NSTRUCTIONS TO CANDIDATES
- Answer ALL the questions in the spaces provided in the question paper. You are NOT allowed to start working with the apparatus for the first 15 minutes of the 2¼ hours allowed for this paper. This time is to enable you to read the question paper and make sure you have all the chemicals and apparatus required.
- ALL working MUST be clearly shown where necessary
- Mathematical tables and electronic calculators may be used.
QUESTION 1
- Solution A; which is 0.02M acidified Potassium Manganate (VII).
- Solution B; which is a mixture of Sodium Oxalate, Na2C2O4 and oxalic acid, H2C2O4
You are required to:-
- Determine the solubility of Sodium Oxalate at room temperature.
- Determine the effect of temperature on the rate of reaction of Potassium Manganate (VII) and Oxalic acid.
Procedure I
- Fill the burette with solution B .Pipette 25.0cm3 of solution A into a clean conical flask. Heat the contents of the conical to about 700c.
- Titrate the hot solution against solution B to a colourless end point.
Record your results in table I below
- Repeat steps (i) and (ii) two more times to fill the table I below.
Keep the remaining solution B and A for procedure II
Table I
|
|
I |
II |
III |
|
Final burette reading (cm3) |
|
|
|
|
Initial burette reading (cm3) |
|
|
|
|
Volume of solution B used (cm3) |
|
|
|
(4 mks)
- Work out the average volume of solution B used. (1 mk)
-
- Calculate the number of moles of potassium manganate (vii) in 25.0 cm3 of solution A. (1 mk)
- Given the following reactions:-
Na2C2O4(aq) → 2Na+ (aq) + C2O42- (aq)
C2O 42-(aq) + 2H+(aq) → H2C2O4(aq)
2KMnO4(aq) + 5H2C2O4(aq)+ 3H2SO4(aq) → K2SO4(aq) + 2MnSO4(aq) + 8H2O(l) + 10CO2(g)- Calculate the number of moles of oxalic acid that reacted with Potassium Manganate (VII)(1 mk)
- Determine the mass of oxalic acid in the average volume used.
(H2C2O4. 2H2O) (H= 1.0, C= 12.0, O = 16.0). (1 mk)
- Given that solution B was prepared by dissolving 7.68 g of the mixture of oxalic acid and Sodium oxalate in 1000cm3 of a solution.
- Using your answer in b (II) to work out the mass of oxalic acid in 1000 cm3 of solution B.(1 mk)
- From your answer above, calculate the mass of sodium oxalate in 1000 cm3 of the mixture. (1 mk)
- Hence calculate the solubility of sodium oxalate in g/100g of water. (1mks)
Procedure II- Using a measuring cylinder, transfer 5.0 cm3 of solution A into a clean boiling tube.
- Label five test tubes 1-5
- Using the burette measure 5 cm3 of oxalic acid, solution B into five test tubes labelled 1 – 5
- Heat solution A until it reaches 800C.
- To the hot solution in (iii) add 5.0 cm3 of solution B from test tube 1 and start the stop watch at the same time. Stir the mixture using the thermometer and record time taken for the purple color to disappear.
- Repeat procedure (i) – (iv) at the temperatures shown using contents of test tubes 2, 3, 4 and 5 respectively.
Table II
Temperature before mixing 0°C 80 70 60 50 40 Time taken for purple colour to disappear in (sec)
1/time (sec−1) (5 mks)
- On the grid provided, plot a graph of 1/ t (y – axis) against temperature at which the purple colour disappear. (3 mks)
- From the graph:
- Determine the time taken for the purple colour to disappear at 47.5°C. (1mk)
- How does temperature change affect 1/t in this experiment? Explain. (1mk)
QUESTION TWO:
You are provided with 10 cm3 of solution C, which contains two cations and one anion. Carry out the tests below and record your observations and inferences in the spaces provided.
