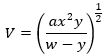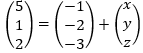- This paper consists of two sections: Section I and Section II.
- Answer all questions in section I and any five questions in Section II.
- Show all the steps in your calculations, giving your answers at each stage in the spaces below each question.
- Marks may be given for correct working even if the answer is wrong.
- KNEC Mathematical tables may be used.
Section I
- Paint x cost Ksh 50 per litre while paint y cost Ksh 70 per litre. In what proportion must x be mixed with y to produce a mixture costing Ksh 58 per litre? (3 marks)
- The first, third and seventh terms of an increasing arithmetic progression are the three consecutive terms of a G.P. If the first term of the A.P is 10, find the common difference of the AP. (3 marks)
- Given that the expression 9x2 − 30x + k is a perfect square, find the value of k. (2 marks)
- Make y the subject of the formula. (3 marks)
- Four quantities are such that P varies directly as the square of R and square root of Q and inversely as the fourth root of M. Given that P = 300 when R =2, Q = 9 and M = 16, find the value of Q when P = 2500, R = 5 and M = 81. (4 marks)
- Construct rectangle ABCD in which AB = 4 cm and BC = 3 cm. Inside the rectangle, construct the locus of point;
- L1 which is 2 cm from A. (2 marks)
- L2 which is equidistant from the line AB and AD. (1 mark)
- L3 which is 2 cm from the line AB. (1 mark)
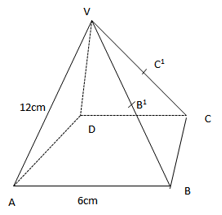
- The figure below shows a right pyramid VABCD with a square base of side 6cm.
VA =VB = VC = VD = 12cm
Calculate the height of the pyramid correct to 2 d.p (3 marks) -
- Expand and simplify (2 − 1/3 x)5 up to the term with x3. (1 mark)
- Use the expansion in (a) above to estimate the value of 1.935 (2 marks)
- A plot of land was valued at Sh. 500 000 at the start of 2004. It appreciated by 20% during the year 2004. Thereafter every year it appreciated by 10% of its previous year’s value. Find.
- The value of the land at the start of 2005. (2 marks)
- The value of the land at the end of 2007. (2 marks)
- Solve the equation:
2 cos 4x = −1 for 0 ≤ x ≤ 180° (2 marks) - The time in New York (42°N,74°W) is 1200h while the local time in Rome is 1744h. Find the distance between the two towns in kilometres if they lie on the parallel of latitude. Take the radius of the earth to be 6370 km and π=22/7. (3 marks)
- A bag contains blue green and red pens of the same type in the ration 8:2:5 respectively. A pen is picked at random without replacement and its colour noted. Determine the probability that the first pen picked is
- Blue (1 mark)
- Either green or red. (2 marks)
- A point P has the coordinates (1,2,3) if PQ = 5i + j + 2k, find:-
- The coordinates of point Q (2 marks)
- The modulus of PQ (1 mark)
- Triangle PQR is mapped onto triangle P'Q'R' by a transformation whose matrix is
. If the area of the triangle P'Q'R' is 40 sq. units, find the area of the triangle PQR. (3 marks)
- The table below shows values of the function y = x2 + 3
x 0 0.5 1 1.5 2 2.5 3 3.5 4 4.5 5 5.5 6 y 3 4 5.25 7 12 15.25 19 28 39 - Complete the table. (1 mark)
- Use the mid ordinate rule with six ordinates to estimate the area bounded by
y = x2 + 3, the y – axis, the x – axis and the line x = 6. (2 marks)
- Solve for x in the equation
Log (5x + 75) − 2 log 3 = log (2x − 9) +1 (4 marks)
SECTION II 50 Marks
Answer any five questions ONLY in this section.
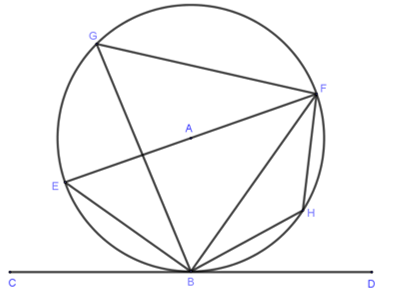
- In the figure below, EF is diameter of the circle BEGFH centre A. CBD is a tangent to the circle at B, BH = FH and angle BFE =38°
Giving reasons determine the following angles- Angle EBC (2 marks)
- Angle EGF (2 marks)
- Angle FBH (2 marks)
- Angle HEB (2 marks)
- Angle HAF (2 marks)
- John bought 3 brands of tea A, B and C. The cost price of the three brands were Sh. 25, Sh. 30 and Sh. 45 per kilogram respectively. He mixed the three brands in the ratio 5:2:1 respectively. After selling the mixture, he made a profit of 20%.
