Displaying items by tag: revision notes
Natural and Built Environments - CBC Grade 5 Social Studies Revision Notes
Natural Environment
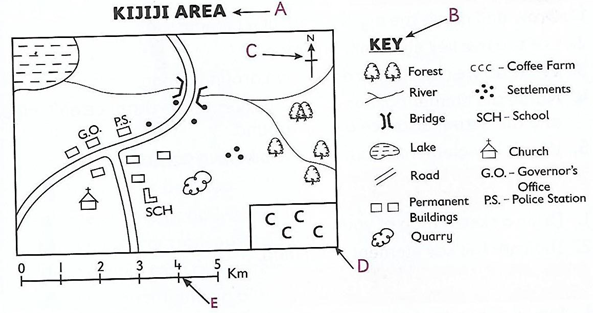
Elements of a Map
A map is a drawing that represents the earth or part of it on a flat surface.
The key elements of a map include:
- Title - is the name given to a map. It is usually written at the top or the bottom of the map
- Frame - is the border that is drawn around a map
- Key/legend - contains the symbols and signs that have been used on a map. It shows what the signs and symbols represent. Symbols are small pictures, drawings or letters. They represent real objects on a map.
- Scale - shows the relationship between the distance on the map and the real distance on the ground.
- Compass - shows the direction of places on a map. A good map should have the five key elements.
Importance of Maps include:
- Locating the directions and position of places
- Identifying the direction and position of places
- Identifying our neighbours
- Locating various physical features
- Guiding tourists to their destination.
Map Interpretation
This referred to giving meaning to the features and symbols used on a map.
We use the key elements of a map to read and interpret maps. Symbols and signs helps us to identify the different features, areas and activities on a map e.g.
The presence of a quarry shows that mining is taking place in the area.
- Market - shows that trading activities is taking place in the area
- Game reserved - shows the presence of wild animals.
- A sawmill - shows that timber processing takes place in the area.
- Scrubland - shows that the area is dry.
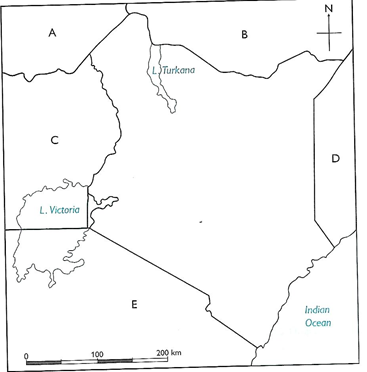
Location, Position and Size of Kenya
Position of Kenya in relation to her neighbours
Kenya has several neighbouring countries. Kenya is surrounded by:
- Tanzania is to the south
- Uganda is to the west
- Ethiopia is to the north
- Somalia is to the east
- South Sudan is to the north west
- Indian ocean to the south east.
Ways in which Kenya maintains good relations with her neighbours.
- Trade - Kenya exports and imports goods from her neighbours e.g. Bananas from Uganda.
- Games and sports - kenya participates in games such as football, with her neighbours.
- Ambassadors - Kenya has an ambassador in each of her neighbouring countries. These ambassadors represent Kenya in these countries.
- Free movement of people from Kenya to her neighbours and from her neighbours to Kenya.
- Use of common language - Kenya shares a common language (Kiswahili) with some of her neighbours, for example, Tanzania. This helps to maintain good relations.
The size of Kenya
Kenya covers an area of about 582, 646km square.
It is about 850 km from East to West and about 1025 km from North to South.
Main Physical Features In Kenya.
Physical features are natural things found on the earth's surface.
The physical features are divided into two main categories i.e. relief and drainage features.
Relief features are physical features that are seen above the surface of the earth.
Relief features include:
- Mountains
- Hills
- Plains
- Valleys
- Plateaus
Drainage features are physical features that are associated with water. They include
- Swamps
- Rivers
- Lakes
- Oceans
- Dams
Weather and Climate in Kenya
Weather is the condition of the atmosphere of a place at a particular time. The weather of a place changes from time to time.
Elements of weather are the conditions of the atmosphere, they include:
- Rainfall - rain, supports the growth of vegetation.
- Wind - warm and moist winds bring rain
- Temperature - the hotness or coldness of a place
- Cloud cover - heavy cloud cover brings heavy rainfall
The weather conditions of a place can be observed, measured and recorded for a period of time. The recorded observations are used to calculate the average weather conditions of that place.
