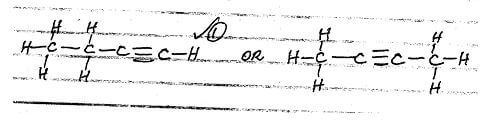CHEMISTRY
FORM 4
END TERM EXAMS
TERM 1 2021
PAPER 1
TIME 2 hrs
INSTRUCTIONS
- Answer all the questions
-
- State one disadvantage of using flower extracts as acid – base indicators. (1mk)
- Name the indicator that can be used in the laboratory to tell the pH of lemon juice.(1mk)
- Differentiate between strong and weak acids. (1mk)
-
- What are isotopes? (1mk)
- Determine the number of neutrons in (1mk)
- When magnesium is burnt in air it reacts with both oxygen and nitrogen gas giving a white ash. Write two equations for the reactions that take place. (1mk)
- A solution contains 29.1g per litre of aluminium Sulphate. Calculate the number of Sulphate ions in 350cm3 of the solution.(Al = 27, S = 32, O = 16) Avogadro’s constant = 6.0 x 1023. (2mks)
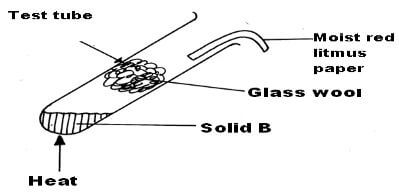
- When a solid B was heated in a test-tube, it gave off two gases. The two gases were seperates by passing them through a plug of glass wool in a test-tube as shown below.
The first gas which evolved turned moist red litmus paper to blue. Later the other gas involved turned the litmus back to red.- Identify solid B (1mk)
- Write the equation for the reaction that take place in the test tube (1mk)
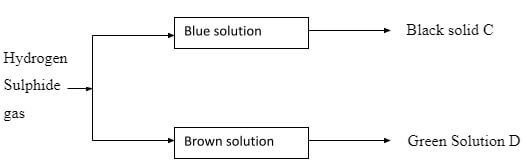
- Hydrogen Sulphide gas was bubbled into two solutions of metallic nitrates as shown in the flow diagram below
- Identify the black solid C (1mk)
- Write an ionic equation for the formation of the green solution (1mk)
- State the property of Hydrogen Sulphide shown by the formation of solution D (1mk)
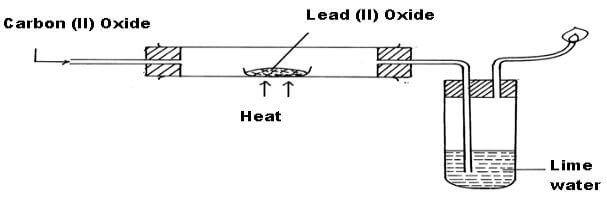
- The apparatus shown below was used to investigate the effect of Carbon (II) Oxide on Lead (II) Oxide.
- State the observation made in the combustion tube during the experiment. (2mks)
- Write the equation for the reaction that take place in test-tube E. (1mk)
-
- Lime water is also used to soften hard water. Why is this method not preferred to soften hard water. (1mk)
- Name a compound that causes temporary hardness of water. (1mk)
- State one disadvantage of using hard water for domestic purpose. (1mk)
-
- Name the compound below
CH3CH2CH = CH2 - Draw and name other isomers of the compound in (a) above. (2mks
- Name the compound below
- A white solid dissolve in water to form a colourless solution. The colourless solution forms a white precipitate with Ammonia solution but dissolve in excess alkali. The colourless solution forms a white precipitate with Lead (II) Nitrate solution. The white Precipitate dissolve on warming to form a colourless solution.
- Write the chemical formulae for the ion formed when the colourless solution react with excess ammonia solution. (1mk)
- Write the name of the ion present in the white solid. (1mk)
- What is an alkali (1mk)
- The solubility of Potassium Manganate (VII) at 20ºC is 13g per 100g of water and at 90ºC is 60g per 100g of water.
