
- The distance PQ in metres correct to 1 decimal place. (4 marks)
MARKING SCHEME
| No | Working | Remarks | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 1. | N⟹7/3 − (5/3 ÷ 5/9) = −2/3D ⟹ (4/7 × 7/3) − 16/7 = −20/21
N/D = −2/3 × − 21/20 = 7/10
|
M1M1 A1 |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 2. |
N ⟹ 18x (y−r)
D ⟹ −9x(y−r)
N/D ⟹ 18x(y−r) = −2
−9x(y−r) |
M1 M1 A1 |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 3. | (½) = 30°
But sine is negative in 3rd and 4th quadrants
5/2x = 210°, 330°, 570° and 690°
x = 84°, 132°, 228° and 276°
|
B1 for sine inverse B1 B1 |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 4. | (2n−4)90 = 1800
2n−4 = 20
n = 12 sides
ext angle = 360/12 = 30°
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 5. | r = 8×sin 36.85 = 5 cm sin 106.3
Area of segment = (106.3 × 22 × 25 − (½ × 25 × sin 106.3) 360 7 = 23.19 – 12
= 11.192
|
M1 M1 M1 A1 |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 6. | √48 × √5 − √3 √5 + √3 √5 − √3 (√48 × √5) − (√48 × √3) 5 − 3 4√15 − 12 ⇒ 2√15 − 6 2 |
M1 for conjugate pair M1 simplification A1 |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 7. | −2 ± √36 4 p = 1 OR p = −2 |
M1 M1 A1 |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 8. |
25(x−3) ÷ 23(x−4) = 26−x
5x −15 − 3x + 12 = 6−x
5x − 3 + x = 15 −12 + 6.
3x = 9
x = 3
|
M1 M1 A1 |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 9. | 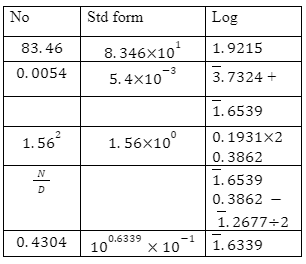 |
M1 All correct logs
M1 Addition and Subtraction M1 Square root
A1 correct answer
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 10. | F2 = H − 2WL 3H 3HF2 = H − 2WL H − 3HF2 = 2WL H = 2WL 1 − 3F2 |
M1 M1 A1 |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 11 |
ASF = LSF2
(4/3)2 = 16/9
Area of triangle ACD = 16 × 24
9 = 422/3cm2
|
M1 M1 A1 |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 12. |
log (3x+8) = log x − 4
23 3x+8 = x−4
8 3x+8 = 8x−32
5x = 40
x = 8
|
M1 Appropriate use of logarithmic laws |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 13. |
<x = 90 − 26 = 64°
<y = 2×26 = 52°
<z = 180−64 =116°
|
B1 B1 B1 |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 14. | Total Ksh received = 5000 x 75.60 = Ksh.378 000
Bal in Ksh 378000 − 189000 = Ksh.189 000
UK £ recieved = 189000 = UK£ 1,632.12
115.80 |
M1 M1 A1 |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 15. | Working area = 18.5×12.4 = 229.4cm2
Maximum area = 18.55×12.45 = 230.9475cm2
Minimum area = 18.45×12.35 = 227.8575cm2
Absolute error in area = 230.9475 − 227.8575 =1.545
2 Percentage error = 1.545 × 100 = 0.6735%
229.4 |
M1 max and min area M1 absolute error A1 |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 16. |
x+1 ≤ 4x − 5
−3x ≤ −6
x ≥ 2
4x − 5 < 3x+2
x < 7
Integral values 2,3,4,5, and 6
|
M1 M1 A1 |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| SECTION II | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 17. |
|
M1 M1 A1 M1 A1 M1 A1 M1 M1 A1 |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 18. |
|
M1 A1 M1 M1 M1 M1A1 M1 M1 A1 |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 19. |
|
M1 A1 M1 A1 M1A1 B1 B1 M1A1 |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 20. | 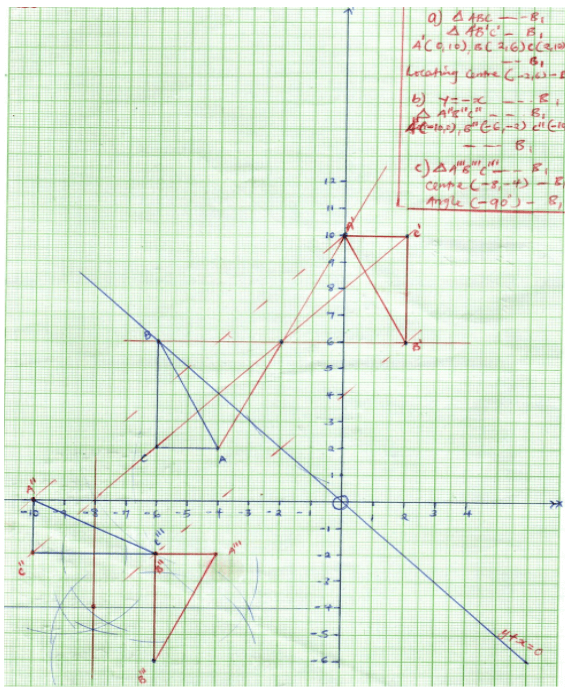 |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 21. |
|
M1 M1A1 B1 M1A1 M1 M1 M1A1 |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 22 |
|
M1 A1 M1 M1 M1 M1A1 M1 M1 A1 |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 23. |
|
B1
B1
B1 for fx column
B1 for f column
M1 A1
B1 for scale
B1 for blocks
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 24. |
|
A1 |
Download Mathematics Paper 2 Questions and Answers - Form 3 End Term 2 Exams 2023.
Tap Here to Download for 50/-
Get on WhatsApp for 50/-
Why download?
- ✔ To read offline at any time.
- ✔ To Print at your convenience
- ✔ Share Easily with Friends / Students