Climate - refers to the average weather conditions of a particular place over a long period of time. Climate can be described as wet, dry, hot, cold, warm or cool.
The characteristics of climatic regions in Kenya are:
- Modified equatorial climate
- Covers the coastal areas near Indian ocean and Lake Victoria.
- Experiences heavy convectional rainfall 1000 mm - 1500 mm.
- It has two rainy seasons - long and short rains.
- The region receives convectional rainfall. This type of rainfall is formed by warm air which rises from the surface of the Indian Ocean or Lake Victoria.
- Rainfall is well distributed throughout the year
- Rainfall is affected by the winds blowing from the ocean to the coast.
- Temperature range between 25°C - 30°C
- The region is mainly hot and wet.
- Modified tropical climate
- Covers the Kenya highlands and parts of the Rift valley
- The area receives rainfall throughout the year
- Rainfall is between 1200 mm - 2000 mm
- Low temperatures ranging between 18°C - 21°C
- The region is mainly cools and wet
- It is modified by the high altitude.
- Mountain climate
- The region covers areas with high mountains like Mount Kenya and Mount Elgon.
- Experiences cool and wet conditions
- The region is cold and wet
- Temperatures range from 0°C - 15°C
- High rainfall of between 1250mm and 2200 mm.
- The region is characterized by two sides, the leeward side and the windward side.
- The windward side receives relief rainfall and the leeward side is drier.
- The climate is mainly influenced by altitude.
- Tropical Climate
- The region covers Kwale, taita and Narok areas
- Experiences high temperatures
- It has one rainy season
- In some parts the dry season lasts up to five months
- Rainfall of not above 1000mm per year.
- Semi-desert climate
- Covers areas in Northern, North-eastern and some parts of Eastern Kenya.
- Temperatures are high during the day and low at night.
- Experiences high temperatures which may rise to 38°C
- Mainly hot and dry
- Low rainfall of below 250mm per year
- The sky is clear.
- Desert Climate
- Experienced in Chalbi and Taru deserts
- Most of the months are dry causing droughts
- High temperatures throughout the year - average 38°C
- Clear skies
- High daytime temperatures and low night temperatures.
The Built Environments
These are structures/environments that remind us of our history or where we have come from.
They include:
- Fort Jesus
- Tom mboya monument
- National museum of Kenya
- Jomo Kenyatta monument
- Nyayo monument
Importance of Historic Built Environments
- They remind us and teach us about our culture
- They are sources of employment for people who work there
- They attract tourists who bring money to our country
- They are sources of information for learning
- They allow us interact with other people when we visit them
- They are used as recreational areas for relaxation
Caring for Historic built Environments in our country
- Repair the destroyed parts of historic built environments
- Handle items in the historic environments with care
- Develop conservation messages and place them at historic built environments
- Educate other people on the importance of historic built environment.
Computing Devices - Grade 5 Science and Technology Revision Notes
- Handling data - word processing
Handling data - word processing
- A word processor is computer software used to compose, format, edit and print documents. Examples include:
- Microsoft word
- Open office .org Writer
- Word pad
- Word perfect
- Open office writer
Creating a word document
- Open Microsoft word 2010 by searching through windows “Microsoft word”
- Launch Microsoft word 2010 by double clicking.
- On the landing page (immediate page) click blank and Microsoft word 2010 document will open
Components of A word document
- They include:
- Title bar
- Ribbon
- Horizontal scroll bar
- Status bar
- Typing area
- Vertical scroll bar
Keying information (typing)
- Create a word document
- Key in the information by doing the following:
- Type on the keyboard to create text
- Use the mouse to move the insertion point (blinking line - indicates where you can enter or key in text on the page) to a specific place in your document. Click the location in the text where you want to place it.
- Press the spacebar on the keyboard to add space after a word or in between text.
- Press enter on the keyboard to move the insertion point to the next paragraph.
Editing a word document.
- Click and drag across the text you want to select.
- You can select any amount of text with this method, from a single character to your entire document.
- Here are some other ways to select text you’ll find useful:
- Press and hold down the Shift key, and move the insertion point either with your mouse or the arrow keys to select text.
- Double-click a single word to select it.