- Determine the mass of Pottassium (VII) Manganate present in 80g of saturated solution at 90ºC. (1mk)
- Calculate the mass of Pottassium (VII) Manganate that would crystallize out if the solution in (a) were cooled to 20ºC. (2mks)
-
- Explain why concentrated Sulphuric (VI) acid is a poor electrolyte and has no effect on blue litmus paper whereas 2M Sulphuric (VI) acid conducts electricity and changes blue litmus paper red. (1mk)
- What is a binary electrolyte. (1mk)
- An element F has a relative atomic mass of 88. When a current of 0.5 amperes was persed through the fused chloride of F for 20 minutes and 20 seconds, 0.278g of F were deposited at the cathode. Determine the charge on ion of F (1Faraday = 96500C). (2mks)
- Below is a cross- section of a charcoal burner
- Charcoal is a form of impure carbon. Name any other two allotropes of carbon. (1mk)
- Write an equation for the reaction taking place at the part marked B. (1mk)
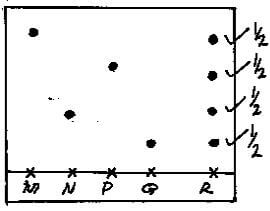
- The diagram below represents paper chromatogram of four types of sugar.
- Identify the most stable sugar. (1mk)
- On the diagram, show the chromatogram of R. Given that R contains all the other sugars(2mks)
- The empirical formula of a hydrocarbon is C2H3. The hydrocarbon has a relative molecular Mass of 54. (H = 1, C = 12)
- Determine the molecular formula of the hydrocarbon. (1mk)
- Draw the structural formulae of the hydrocarbon in (a) (1mk)
- To which homologous series does the hydrocarbon in (b) above belong? (1mk)
- State three factors that increase the rate of reaction for the following reaction. (3mks)
CaCO3(s) + 2HCl(aq) CaCl2(aq) + CO2(g) + H2O(aq) - In terms of structure and bonding explain the following
- Melting point of Magnesium is higher than that of Sodium. (3mks)
- Melting point of Chlorine is lower than that of Iodine. (1mk)
- The set-up below was used to prepare a solution of hydrogen chloride gas
- Identify solid S (1mk)
- Identify one mistake in the set up. (1mk)
- Write an equation for the reaction taking place in the flask. (1mk)
-
- State Gay-Lussac’s law (1mk)
- 10cm3 of a gaseous hydrocarbon, CxHy required 30cm3 of oxygen for complete combustion. If steam and 20cm3 of Carbon (IV) oxide were produced, what is the value of x in CxHy. (2mks)
- Starting with lead metal, describe how a dry sample of Lead(II) chloride can be prepared in the laboratory. (3mks)
- An ion T2- has an electronic arrangement of 2.8
- What is the atomic number of the element. (1mk)
- To which group and period does the element belong to;
Group__________________________________________________ (1mk)
Period__________________________________________________ (1mk)
- Using dot (.) and cross (x) diagram show the type of bond present in hydrogen ion, H3O+
(H = 1, O = 8) (2mks) - A mixture of Hydrogen gas and Carbon (IV) oxide are passed through Potassium hydroxide solution as shown below.
- State the observation made in the conical flask. (1mk)
- Write the equation for the reaction that takes place in:-
- the conical flask (1mk)
- the burning of gas x (1mk)
- 20cm3 of a solution containing 4g per litre of Sodium hydroxide was neutralized by 8cm3 of dilute Sulphuric (VI) acid. Calculate the concentration of the acid in moles per litre.(Na = 23, O = 16, H=1) (3mks)
- Given that the hydration energies of Ca2+(g) and Cl-(g) are -1562KJ/Mole and -364KJ/Mole respectively. The heat of solution (Hsoln) for one Mole of CaCl2 is -82.9 KJ/Mole. Determine the lattice energy for CaCl2. (2mks)
- The diagram below is used to prepare nitrogen (IV) oxide gas.
- Identify substance V (1mk)
- State and explain one precaution taken when carrying out the experiment. (2mks)
- Electrode potentials for the half cells are shown below. Use the information to answer the questions that follow.