- Add 20 cm3of 2M aqueous sodium hydroxide to all of solution C provided. Shake well and filter the mixture into conical flask. Retain both the residue (on the filter paper) and filtrate.
Observations
Inferences
(1 mk)
(1 mk)
-
- To about 2cm3 of the filtrate, add 2M Nitric acid drop wise until in excess. (i.e. about 1cm3 of the acid).. Retain the mixture.
Divide the mixture in b (i) above into two portions.Observations
Inferences
(1 mk)
- To the first portion, add aqueous sodium hydroxide drop wise until in excess.
Observations
Inferences
(1 mk)
(1mk)
- To the second portion, add aqueous ammonia drop wise until in excess.
Observations
Inferences
(1 mk)
(1mk)
- To about 2cm3 of the filtrate, add 2M Nitric acid drop wise until in excess. (i.e. about 1cm3 of the acid).. Retain the mixture.
- To 2 cm3 of the filtrate, add 3 drops of Potassium iodide
Observations
Inferences
(1 mk)
(1mk)
- To 2 cm3 of the filtrate, add 3 drops of acidified Barium nitrate solutions.
Observations
Inferences
(1 mk)
(1mk)
- To the residue in (a), add 8 cm3 of dilute nitric acid and allow it to filter into a boiling tube.
To 2 cm3 of this filtrate, add aqueous ammonia drop wise until in excess.
Observations
Inferences
(1 mk)
(1mk)
QUESTION THREE:
You are provided with solid D. Place all the solid D in the boiling tube. Add 10 cm3 of distilled water and shake well. Divide the resulting mixture into four portionS
|
Observations |
Inferences |
|
(1 mk) |
(1mk) |
- To the first portion add 2 drops of universal indicator. Compare the result with the PH chart.
Observations
Inferences
(½ mk)
(½mk)
- To the second portion add two drops of Bromine water.
Observations
Inferences
(½ mk)
(½mk)
- To the third portion add drops of acidified potassium manganate (VII) solution A.
Observations
Inferences
(1 mk)
(1mk)
- To the fourth portion add, a little amount of NaHCO3
Observations
Inferences
(½ mk)
(½ mk)
CONFIDENTIAL
In addition to the normal fittings and apparatus in the laboratory, each candidate would need the following:
- 150 mls of solution A
- 200 mls of solution B.
- 25 mls pipette
- 50 ml burette
- Pipette filler
- Thermometer (-10°c – 110°c)
- Stop-watch
- At least six test-tubes
- Two boiling tubes
- 250ml Distilled water in a wash bottl
- Five labels
- 2 conical flasks
- 10 ml measuring cylinder
- 50 ml measuring cylinder
- 10cm3 of solution C
- 20cm3 of 2M NaOH
- Two filter paper
- 0.2g of solid D
- pH chart
- white tile
- filter funnel
- clamp and stand
Access to the following:-
- Source of heat
- Water bath
- 2M Nitric (V) Acid
- 2M Sodium Hydroxide
- 2M Ammonia solution
- 0.1M Potassium iodide
- 0.5M acidified Barium Nitrate (Acidified with Nitric (V) Acid)
- Bromine water
- Sodium hydrogen carbonate solid.
- Universal indicator solution.
Notes
- Solid D is maleic acid.
- Solution C is a mixture of Copper (II) Sulphate and Aluminium Sulphate. It is prepared by mixing two grams of each in water to make 20cm3 of solution. (Prepare as per the number of candidates.)
- Solution A is prepared by dissolving 3.16 g of KMnO4 and topping up to one litre.
- Solution B is prepared by mixing 5g of oxalic acid ad 2.86g of sodium oxalate and dissolve in one litre.
MARKING SCHEME
QUESTION I
PROCEDURE 1
Table 1 ………………………………………………………………………………………(5mks)
Distributed as follows:-
- Complete table ………………………………………………………………………(1 mk)
Conditions:- Complete table with 3 readings ………………………………………………………(1 mk)
- Incomplete table with 2 readings ……………………………………………………( ½ mk)
- Incomplete table with 1 reading ……………………………………………………(0 mk)
Penalties
Penalize ½ mk once for any of the following;- Wrong arithmetic
- Inverted table
- Reading beyond 50 cm3 unexplained.
