AGRICULTURE
Paper 2
Instructions to candidates.
- This paper consists of THREE sections A,B and C.
- Answer ALL questions in section A and B.
- Answer any TWO questions in Section C.

Questions
SECTION A (30 MARKS)
Answer all questions in this section
- State four characteristics of exotic dairy breeds. 2mks
- Differentiate between the following terms:- 2mks
- A steer and a bullock
- Boar and sow
- Name two tools used for dehorning 1mk
- Name two hormones that control milk let-down. 1mk
- State four signs of farrowing in pigs. 2mks
- Outline four management practices carried out while rearing a heifer. 2mks
- State two effects caused by keds in sheep. 1mk
- Outline four characteristics of an African wild bee. 2mks
- Name the breeding terms used to describe parturition in the following farm animals:- 2mks
- Cattle
- Goat
- Sheep
- Rabbi
- Name four routes through which the vaccines can be administered. 2mks
- State two abnormalities observed during egg candling. 1mk
- State four advantages of natural incubation. 2mks
- Outline four disease causing micro-organism 2mk
- State two factors that determine amount of water required by a dairy cow. 1mk
- Name two dual purpose sheep breeds. 1mk
- Name four parts found in a piggery unit. 2mks
- State four advantages of embryo transplant. 2mks
- Name four disorders caused by mineral imbalances in cattle. 2mks
- Outline two physiological body functions that indicate illness in livestock. 1mk
SECTION B (20MARKS)
Answer ALL questions in this sectionSECTION B (30 MARKS)
-
- Study the following diagrams and answer the questions that follows.
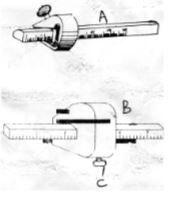
- Name the workshop tools marked A and B. (2 marks)
- Name the part of tool B marked C. (1 mark)
- Give one functional difference between tool A and B. (1mk)
- List down four maintenance of a wheel barrow. (2 marks)
-
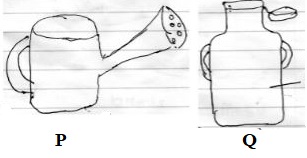
- Name the tool marked P & Q.
P _______________________ Q _________________ - Give two advantage of using the tool marked P. (2 marks)
- Name the tool marked P & Q.
- Study the following diagrams and answer the questions that follows.
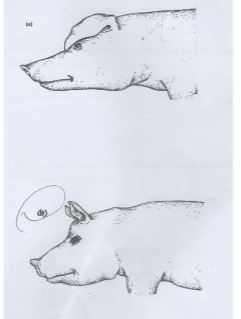
- Study the diagram of pigs shown below:
- Name the breeds of pigs marked a and b. (2 marks)
- Give two distinguishing features between (a) and (b) (2 marks)
- List down two routine management that should be carried on the young ones of a and b in the first one week (2 marks)
-
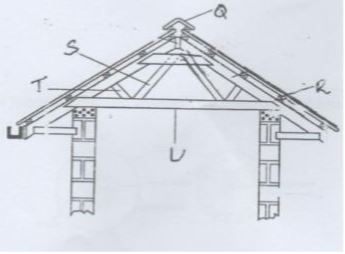
- The following diagram represents part of the roof for construction of a farm study and answer the following questions.
- Name the part of roof marked Q R S T U (5 marks)
- Name the four tools that are used in assembling the structure. (2 marks)
- State four routine management practices that are carried out in a crush. (2 marks)
- The following diagram represents part of the roof for construction of a farm study and answer the following questions.
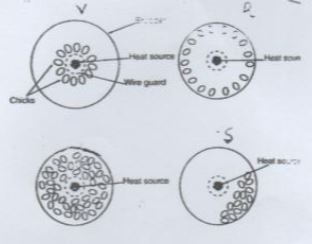
- The following diagram represent the behavior of chicks with heat variation.
-
- What does V, R & S represent? (3 marks)
- Which is the correct temperature? (1 mark)
- State two requirements in an artificial brooder. (3 marks)
-
- Name two systems of rearing poultry. (2 marks)
- State two factors that encourage egg eating in layers.