Sn2+(aq)+2e- Sn(s) ; = -0.14V
Cu2+(aq)+2e- Cu(s) ; = -0.34V- Write the cell representation for the cell made up of two half cells. (1mk)
- Write the cell equation for the cell reaction. (1mk)
- Calculate the value for the cell. (1mk)
- State the function of each of the following in the solvay process of production of Sodium Carbonate.
- Coke (1mk)
- Cold water on the carbonation. (1mk)
- Ammonia a generator. (1mk)
-
- A student in form three was given two gases C2H6 and C2H4. He added acidified Potassium Manganate (VII) to each solution. State the observations the student made. (2mks)
- State one use of C2H4.
MARKING SCHEME
- State one disadvantage of using flower extracts as acid – base indicators. (1mk)
- The composition of the extract continuously changes with time so the acid or base and also changes with colour with time.
- Name the indicator that can be used in the laboratory to tell the pH of lemon juice.(1mk)
- Universal indicator
- Universal indicator
- Differentiate between strong and weak acids. (1mk)
- A strong acid is one that dissociate fully in aqueous solution A weak acid is one which dissociate partially in aqueous solution.
- State one disadvantage of using flower extracts as acid – base indicators. (1mk)
-
- What are isotopes? (1mk)
- Are atoms of the same element with the same atomic number but different mass number.
- Determine the number of neutrons in 1818O(1mk)|
- 18 – 8 = 10 neutrons
- 18 – 8 = 10 neutrons
- What are isotopes? (1mk)
- When magnesium is burnt in air it reacts with both oxygen and nitrogen gas giving a white ash. Write two equations for the reactions that take place. (1mk)
- -2Mg(s) + O2(g)→2MgO(s)
-3Mg(s) + N2(g)→Mg3N2(s)
- -2Mg(s) + O2(g)→2MgO(s)
- A solution contains 29.1g per litre of aluminium Sulphate. Calculate the number of Sulphate ions in 350cm3 of the solution.(Al = 27, S = 32, O = 16) Avogadro’s constant = 6.0 x 1023. (2mks)
- Molar mass of Al2(SO4)3 = 27 x 2 + (32 x 3) + (16 x 4 x 3) = 342
Moles of Al2(SO4)3 in 1000cm3 = ✓ ½
Moles of Al2(SO4)3 in 350cm3 =
Al2(SO4)3(aq) →2Al3+(aq) + 3SO42-(aq)
1 mole of Al2(SO4)3 produce 3 moles of SO42- ions
0.02979 moles → 0.02979 x 3 moles of SO42- ions
Number of SO42- ions = 0.08937 x 6.0 x 1023 = ✓5.36 x 1022 ions.
- Molar mass of Al2(SO4)3 = 27 x 2 + (32 x 3) + (16 x 4 x 3) = 342
- When a solid B was heated in a test-tube, it gave off two gases. The two gases were seperates by passing them through a plug of glass wool in a test-tube as shown below.
The first gas which evolved turned moist red litmus paper to blue. Later the other gas involved turned the litmus back to red.- Identify solid B (1mk)
- Ammonium Carbonate
- Ammonium Carbonate
- Write the equation for the reaction that take place in the test tube (1mk)
(NH4)2 CO3(S) 2NH3(g) + CO2(g) + H2O(l)
- Identify solid B (1mk)
- Hydrogen Sulphide gas was bubbled into two solutions of metallic nitrates as shown in the flow diagram below
- Identify the black solid C (1mk)
Copper(II) Sulphide. - Write an ionic equation for the formation of the green solution (1mk)
Fe3+(aq)→Fe2+(aq)+e- - State the property of Hydrogen Sulphide shown by the formation of solution D (1mk)
Reducing agent
- Identify the black solid C (1mk)
- The apparatus shown below was used to investigate the effect of Carbon (II) Oxide on Lead (II) Oxide.
- State the observation made in the combustion tube during the experiment. (2mks)
- Yellow solid changes to✓ orange then to grey✓1
- Yellow solid changes to✓ orange then to grey✓1
- Write the equation for the reaction that take place in test-tube E. (1mk)
CO2(g)+CO2(OH)2(aq)→CaCO3(s)+H2O(l)
- State the observation made in the combustion tube during the experiment. (2mks)
-
- Lime water is also used to soften hard water. Why is this method not preferred to soften hard water. (1mk)
- Only remove temporary✓1 water hardness and not permanent water hardness.