- Press the Ctrl key and click in a sentence to select it.
- Triple-click in a paragraph, or double-click in the left margin next to a paragraph, to select it.
- Click in the left margin to select an entire line, or click and drag in the left margin to select multiple lines.
- Press Ctrl + A to select everything in the document
Edit Text
- Select the text you want to replace, then start typing the new text.
Changing font size
- Create a word document
- Type a short essay on good citizenship
- Select the text you want to edit
- left - click or long press the drop-down arrow next to the font size box on the home tab.
- Move your cursor over the various font sizes
- Left-click the font size you want to use. The font size will change on the document.
Changing font style
- Use the text you typed on good citizenship. Select the text you want to edit.
- Left-click the drop-down arrow next to the font style box on the home tab.
- Move your cursor over the various font styles
- Left-click the font style you want to use. The font style will change in the document.
Changing font colour
- Use the text you typed on good citizenship. Select the text you want to edit
- Left-click the drop down arrow next to the font colour box on the home tab.
- Move your cursor over the various font colours.
- Left-click the font colour you want to use. The font colour will change in the document.
Changing text into bold, italic and underlining
- Open an existing word document or start a new document and type your text.
- Change some of the text that you have already types to a different font
- Select the text that you wish to edit or change for the formatting.
- To change the selected font to bold, click B in the formatting ribbon at the top of the document
- To change the selected font to italics, click I in the formatting ribbon at the top of the document
- To change the selected so that it is underlined, click U in the formatting ribbon at the top of the document
Changing Text Case
- Select the text you want to edit
- Click the change case command in the font group on the Home Tab.
- Select one of the case options from the list.
- Write down the different options on the case list.
Changing text alignment
- Open an existing word document or start a new document and type your text. The default layout is left align, where text will be aligned to the left margin of the document.
- To change the layout of your text, select the text that you wish to change using the mouse.
- To center the selected text, click on
icon in the formatting ribbon at the top of the document.
- To right align the selected text, click on
icon in the formatting ribbon at the top of the document.
- To left align the selected text, click on
icon in the formatting ribbon at the top of the document.
- To justify text so that it is aligned both right and left, click on
icon in the formatting ribbon at the top of the document.
Inserting Text
- Create a new word document
- Type some text into the document
- Move your mouse to the location where you want text to appear in the document.
- Left-click the mouse. The insertion point appears.
- Type the text you want to appear.
Deleting text
- Create a new word document
- Type some text into the document
- Place your cursor next to the text you want to delete
- Press the backspace key on your keyboard to delete text to the left of the cursor.
- Press the Delete key on your keyboard to delete text to the right of the cursor.
Selecting text
- Create a new word documentb.
- Type some text into the document
- Place the insertion point next to the text you want to select.
- Left-click your mouse. While holding it down, drag your mouse over the text to select it.
- Release the mouse button. You have selected the text
- A highlighted box will appear over the selected text.
Copying and pasting
- Create a new word document
- Type some text into the document
- Select the text you want to copy
- Click the copy command on the Home Tab.
- Place the insertion point where you want the text to appear.
- Click the paste common on the Home tab. The text will appear.
Saving a document
- When saving the document for the first time:
- Choose file. Then save from the menu bar. The save as dialog box appears
- Another option is clicking the save button on the standard toolbar.
 Then save as dialog box appears.
Then save as dialog box appears. - There as a last option of choose file, the save as from the menu bar. The save as dialog box appears.
- Before clicking save button in the save as dialog box, first name your file with a descriptive name that you will remember.
- To name you file, once the save as dialog box is open, the current file name appears highlighted, ready for you to change it.
- Type a short descriptive name in the file name box. File names can include spaces and capital letters but not special
characters. - If you do not choose a file name, word program will assign a file name for you. It assigns the first line of text in your document. If you save a blank document, the file will be saved as Doc1, Doc2 and so forth.
- After you name your file, choose a file location. This will keep your files orderly and easy to find. My documents is the default file location in word program.
- To save a file in My documents, make sure My documents is the current file location in making sure the left column and save in drop-down box state my documents.
- Click save button.
NOTE
- Save - is used when saving file for the first time, it doesn't matter if you choose to save it using save or save as.both commands open the save as dialog box.
- Save as - lets you save an existing file under a new name, allowing you to create a new file.