- Titre values less than 1 cm3
- Use of decimals …………………………………………………………………(1 mk)
- It’s tied to the 1st and 2nd rows only.
- Accept 1 or 2 d.pls used consistently otherwise penalize fully.
- If the second decimal place is used, it must be a ‘zero’ or a ‘five’ otherwise penalize fully.
- Accuracy …………………………………………………………………………(1 mk)
Compare the candidate’s titre values to the school values and award as follows:-- If any within ±0.1 of S.V. …………………………………………………(1 mk
- If non within ±0.1 but within ±0.2 of S.V. award ………………………( ½ mk)
- If non is within ±0.2 of S.V. …………………………………………………(0 mk)
- Principles of averaging ……………………………………………………………(1 mk)
Conditions:- If 3 consistent values are averaged ……………………………………………(1 mm)
- If 3 titrations done, only two are consistent and averaged ………………...................(1 mk)
- If only two titrations done and are consistent and averaged …………………(1 mk)
- If 3 titrations are done, are consistent and only two are averaged………………(0 mk)
- If 3 titrations are done, all are consistent, yet averaged…………………………(0 mk)
Penalties:- Wrong arithmetic, error outside + 2 units in the 2ns d.pl. penalize ½ mk.
- If no working shown but answer given is correct penalize ½ mk.
- If answer is rounded off to the 1st d.pl. penalize ½ mk unless if it works out exactly.
- If no working is shown and the answer given is wrong, penalize fully.
- Final answer ……………………………………………………………………(1mk)
- Compare the school values with the correct titre average.
Conditions: - If within ±0.1 ……………………………………………………………………(1mk
- If answer is within ±0.2……………………………………………………(½ mk)
- If beyond±0.2, the award ‘0’ marks
- Compare the school values with the correct titre average.
N/B
- Final answer mark to the correct principles of averaging otherwise penalize fully.
Calculations; -
- Moles of mnO-4 = 25 x 0.02✓ ½
1000
= 0.0005✓ ½
N/B
No. of moles in b (i) must be exact as above, otherwise penalize fully. -
- Moles of oxalic acid
= 0.0005 x 5✓ ½
2
= 0.00125 moles✓½
OR
= 0.0005 x 2.5 ✓ ½
= 0.00125 moles ✓ ½ - Mass of oxalic= R.F.M. x Ans b(i) I
= 126 ×✓½ Ans b (i) I
= 0.1575g ✓½
- Moles of oxalic acid
- Moles of mnO-4 = 25 x 0.02✓ ½
-
- Mass of oxalic acid in 1000 cm3.
Ans b(ii) II x 1000 ✓ ½
Average titre
= Corr. Ans. ✓½ - Mass of Sodium Oxalate in 1000 cm3 = 7.68 – Ans c(i) ✓ ½
= Corr. Ans. ✓½ - Solubility of sodium oxalate
= Ans.c(ii) x 100✓½
1000
= Corr. Ans. ✓ ½
- Mass of oxalic acid in 1000 cm3.
Penalties
- All answers in b(i) – b(ii) must be exact as indicated, otherwise penalize fully.
- For c(i) – c (iii) Accept rounding off upto the 4th decimal place, otherwise penalize ½ mk on the answer.
- Units must be correct if they are shown otherwise penalize ½ mk on the answer.
- For c (iii) the units must be shown and be correct otherwise penalize ½ mk on the answer.
- Penalize fully for the strange values if they are used.