- Only remove temporary✓1 water hardness and not permanent water hardness.
- Name a compound that causes temporary hardness of water. (1mk)
- Calcium hydrogen Carbonate
- Magnesium hydrogen carbonate
- State one disadvantage of using hard water for domestic purpose. (1mk)
- Wastes soap due to formation of scum
- Lime water is also used to soften hard water. Why is this method not preferred to soften hard water. (1mk)
-
- Name the compound below
CH3CH2CH = CH2- But-1-ene (1mk)
- But-1-ene (1mk)
- Draw and name other isomers of the compound in (a) above. (2mks)
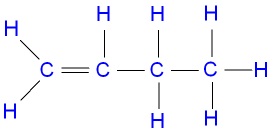
- Name the compound below
- A white solid dissolve in water to form a colourless solution. The colourless solution forms a white precipitate with Ammonia solution but dissolve in excess alkali. The colourless solution forms a white precipitate with Lead (II) Nitrate solution. The white Precipitate dissolve on warming to form a colourless solution.
- Write the chemical formulae for the ion formed when the colourless solution react with excess ammonia solution. (1mk)
- [Zn(NH3)4]2- (1mk)
- [Zn(NH3)4]2- (1mk)
- Write the name of the ion present in the white solid. (1mk)
- Chloride ion (1mk)
- Chloride ion (1mk)
- What is an alkali (1mk)
- An alkali is a soluble base (1mk)
- An alkali is a soluble base (1mk)
- Write the chemical formulae for the ion formed when the colourless solution react with excess ammonia solution. (1mk)
- The solubility of Potassium Manganate (VII) at 20ºC is 13g per 100g of water and at 90ºC is 60g per 100g of water.
- Determine the mass of Pottassium (VII) Manganate present in 80g of saturated solution at 90ºC. (1mk)
- 60g per 100g of water;total mass of saturated solution = 16g
- 160g of saturated solution→13g of KMnO4
- 80g of saturated solution→80x60/160 30g ✓ ½ of KMnO4 1mk
- Calculate the mass of Pottassium (VII) Manganate that would crystallize out if the solution in (a) were cooled to 20ºC. (2mks)
- At 20ºC:
113g of saturated solution →13g of KMnO4
80g of saturated solution → 80x13/113=9.204
At 90ºC: - 80g of saturated solution →30g of KMnO4
- At 200C:80g of saturated solution →9.204g
- Mass of KMnO4 crystalizes out
- 30-9.204g ✓ ½ (2mks)
- At 20ºC:
- Determine the mass of Pottassium (VII) Manganate present in 80g of saturated solution at 90ºC. (1mk)
-
- Explain why concentrated Sulphuric (VI) acid is a poor electrolyte and has no effect on blue litmus paper whereas 2M Sulphuric (VI) acid conducts electricity and changes blue litmus paper red. (1mk)
- Concentrated Sulphuric (iv) acid has no ions ✓ ½ (it is covalent) 2M of Sulphuric (vi) acid has H+ ions and SO42- ions ✓ ½ (1mk)
- What is a binary electrolyte. (1mk)
- A substance in molted form conducts electricity but contains only two specifically one type of cation ion and specially one type of anion.(1mk)
- A substance in molted form conducts electricity but contains only two specifically one type of cation ion and specially one type of anion.(1mk)
- Explain why concentrated Sulphuric (VI) acid is a poor electrolyte and has no effect on blue litmus paper whereas 2M Sulphuric (VI) acid conducts electricity and changes blue litmus paper red. (1mk)
- An element F has a relative atomic mass of 88. When a current of 0.5 amperes was passed through the fused chloride of F for 20 minutes and 20 seconds, 0.278g of F were deposited at the cathode. Determine the charge on ion of F (1Faraday = 9650ºC). (2mks)
- Quantity of electricity Q=It
=0.5x[(20x60)+20]
=61ºc ✓ ½
9650ºc→ 1 Faraday ✓ ½
61º → 0.006321244 x 88/0.278
The change on the ion is +2 ✓ ½ (2mks)
- Quantity of electricity Q=It
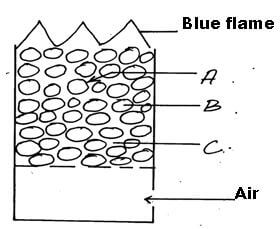
- Below is a cross- section of a charcoal burner
- Charcoal is a form of impure carbon. Name any other two allotropes of carbon. (1mk)
- Diamond ✓ ½
- Graphite ✓ ½ (1mk)
- Write an equation for the reaction taking place at the part marked B. (1mk)
CO2(g)+C(s) →2CO(g) (1mk)
- Charcoal is a form of impure carbon. Name any other two allotropes of carbon. (1mk)
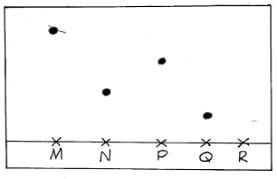
- The diagram below represents paper chromatogram of four types of sugar.