Retrieving documents
- Open a Microsoft word
- Click file in the upper left-hand corner of the screen.
- Click open
- An open dialog box will pop up. From this, find your way to the file in which your document is saved. Files that are on your computer can be located by clicking browse.
- Once you have located your document and clicked on it to select it, its name will be shown in the file name box at the
bottom of the dialog box. - Click open. The document will then be opened.
Safety when using computer devices
- Turn on the computer correctly. Follow the right process.
- Respect yourself by not giving your name and password.
- Prepare early for each task. Using time wisely
- Respect others by sharing computer devices.
- Report problems with the computer devices. It saves time and energy.
- Take responsibility for your actions.
- Log off and leave the computer station ready for the next person to use.
Human Beings - Grade 5 Science and Technology Revision Notes
- Sense Organs
- Skeleton and Muscles
- Types of Muscles
- Breathing system
Sense Organs
- Human have five basic senses, namely sigh, smell, taste and feeling or touch
- The organs associated with each senses send informations to the brain to help us understand and perceive the world around us.
Functions of sense organs
- These organs include;
- Tongue - for taste
- Ears for hearing
- Nose for smell
- Skin – for feeling or touch
Cares for various sense organs
- Bathing daily with soap and clean water
- Applying oil to keep the skin moist
- Brushing tongue and teeth when cleaning the mouth
- Keeping the nose clean by using the handkerchief.
- Clean the ears using cotton buds.
- By no putting sharp objects into the nose or ears.
Skeleton and Muscles
Parts of a human skeleton
- The human body is a complex design made of various system and structures
- The parts that make the human skeleton are the skull, the rib cage and the smooth muscles.
Functions of human skeleton
- This is the structure made of bones, cartilages and connective tissues; it serves the following functions;
- The skull protects the brain from injuries
- Backbone provides support to the body and helps the body to remain upright
- It also makes the person flexible.
- It is also known as human spine
- It is made up of 33 bones called the vertebrae . these bones stretches from the neck to the pelvis and protect the spinal cord.
- The backbone provides support to the body,allowing the body to stand , bend or twist.
- The backbone also protect the brain and the body
- The rib cage protects the heart and the lungs
- It is made up of curved bones called lungs
- It is found in the chest area
- It protects a person’s internal organs from damage and gives structures to the test.
- Most human beings have 12 pairs of rib bones
- The limbs bones support the weight of the human body.
- They also help a person to move
- There are 30 bones in each lower limps(leg) these are,
- Femur – is a single bon of the thigh, its rounded head connects with the hip socket to form the hip join. There are 30 bones in each upper limb (arm)
- The humerus is the single bone of the upper arm and the ulna and the radius are the paired bones of the forearms. Other bones include:
- Tibia
- Fibula
- Seven tarsal bones
- Five metarsal bones and 14 phalanges
Types of Muscles
- It is a tissue that functions as a source of power
- It is a bundle of fibrous tissue in a human or animal body that can contract, producing movements in the body maintaining the position of the part of the body.
- The human body has three types of muscles
- Cardiac muscles – these muscles make up the mass of the heart and are responsible for the heart’s rhythmic contractions.
- Skeleton muscles - they connect to and control the motions of the human skeleton. They are found between the bones and use tendons to connect to bones. They are controlled voluntarily and are concerned with movement, posture and balance of human body.
- Smooth muscles – are control involuntarily. They are found in the walls of blood vessels ,urinary bladder , the intestine and stomach
Functions of Skeleton Muscles (Voluntary muscles)
- support and help the body move
- Control the body temperature
- Keep the body upright
- Protect the organs of the body
Breathing system
Parts of human breathing system
- System – the human body is like a factory that is made of many parts. These parts work in groups called system
- The breathing system has both visible parts such as the nose, internal parts such as the trachea, lungs and diaphragm. These parts work together to enable human being to breathe.
Functions of breathing system
- Breathing – this is the mechanism of taking air and blowing out air.\
- Air blow from outside into the nose through nostril. The nose has tiny hairs that clean the air by trapping dusts. At the back of the nose these is membrane that produces mucus which makes the air moist, warm and clean.