- How much profit did he make per kilogram of the mixture? (3 marks)
- After one year the cost price of each brand was increased by 12%.
- How much did he sell one kilogram of the mixture to make a profit of 20%? Give your answer to the nearest 5 cents. (4 marks)
- What would have been the percentage profit if he sold one kilogram of the mixture as Sh. 40.25. (3 marks)
- Mr. Njagi, a civil servant earns a basic salary of Sh 38,300 house allowance of Sh 12,000 and medical allowance of Sh. 3600 every month. He claims a family relief of Sh 1172 and insurance relief of 3% of the premiums paid. Using tax table below
Taxable income (£) p.a Tax Ksh/£ 1 - 8800 2 8801 -16800 3 16801 - 24800 5 24801 - 36800 7 36801 - 48800 9 Over 48800 10 - Calculate Mr. Njagi’s annual taxable income in Kenya pounds per annum (2 marks)
- Tax due every month from Mr. Njagi to 2 decimal places (5 marks)
- If further deductions are made every month from his salary
- WCPS of 2 % of basic salary
- Life insurance premium of Sh. 4600
- Sacco loan repayment Sh. 14200
Calculate- Total deductions (1 mark)
- His net pay per month (2 marks)
- A successive transformation is represented by LUV and it maps an object ABC whose coordinates are A (2, 1) B (4, 1) and C (3, 4) onto its successive images.
- On the grid provided, draw the object. (1 mark)
- Determine the coordinates of the successive images hence plot them on the same axes provided above given that
(6 marks)
- Determine a single matrix that maps the object onto the final image. (2 marks)
- Calculate the area of the object ABC. (1 mark)
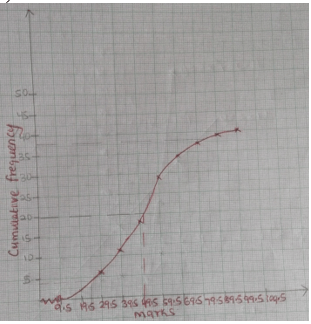
- The table below shows the marks scored by 40 form 4 students in a mathematics test.
Mark 10 -19 20 - 29 30 - 39 40 - 49 50 - 59 60 - 69 70 - 79 80 - 89 90 - 99 Frequency 2 4 5 7 10 6 3 2 1 - Using an assumed mean score of 55, calculate the mean of the data. (3 marks)
- Calculate the lower quartile. (2 marks)
- On the grid provided draw the cumulative frequency curve to represent the above distribution. (3 marks)
- From the graph estimate;
- The 5th decile. (1 mark)
- Range of marks of the middle 80% of the students. (1 mark)
-
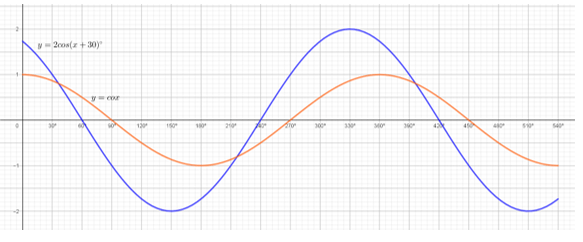
- Complete the table below, leaving all your values correct to 2 d.p. for the functions y = cos x and y = 2 cos (x + 30)° (2 marks)
x° 0° 60° 120° 180° 240° 300° 360° 420° 480° 540° Cos x 1.00 − 1.00 0,50 2cos(x+30)° 1.73 −1.73 0.00 - For the function y = 2cos(x+30)°
State:- The period (1 mark)
- Phase angle (1 mark)
- On the same axes draw the waves of the functions y = cos x and y = 2cos(x+30)° for 0 ≤ x ≤ 540 . Use the scale 1cm rep 300 horizontally and 2 cm rep 1 unit vertically. (4 marks)
- Use your graph above to solve the inequality 2cos(x +30) ≤ cos x. (2 marks)
- Complete the table below, leaving all your values correct to 2 d.p. for the functions y = cos x and y = 2 cos (x + 30)° (2 marks)
- The velocity V metres per second of a particle projected into space is given by the formula V = 4t2 − 2t + 9, where t is time in seconds. Determine;
- Acceleration of the particle when t = 2 seconds. (3 marks)
- The value of t when acceleration is minimum. (2 marks)
- The velocity when the acceleration is minimum. (2 marks)
- The distance covered between the 1st and 2nd seconds. (3 marks)
-
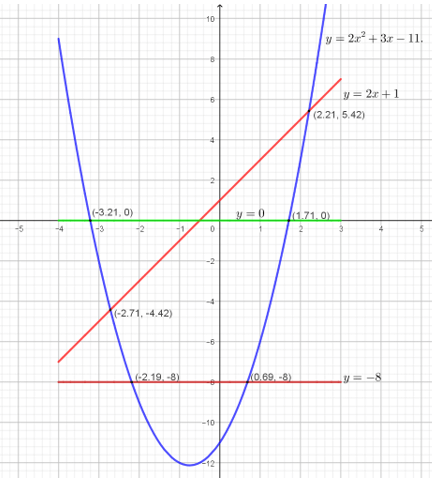
- Complete the tale below for the equation y = 2x2 + 3x − 11 (2 marks)
x −4 −3 −2 −1 0 1 2 3 2x2 32 8 0 2 8 18 3x −12 −6 0 6 9 −11 −11 −11 −11 −11 −11 −11 −11 −11 y 9 −9 −11 16 - On the grid provided, draw the graph of y = 2x2 + 3x − 11. (3 marks)