- Identify the most stable sugar. (1mk)
Q - On the diagram, show the chromatogram of R. Given that R contains all the other sugars(2mks)
- Identify the most stable sugar. (1mk)
- The empirical formula of a hydrocarbon is C2H3. The hydrocarbon has a relative molecular Mass of 54. (H = 1, C = 12)
- Determine the molecular formula of the hydrocarbon. (1mk)
- (C2H3)x =54 ✓ ½
x[12x2 + 3x1] =54
24x+3x=54
24x=54
x = 54/27
x=2
(C2H3)2 =C4H6 ✓ ½ (1mk)
- (C2H3)x =54 ✓ ½
- Draw the structural formulae of the hydrocarbon in (a) (1mk)
- To which homologous series does the hydrocarbon in (b) above belong? (1mk)
- Alkynes ✓ 1(reject alkyne without ( s))
- Alkynes ✓ 1(reject alkyne without ( s))
- Determine the molecular formula of the hydrocarbon. (1mk)
- State three factors that increase the rate of reaction for the following rection. (3mks)
CaCO3(s) + 2HCl(aq) CaCl2(aq) + CO2(g) + H2O(aq)- Surface area of CaCO3 ✓1
- Concentration of HCl ✓1
- Temperative increase ✓1
- In terms of structure and bonding explain the following
- Melting point of Magnessium is higher than that of Sodium. (3mks)
- Magnesiun metal has storage metalic✓ ½ bond than sodium in its giant metallic✓ ½ structure due to increase in number of delocalized electrons in magnesium✓1 (2mk)
- Magnesiun metal has storage metalic✓ ½ bond than sodium in its giant metallic✓ ½ structure due to increase in number of delocalized electrons in magnesium✓1 (2mk)
- Melting point of Chlorine is lower than that of Iodine. (1mk)
- Iodine has strong vander walls✓ ½ forces in its molecular structure,chlorine has weak vander waals✓ ½ forces in its molecular structure.(1mk)
- Iodine has strong vander walls✓ ½ forces in its molecular structure,chlorine has weak vander waals✓ ½ forces in its molecular structure.(1mk)
- Melting point of Magnessium is higher than that of Sodium. (3mks)
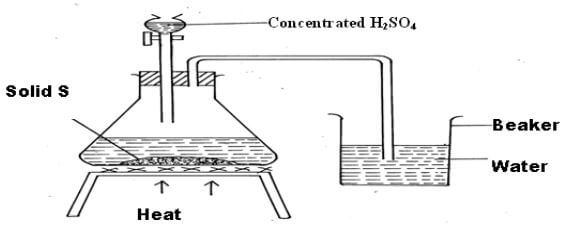
- The set-up below was used to prepare a solution of hydrogen chloride gas
- Identify solid S (1mk)
Sodium chloride or any other chloride of metal. (1mk) - Identify one mistake in the set up. (1mk)
Delivery tube to dissolve HCl(g) in water (1mk) - Write an equation for the reaction taking place in the flask. (1mk)
NaCl(s)+H2SO4(l)→NaHSO4(s)+HCl(g) (1mk)
- Identify solid S (1mk)
-
- State Gay-Lussac’s law (1mk)
- When gases react they do so in volumes which are in whole number ratio and to the volume of the products if gaseous at constant temperature and pressure.