-
SECTION C (40MARKS)
Answer ANY TWO questions in this section
-
- Name two methods of incubation (2mks)
- Explain the condition necessary in an artificial incubation (8mks)
- Describe the management of layers from the point of lay (10mks)
-
- Outline the procedure for castrating a piglet surgically (5mks)
- Explain foot rot under the following subheadings
- Predisposing factors (5mks)
- Symptoms (5mks)
- Control (5mks)
-
- Give five functions of proteins in a cow (5mks)
- Name five factors affecting digestibility of roughage in livestock (5mks)
- Outline five advantages of a live fence (5mks)
- Give four non-chemical methods of controlling ticks (5mks)

Marking Scheme
- Physical characteristics of exotic breeds
- Straight top line
- Wedge/triangular shape
- Absence of hump
- Prominent milk veins
- Well set hindquarters and large teats
- Steer –young castrated male cattle Bullock –mature castrated male cattle
- dehorning tools
- dehorning wire or saw
- dehorning iron/ disbudding iron
- dehorning collodion
- Caustic potash stick
- Rubber ring and elastrator
- Has antibodies that help resist early disease infections
-
- Oxytocin
- Adrenalin
- Signs of farrowing
- Restlessness
- Loss of appetite
- Enlarge of the udder and teats
- Sow collects bedding and build a nest
- Enlargement of vulva
- Management practices of a heifer
- Disease and parasite control
- Vaccination
- feeding
- Deworming
- identification
- Dehorning
- Effects of keds
- Cause irritation
- damage of wool
- Retarded growth
- Anaemic conditions
- Characteristics of African wild bee
- Adapted to local weather conditions
- Highflying power hence fly for longer distances
- Active in search of food and water -Vicious if manhandled
- Resistant to diseases like Acarive and American foul brood disease
-
- Cattle-calving
- Goats-kidding
- Sheep- lambing
- Rabbits- kindling
- Routes for vaccination
- Nose
- Mouth
- Cloaca
- Skin
- Candling abnormalities
- Double yolk
- Broken egg shell
- Hair cracks
- Blood/ meat spots
- Advantages of natural incubation
- Low marginal cost
- Requires less skills
- Suitable for small scale farmers
- Les laborious since it does not involve egg turning
- disease causing micro-organism
- bacteria
- virus
- protozoan
- fungi
- Factors that determine amount of water taken by a dairy cow
- Animal requires more water during hot season due to sweating
- Type of feed eaten by the animal
- Level of production
- Weight of the animal or the body size
- Dual purpose breeds I sheep
- Corriedale
- Hampshire Down
- Romney Marsh
- Parts of a piggery
- Feed store
- record room
- Water trough /drinking nipples
- Running yard
- pig pens: gilt, boar, in
- pig, weaner, fattener pig pen
-
- increase in the number of offspring per female
- easier and more rapid exchange of genetic material between countries
- less transport of live animals, thereby reducing risks of disease transmission
- storage and expansion of rare genetic stock.