- The trachea is called windpipe, it receives air from the nose,it has C- shaped ring that keep it strong and open. The walls of the windpipe have mucus and tiny hairs that filter air and keep it clean. The trachea acts as a passage for air from the nose into the lungs
- A human being has two lungs
- Membrane that produces mucus, which makes the air moist, warm and clean.
- The trachea is also called the windpipe. It receives air from the nose. It has C-shaped rings that keep it strong and open. The walls of the windpipe have mucus and tiny hairs that filter the air and keep it clean. The trachea acts as passage for air, from the nose into the lungs
- A human being has two lungs located inside the chest. The lungs are a pair of airfilled organs. The lungs take in the oxygen in the air and take out carbon dioxide that the body does not need.
- The diaphragm is located under the lungs. It controls breathing. It separates the chest from the abdomen. It helps to fill the lungs with air when breathing in.
- It also helps to take out air when breathing out.
- Breathing is essential for the living process of human beings to continue.
Diseases that affect the human breathing system
- The human breathing system is affected by many diseases. They include:
Tuberculosis (TB)
- Is a disease that affects the breathing system. It mainly affects the lungs. TB is caused by bacteria. It spreads from one person to another
through sneezing, coughing or spitting.
- Night sweats
- Coughing up blood
- Unintentional weight loss
- Coughing that last for three or more weeks
- Chest pain or pain when breathing or coughing
- Staying dust free, well-ventilated rooms
- Vaccinating infants
- Covering the mouth when sneezing
- Wearing a mask in public if you are already infected
- An infected person should finish his or her entire course of medication
Pneumonia
- Is caused by germs such as bacteria and viruses. It can also be called fungi.
Signs and symptoms of Pneumonia
- Chest pains when breathing or coughing
- Cough that may produce mucus
- Sweating and shaking
- Nausea, vomiting or diarrhoea
- Fatigue
- Shortness of breath
- Fever
- Vaccination against pneumonia
- Keeping immune system strong
- Practicing good hygiene
- Not smoking
Colds
- Colds are caused by a virus. The virus affects the nose and the throat.
- Children under the age of six years are at greatest risk of getting it.
- Running or stuffy nose
- Congestion in the nose
- Sneezing
- Mild fever and generally feeling unwell
- Sore throat and cough
- Mildhead.
- Wash your hands thoroughly with soap and clean water.
- Disinfecting items
- Covering the mouth when coughing or sneezing
- Avoid sharing utensils
Asthma
- Is a disease that narrows and swells the airways in the lungs, producing extra mucus. This makes breathing difficult. Being exposed to substances such as pollen, dust mites, infections such as common cold, cold air, pollutants such as smoke, strong emotions and some kinds of medications can cause asthma.
- Shortness of breath
- Chest pains
- A whistling sound when breathing out
- Getting vaccinated for influenza na pneumonia
- Identifying and avoiding asthma triggers
- Monitoring your breathing
- Treating early attacks
- Taking medication as prescribed by the doctor.
- Carefully following your medication plan.
Coughs
- Can be caused by smoke exposure, infections, asthma and presence of mucus in the throat.
- Frequent throat clearing and sore throat
- Wheezing and shortness of breath
- Persistent coughing
- Running nose
- Hoarse voice
- Avoiding smoke particles and dusty places
- Avoiding smoking
- Drinking a lot of water
- Avoiding unhealthy surroundings and crowded places
Influenza
- It is commonly called the flu. It is caused by a virus. The flu is transmitted through the air in droplets when someone with the infection coughs, sneezes or talks.
Signs and symptoms of influenza
- A high fever
- Chills and sweats
- Dry and persistent cough
- Nose congestions
- Aching muscles
- Headache
- Fatigue and weakness
- Sore throat
- Yearly flu vacation for any person who is six months old and above.
- Thorough and frequent hand-washing
- Covering your mouth and nose when sneezing or coughing
- Avoiding crowds during peak flu season.
Coronavirus Disease 2019 (COVID - 19)
- COVID-19 is a disease of the breathing system. It is caused by a virus, known as coronavirus. The virus looks like a round ball with
a spiky crown. - When an infected person sneezes or coughs, tiny droplets are spread into the air. These droplets contain the virus.