- When gases react they do so in volumes which are in whole number ratio and to the volume of the products if gaseous at constant temperature and pressure.
- 10cm3 of a gaseous hydrocarbon, CxHy required 30cm3 of oxygen for complete combustion. If steam and 20cm3 of Carbon (IV) oxide were produced, what is the value of x in CxHy. (2mks)
- CxHy(g)+O2(g)→CO2(g)+H2O(g) ✓ ½
10cm3 30cm3 20cm3
Their volumes to mole ratio
CxHy(g)+O2(g)→CO2(g)+H2O(g) ✓ ½
1mole 3moles 2moles
CxHy(g)+3O2(g)→2CO2(g)+H2O(g) ✓
Then 2 atoms of carbon were present in CxHy and 4 atoms of Hydrogen.
C2H4(g)+3O2(g)→2CO2(g)+2H2O(g)
Thus x = 2✓ ½ (2mks)
- CxHy(g)+O2(g)→CO2(g)+H2O(g) ✓ ½
- State Gay-Lussac’s law (1mk)
- Starting with lead metal, describe how a dry sample of Lead(II) chloride can be prepared in the laboratory. (3mks)
- React excess✓ ½ Lead metal with dilute nitric(v) acid.Then filter of the unreacted lead metal to Lead (II) nitrate as filtrate.Add a solution of sodium chloride to the filtrate.A white precipitate forms✓ ½ which is Lead (II) chloride.Filter the precipitate✓ ½ and wash it with distilled water then dry it between filter paper. (3mks)
- React excess✓ ½ Lead metal with dilute nitric(v) acid.Then filter of the unreacted lead metal to Lead (II) nitrate as filtrate.Add a solution of sodium chloride to the filtrate.A white precipitate forms✓ ½ which is Lead (II) chloride.Filter the precipitate✓ ½ and wash it with distilled water then dry it between filter paper. (3mks)
- An ion T2- has an electronic arrangement of 2.8
- What is the atomic number of the element. (1mk)
8 (1mk) - To which group and period does the element belong to;
Group VI (1mk)
Period 2(1mk)
- What is the atomic number of the element. (1mk)
- Using dot (.) and cross (x) diagram show the type of bond present in hydrogen ion, H3O+
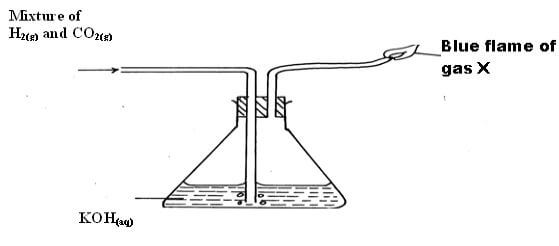
(H = 1, O = 8) (2mks) - A mixture of Hydrogen gas and Carbon (IV) oxide are passed through Potassium hydroxide solution as shown below.