- On the same axes draw the graph of y = 2x+1 (2 marks)
- Use your graph to solve the quadratic equations;
- 2x2 + 3x − 11 = 0 (1 mark)
- 2x2 + x −12 = 0 (1 mark)
- 2x2 + 3x − 3 = 0 (1 mark)
- Complete the tale below for the equation y = 2x2 + 3x − 11 (2 marks)
MARKING SCHEME
| No. | Working | Comment | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 1. | 50x+70y = 58 x+y
50+70y = 58x+58y 8x = 12y
x:y = 3:2
|
M1 M1 A1 |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 2. | 10+6d = 10+2d 10+2d 10 (10+2d)2 = 10(10+6d)
100 + 40d + 4d2 = 100 + 60d
4d2 = 20d
4d = 20
d = 5
|
M1 M1 A1 |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 3. |
(-30/2)2 = 9k
900/4 = 9k
36k = 900
k = 25
|
M1 A1 |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 4. |
V2 = (ax2y)
(W-y) V2W − V2y = ax2y
V2W = V2y + ax2y
y = V2W
V2 + ax2 |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 5. | P = KR2√Q ∜M K = 300×∜16 = 300×2 = 50
22 × √9 4×3 P = 50R2√Q
∜M 2500 = 50×52×√Q
∜81 Q =
|
M1 M1 M1A1 |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 6. | 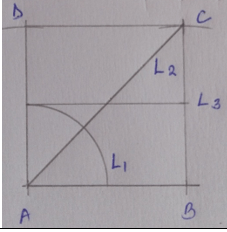 |
B1 – rectangle
B1 – L1
B1 --L2
B1 --L3
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 7. | AC = √(62 + 62) = √72
Ax = ½AC = 3√2
Vx2 = 122 − (3√2)2 = 144 − 18 = 126
Vx = √126 = 11.22 cm
|
M1 M1 A1 |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 8. |
|
B1 M1 |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 9. |
|
M1A1 M1 A1 |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 10. | cos4x = −0.5
Cosine is negative in 2nd and 3rd quadrants
4x = 120°,240°,480°,600°
x = 30°,60°,120°,150°
|
M1 A1 |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 11. | Time difference = 5 hr 44 mins = 344 mins
Latitude difference = 344/15 = 22.93°
Rome (42°N,44.7°W)
Distance = 22.93 × 2 × 22 × 6370 × cos42
360 7 =1895.3 km
|
M1 M1 A1 |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 12. |
|
B1 M1A1 |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 13. |
|
M1 A1 B1 |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 14. |
det = −4-− 1 = −5
ASF = |det| = 5
Area of triangle PQR = 1/5 × 40 = 8 sq.units
|
M1 M1A1 |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 15. |
a)
b)A = 1(3.25 + 5.25 + 9.25 + 15.25 + 23.25 + 33.25)
=89.5 sq units
|
B1 – all values |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 16. |
log (5x+75) − log 9 = log(2x−9) + log 10
(5x+75) = 10(2x−9)
9 5x+75 = 90(2x−9)
180x − 5x = 810 + 75
x = 885/75 = 11 4/5
|
M1 M1 M1 A1 |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 17. |
|
B1 B1 B1 B1 B1 B1 B1 B1 B1 B1 |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 18. |
|
M1 M1 A1 M1 M1 M1A1 M1 M1A1 |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 19. |
|
M1A1 M1 M1 M1 M1A1 M1 M1 A1 |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 20. |  |
B1 B1 B1 B1 B1 B1 B1 M1A1 B1 |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 21. |
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 22. |
a)
b)
c) |
B1 – for cosx
B1 – for 2 cos(x+30)
B1 B1 B1 |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 23. |
|
M1 M1A1 M1 A1 M1 A1 M1 M1 A1 |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 24. |
|
B1 B1 B1 B1 |
Download Mathematics Paper 2 Questions and Answers - Form 4 Term 3 Opener Exams 2023.
Tap Here to Download for 50/-
Get on WhatsApp for 50/-
Why download?
- ✔ To read offline at any time.
- ✔ To Print at your convenience
- ✔ Share Easily with Friends / Students