- One can get infected if he or she touches a surface with the virus. The virus enters a person’s system if one touches their nose, eyes or mouth
Signs and symptoms of COVID-19
- Fever
- Dry cough
- Sore throat
- Headache
- Tiredness
- Loss of taste or smell
- Wash your hands well frequently for at least 20 seconds withsoap and running water. If soap and water are not available, use an alcohol- based hand sanitizer.
- Use a handkerchief or tissue when sneezing or coughing. If you do not have one, sneeze or cough into your elbow.
- Avoid touching your eyes, nose and mouth
- Clean and disinfect surfaces and objects.
- During an outbreak, stay home. If you need to go out put on the right face mask
- During an outbreak, keep social distance of about 2 metres from other people
- If you feel sick, tell your parents or guardians. You will be taken to see a doctor. You will be put on treatment.
Making Work Easier - Class 6 Science Revision Notes
Force
Force is a pull, push or lift.
It is measured in Newtons (N)
A moving object is said to be in motion while an object at rest is said to be stationary.
Force is measured by the use of a spring balance.
Examples of Force
- Force of gravity (weight)
- Frictional force
- Magnetic force
- Inertial force
Effects of Force
- Makes an object to start moving
- Stops a moving object
- Change direction of a moving object
- Speeds up a moving object
- Change the shape of an object.
Properties of Matter - Class 6 Science Revision Notes
Composition of Air
Air is a mixture of gases
Air mainly consists of :
- Gases
- Water vapour
- Dust particles
Components of Air
Uses of Oxygen
- Breathing ( Respiration)
- Germination
- Burning ( Combustion)
- Rusting.
Uses of Carbon Dioxide
- Photosynthesis
- Preserve soft drinks
- To make fire extinguishers
- Used in baking
- Used in making dry ice.
Uses of Nitrogen
- Used by plants to make proteins
- Used to preserve semen
- It is taken in through the roots as nitrates. Leguminous plants are able to convert nitrogen to nitrates.
Uses of Inert Gases
- They include Argon, Neon, Helium and Krypton
- Used in electric bulbs and light tubes
- Used in coloured advertising signboards.
- Used in hot air balloons.
Energy - Class 6 Science Revision Notes
Light
How light travels
- Light travels in a straight line away from the source.
- Light travels to all directions from the source.
Transparent Materials
They are materials that allow all light to pass through them and one can see through them clearly.
Examples: Clear glass, Clear water, air
Uses of transparent materials
- They are used in making:
- Car windscreens
- Spectacles
- Window panes
- Lamps
- Glass walls
Translucent Materials
They are materials that allow only little light to pass through them.
Examples:
- Frosted glass
- Tracing paper
- Oiled or waxed paper
Uses of translucent materials
They are used in making:
- Skylights
- Toilet and bathroom window panes
- Ambulance windows.
Opaque Materials
They are materials that do not allow any light to pass through them.
When light hits an opaque materials a shadow is formed.
Examples:
- Wood
- Stone
- Metals
Reflection of Light
Reflection is the bouncing back of light when Materials that reflect light are called reflectors.
Reflection happens when light hits a smooth shinny surface.
Types of Reflection
- Regular reflection
- Irregular (diffused)
Characteristics of the image in a plane mirror
- The image is upright
- The image is behind the mirror
- The image is the same size as the object
- The image is laterally inverted.
Refraction of Light
It is the process in which light bends or changes direction when it moves from one medium to another. (air to water)
Effects of Refraction
- Objects appear bent or broken
- Objects appear bigger
- Swimming pool appear shallower
Making a Rainbow
A rainbow is formed by the refraction of light. To be formed raindrops and sunshine is required.
The process of splitting light into seven different colours is known as dispersion.
A group of seven colours in the rainbow is known as spectrum
Food and Nutrition - Class 6 Science Revision Notes
Food Preservation
It is the process of storing and handling food properly so as to stop or slow down its spoilage.
Reason for Preserving Food
- To reduce food wastage
- To prevent it from being spoilt
- For easy transport
- To make food available when out of season.
Methods of Food Preservation
Food preservation is classified into;
- Traditional methods
- Modern methods
Traditional Methods
They include;
- Smoking- forms a coat
- Drying- reduce moisture
- Salting- reduce moisture
- Use of honey- prevents oxygen
- Use of ash- reduce moisture
Modern Methods
- Canning-killing germs and preventing oxygen
- Refrigeration- low temperature
- Freezing- low temperature
Drying is both traditional modern method of preserving food. It is also the cheapest method of food preservation.