- State the observation made in the conical flask. (1mk)
- Bubbles are observed (1mk)
- Bubbles are observed (1mk)
- Write the equation for the reaction that takes place in:-
- the conical flask (1mk) -
CO2(g)+2KOH(aq)→K2CO3(aq)+H2O(l) (1mk) - the burning of gas x (1mk) -
2H2(g)+O2(g)→2H2O(g) (1mk)
- the conical flask (1mk) -
- State the observation made in the conical flask. (1mk)
- 20cm3 of a solution containing 4g per litre of Sodium hydroxide was neutralized by 8cm3 of dilute Sulphuric (VI) acid. Calculate the concentration of the acid in moles per litre.(Na = 23, O = 16, H=1) (3mks)
- Molar mass of NaOH = 40✓ ½
Moles of NaOH per littre = 4/40 = 0.4M ✓ ½
Moles of NaOH reacted = ✓ ½
H2SO4(aq)+2NaOH(aq)→Na2SO4(aq)+H2O(l) ✓ ½
2moles of NaOH react with 1mole of H2SO4
Moles of H2SO4 reacting ✓ ½
Molarity of the acid =✓ ½ (3mks)
- Molar mass of NaOH = 40✓ ½
- Given that the hydration energies of Ca2+(g) and Cl-(g) are -1562KJ/Mole and -364KJ/Mole respectively. The heat of solution (Hsoln) for one Mole of CaCl2 is -82.9 KJ/Mole. Determine the lattice energy for CaCl2. (2mks)
∆Hydr of CaCl2 = ∆Hydr Ca2+ +∆Hydr Cl-
=-1562+(-364x2)
=-1562+-728
=-2290Kjmol-1✓
∆Hsol = ∆Hlaq+∆Hydr
∆Hlath = ∆Hsol-∆Hydr✓ ½
= -82.9 = (-2290)✓ ½
= -82.9+2290
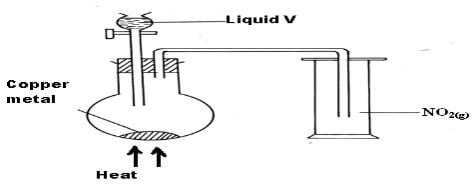
= +2207.1Kjmole-1 ✓ ½ (2mks) - The diagram below is used to prepare nitrogen (IV) oxide gas.
- Identify substance V (1mk)
- Concentrated Sulphuric(VI) acid//H2SO4(l) (1mk)
- Concentrated Sulphuric(VI) acid//H2SO4(l) (1mk)
- State and explain one precaution taken when carrying out the experiment. (2mks)
- The experiment should be done in a fume chamber or in open air✓1
- The gas (NO2) is poisonous✓1 (2mks)
- Identify substance V (1mk)
- Electrode potentials for the half cells are shown below. Use the information to answer the questions that follow.
Sn2+(aq)+2e- Sn(s) ; = -0.14V
Cu2+(aq)+2e- Cu(s) ; = -0.34V- Write the cell representation for the cell made up of two half cells. (1mk)
Sn(s) /Sn2+(aq) //Cu2+(aq) /Cu(s) (1mk) - Write the cell equation for the cell reaction. (1mk)
Sn(s)+Cu2+(aq)→Cu(s)+Sn2+(aq) (1mk) - Calculate the value for the cell. (1mk)
Eθcell = Eθ reduced Eθ oxidation
= +0.34 – ( -0.14)✓ ½
= +0.34++0.14
= +0.48v✓ ½ (1mk)
- Write the cell representation for the cell made up of two half cells. (1mk)
- State the function of each of the following in the solvay process of production of Sodium Carbonate.
- Coke (1mk)
- Produce heat energy to decompose CaCO3// Produce Carbon(iv)
Oxide when burnt in the kiln. (1mk)
- Produce heat energy to decompose CaCO3// Produce Carbon(iv)
- Cold water on the carbonation. (1mk)
- Cold water cools the carbonator (1mk)
- Ammonia a generator. (1mk)
- Recovers ammonia used in the initial stages(1mk)
- Coke (1mk)
-
- A student in form three was given two gases C2H6 and C2H4. He added acidified Potassium Manganate (VII) to each solution. State the observations the student made. (2mks)
- C2H6 did not have effect on acidified potassium manganate(VII)✓1 which C2H4 turned purple potassium manganate(VII) to colourless✓1 (2mks)
- State one use of C2H4.
- manufacture of plastics (any one ) (1mk)
- manufacture of ethanol
- used in ripening of fruits
- preparation of ethan – 1,2 –diol.
- A student in form three was given two gases C2H6 and C2H4. He added acidified Potassium Manganate (VII) to each solution. State the observations the student made. (2mks)
Download Chemistry Paper 1 Questions and Answers - Form 4 End Term 1 Exams 2021.
Tap Here to Download for 50/-
Get on WhatsApp for 50/-
Why download?
- ✔ To read offline at any time.
- ✔ To Print at your convenience
- ✔ Share Easily with Friends / Students