PROCEDURE II
Table II………………………………………………………………(5 mks)
Distributed as follows:-
- Complete table …………………………………………………………………(2 mks)
- Complete table with 5 readings…………………………………………………(2mks)
- Incomplete table with 3-4 readings award ……………………………………(1 mk)
- Incomplete table with 2………………………………………………(½ mk)
- Incomplete table with less than 2 readings ………………………………………(0 mk)
Conditions and penalties- Accept 1/t values to at least 3 d.pl. unless if it works out exactly to less than 3 d.pl.\
- Place a tick (✓ ) or cross x) on ½ values accordingly.
- Penalize ½ mk for each wrong 1/t values to a maximum of 1 mk.
- Decimals ………………………………………………………………………………1 mk
Accept time recorded in seconds as whole numbers, 1 dp or 2 d.p. recorded consistently, otherwise penalize fully. - Accuracy…………………………………………………………………………………..1 mk
- Tied to the time at temperature 800c.
- Compare the students time value at 800 to the school value at the same temperature and award as follows:
- Value with + 5 seconds of s.v………………………………………………………………1 mk
- Value not within + 5 seconds …………………………………………………………….(0 mk)
- Trend …………………………………………………………………………………………….(1 mk)
Accept time values increasing continuously for full credit, otherwise penalize fully. - GRAPH ……………………………………………………………………………………3 mks
Distributed as follows:-- Scale ………………………………………………………………………………1/2 mk
- The plots should cover at least ½ of the graph paper otherwise penalize fully.
- Scale intervals should be uniform otherwise penalize fully.
- Labeling ………………………………………………………………………………… (½ mk)
Accept for full credit if the axes are correctly labelled, otherwise penalize fully. - Plotting ………………………………………………………………………………(1 mk)
- Accept at least 3 -4 correct plots for ………………………………………………(1 mk)
- 2 correct readings plotted …………………………………………………………(½ mk)
- Shape of the curve …………………………………………………………………(1 mk)
Accept the shape of its curve with an increasing gradient for full credit, otherwise penalize fully.
- Scale ………………………………………………………………………………1/2 mk
-
-
- Showing✓ ½
- Stating with ✓½correct conversion. ½
-
- Increase in temp✓ ½ leads to an increase in rate of reaction.
- Explanation : with increase I in temp. reacting particles gain kinetic energy, more movement leading to more collisions.
-
QUESTION 2
|
OBSERVATIONS |
INFERENCES |
|||
|
a) Blue precipitate/ residue ✓ ½ |
NOTE: If the ions are mentioned all the 3 must be present. Otherwise penalize fully. |
|||
|
bi) White ppt. formed. ✓½ |
|
|
|
|
|
ii) White ppt. formed ✓ ½ |
Pb2, Al3+, Zn2+ present |
|||
|
iii) White ppt. formed ✓ ½ |
Al3+ or Pb2+ present ✓ 1 |
|||
|
c) No yellow ppt.✓ 1 |
Al3+ present ✓1 |
|||
|
d) White ppt. formed. ✓ 1 |
SO42- present ✓ 1 |
|||
|
e) Blue ppt.✓ ½ dissolves to form a deep blue solution. ✓ 1 |
Cu2+ confirmed. ✓ ½ |
|||
QUESTION 3.
|
OBSERVATIONS |
INFERENCES |
|
Solid dissolves to form a colourless solution ✓ ½ |
Solid K is a polar substance. ✓ ½ |
|
a) PH 4, 5, & 6.✓ ½ |
Weakly acidic.✓ ½ |
|
b) Yellow bromine water decolourised. ½ |
|
|
c) Purple KMnO4 decolourised. |
Reject; C≡ C, C = C |
|
d) Effervescence /fizzing / ✓ ½ bubbles of a colourless gas. |
R⎯COOH✓ ½ |
Download Chemistry Paper 3 Questions and Answers with Confidential - Form 4 End Term 2 Exams 2023.
Tap Here to Download for 50/-
Get on WhatsApp for 50/-
Why download?
- ✔ To read offline at any time.
- ✔ To Print at your convenience
- ✔ Share Easily with Friends / Students

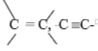 ✓ ½
✓ ½ 