Soil - Class 6 Science Revision Notes
Soil Erosion
Soil erosion is the carrying away of the top soil from one place to another.
Agents of Soil Erosion
They are things that carry soil from one place to another. They include;
- Water
- wind
Factors that Influence Soil Erosion
- Slope of land
- Type of soil
- Vegetation cover
- Amount of rainfall
- Human activities
Types of Soil Erosion
- Splash erosion
- Sheet erosion
- Rill erosion
- Gulley erosion
Splash Erosion
It occurs when raindrops fall on bare loose soil.
It can be controlled by;
- Planting cover crops
- mulching
Sheet Erosion
It occurs when water or wind carries away thin uniform layers of the topsoil.
It is not easily noticed
It occurs on gentle slopes.
Best controlled by;
- Planting cover crops
- Planting trees
- Landslides are caused by sheet erosion
Rill Erosion
It occurs when water flows down a slope and make small shallow channels. The channels are known as rills. it is common on gentle sloping areas.
It can be controlled by;
- Terracing
- Contour farming
- Strip cropping
Gulley Erosion
It occurs when water make deep channels , they are known as gulleys.
Gulley erosion leads to the formation of V-shaped or U-shaped channels.
It is common on bare hill slopes.
It can be controlled by;
- Gabions
- Porous dams
- Check dams
Water - Class 6 Science Revision Notes
Waterborne Diseases
They are diseases that are spread through contaminated water. They include:
- Cholera
- Typhoid
- Bilharzia.
Cholera
It is caused by bacteria. it can cause death within 24 hours if not treated. It causes death through dehydration.
Signs and Symptoms
- Violent diarrhoea (rice water).
- Vomiting.
- Severe abdominal pains
- Wrinkled skin due to dehydration.
- Sunken eyeballs
Typhoid
It mainly affects the intestines. It is also known as typhoid fever.
Signs and Symptoms
- Pain in the joints and muscles
- High fever
- Abdominal pains
- Skin rash
Bilharzia
It is caused by bilharzia worms or blood flukes. It is carried by water snails.
The disease mainly affect the bladder and intestines
Bilharzia worms enter the body through the skin.
Signs and Symptoms
- Blood in urine and stool
- Coughing may occur
- Abdominal pain
- Swimmers itch
- Fever
Animals - Class 6 Science Revision Notes
Animal Feeds
They are classified into:
- Pastures
- Fodder
- Conserved feeds
- Commercial feeds
Pasture
They are grasses and legumes that animals feed on directly.
They are classified into;
Pure stand ; only consist of either grass or legumes only
Mixed stand ; consists of both grass and legumes
Grass
Examples of grass include;
- Kikuyu grass
- Star grass
- Giant sataria
- Rhodes grass
Legumes
There are 4 main legumes used as pasture, they include;
- Clover
- Lucerne
- Glycine
- Desmodium.
Fodder
They are crops that are hervestered or cut then given to the animals. examples;
- Napier grass
- Guatemala grass
- Potato vines
- Maize stalks
- Kales
- Sugar beet
Conserved Feeds
They are animal feeds that are preserved in a special way to be used in future.
They are divided into two;
- Hay
- sillage
Hay
- It is cut and preserved by drying
- It is stored in bales
Silage
- It is harvested when it is about to flower. It is preserved by fermentation.
- It is stored when still green or in the succulent state.
- It is stored in silos
- The molasses is added to speed up fermentation.
Methods of Grazing
- Rotational grazing
- Zero grazing
- Herding
Rotational Grazing
They include:
- Tethering
- Paddocking
- Strip grazing
Tethering
The animal is tied to a peg or post using a rope
The rope allows the animal to graze within a restricted area.
It is practised were few animals are kept
Paddocking
The land is divided into small areas known as paddocks using a permanent fence
A watering point is usually provided in each paddock.
Strip grazing
The animals are enclosed in a small portion of the pasture using a temporary fence.
An electric fence is usually used.
Zero Grazing
It is also known as stall feeding
The animals are confined in a permanent structure (shed)
The shed should have feeding area, watering area, sleeping area and milking area.
Herding
It is a type of grazing where animals are allowed to graze
freely on large areas of land.