- Mineral disorders
- Milk fever
- Anaemia
- Paraketosis
- Oestomalacia
- Grass tetany/stagger/hypomagnecia
- Physiological body functions that indicate illness
- Abnormal appetite
- high /low body temperature
- Abnormal defecation
- High/low respiratory rate
- Abnormal colour of the urine/frequent urination
-
-
-
- A. marking gauge
- B. mortise gauge
- Marking gauge has one spur and hence inscribe one line
Mortise gauge has two spurs which give two marking line at the same time
-
- Maintenance of a wheelbarrow
- Greasing the wheel
- Changing the tyre when worn out
- Repairing the board when worn out
- Washing after use
-
- P – watering can Q – Milk churn
- Advantages of using P
- It spread water over a wide area
- It does to erode the soil
- It does not uproot the seeds
- P – watering can Q – Milk churn
-
-
-
- A - landrace
B -. large white
- A - landrace
-
- a has a straight snout while b has broad and slightly designed snout
- a has bong dropping ears over the face while b has upright ears
- a is white in color while b is white with blue spots
- management practices
- Clipping the teeth
- Blood / surgical castration
- Allowing the young ones to suckle the colostrums
- Weighing them
-
-
-
-
- Q – apex / ridge
- R – purlin
- S – Tie
- T – Strut
- U – Cross tie
-
- Cross cut saw
- Craw hammer
- Tenor saw
- Try square
- Wood chisel
-
-
- Spraying livestock against parasites
- When carrying out identification
- Vaccination
- Administering prophylactic drugs
- Treating sick animal
- Dehorning
- Pregnancy test
- Artificial insemination
- Taking body temperature
-
-
-
-
- V – cold condition
- R - Very hot condition
- S – Draught condition
- T
-
-
- There should be a litter inform of wood shaving
- There should be fresh air to allow gaseous exchange
- There should be a heat source and thermometer to moniter heat
-
-
- Free range
- Fold system
- Deep litter system
- Cage system
-
- Presence of broken or soft shelled eggs
- Bright light in the nest
- Idleness
- In adequate nest
-
-
-
-
- Lack of minerals such as calcium
- Natural incubation ,
- Artificial incubation
-
- Temperature 37.5c-39.4c
- Relative humidity
- Egg turning
- Ventilation (fresh air)
-
- feed them with layer mash
- provide adequate clean water
- ensure enough floor space
- carry out routine vaccination
- provide adequate litter
- hang green leaves in the house for exercise
- provide soluble sand or grit
- deworm regularly
- dust regularly to control external parasites
- isolate and treat sick bird
- clean waterers and feeders regularly
- provide adequate laying nests
- collect eggs regularly
- debeak perpetual cannibal
- cull poor layers
- remove broken eggs from the house
- dispose off dead birds
-
-
-
- Assemble all the required equipmentsi.e scalpel, forceps and iodine
- Wash your hands thoroughly before castration.
- Wear protective gloves
- Palpate the scrotal sac to locate the testicles
- Using the scalpel cut the scrotal sac
- Squeeze out the two testis and cut the epididymis
- Disinfect the cut using iodine solution
- Release the piglet after the castration
- Predisposing factors
- Injury on the hooves
- Long overgrown hooves
- Muddy surrounding
- Unhygienic condition in cows shed
- Age of the animal
- Symptoms
- Lameness
- Fever
- Lack of appetite
- Emaciations
- Swelling of foot
- Rotten smell from hooves
- Grazing while kneeling for the sheep.
- Control
- Isolate the infected animals
- Provide clean and dry surrounding
- Regular hoof trimming
- Treat the animals using the antibiotics
- Use of the foot baths in dipping the animals
-
-
-
- Growth ,repair and replacement of worn out body tissues
- Production of antibodies which protect the animal against diseases
- Production of products egmeat,milk and wool
- Production of certain hormones in the body
- Production of digestive enzymes to break food particles
-
- The quantity of feed already present in the digestive system of an animal
- Chemical composition of feed eg percentage of lignin or cellulose
- The form in which the feed is offered to the animal e.g crashed maize is more digestible than whole maize
- Species of the animal e.g digestibility of grass is higher in sheep than in pig
- Ration of energy to proteins. The higher the ratio the lower the digestibility
-
- The roots hold the soil firmly on the ground ,
- They are cheap and easy to establish
- Tall varieties act as windbreakers,
- They have an aesthetic value
- Some species have medicinal value
- Some species e.gLantana camaraare used as animal feed,
- They provide shade to livestock
-
- Handpicking the ticks from the livestock
- Burning the infested pasture
- Interfering with the tick environment
- Fencing off the pasture land as farm
- Starving the ticks to death
- Use of their natural enemies birds e.g (Egrets)
-
Download Agriculture Paper 2 Questions and Answers - Form 4 Opener Term 1 Exams 2022.
Tap Here to Download for 50/-
Get on WhatsApp for 50/-
Why download?
- ✔ To read offline at any time.
- ✔ To Print at your convenience
- ✔ Share Easily with Friends / Students