BIOLOGY
FORM 4
END TERM EXAMS
TERM 1 2021
PAPER 3
(PRACTICAL)
TIME 2¼ hrs
INSTRUCTIONS
- Answer all questions in this paper.
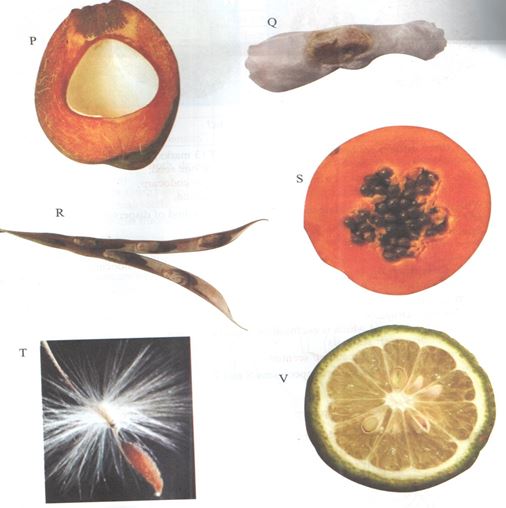
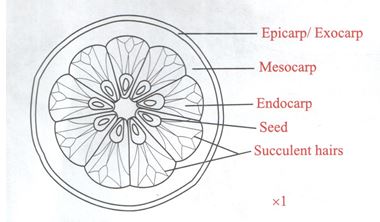
- The photographs below show specimens of different types of fruits. Examine them.
- State four differences between specimens P and R. (4mks)
- State the types of gynoecium and placentation of specimens P, S and V. (3mks)
Specimen Gynoecium Placentation P S V - In the table below name the mode of dispersal for each specimen and the features that adapt the specimen its mode of dispersal. (6mks)
Specimen Mode of dispersal Adaptive features P Q R S T V - Draw and label a plan diagram of specimen V. (2mks)
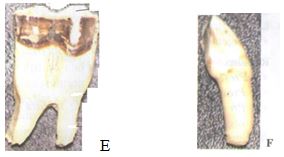
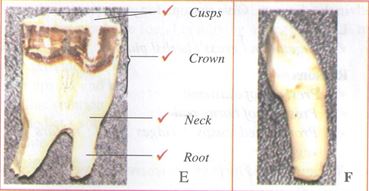
- Below are photographs of specimens labeled E and F which were obtained from the same animal. Examine them.
- With reasons, identify E and F. (2mks)
- Specimen E
Identity
Reason - Specimen F
Identity
Reason
- Specimen E
- On photograph E, label any four parts of the specimen. (4mks)
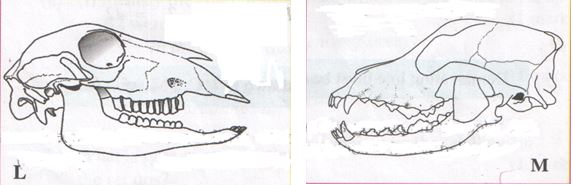
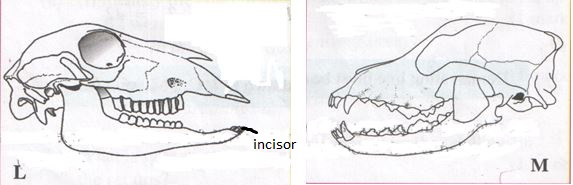
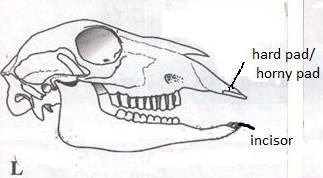
- Examine the following diagrams labeled L and M.
- Suggest the diet of each of the animals whose skulls are shown in the diagram. Give reasons for your answer. (4mks)
- Skull L
Diet
Reason - Skull M
Diet
Reason
- Skull L
- Label the incisor tooth in diagram L. (1mk)
- Write the dental formula of the animals whose skulls are shown in diagrams L and M. (2mks)
- Identify the photograph of the skull from which specimens labeled E and F could have been obtained. (1mk)
Specimen E
Specimen F - On the appropriate photograph, label the position where the horny pad would be found in a living animal. (1mk)
- Suggest the diet of each of the animals whose skulls are shown in the diagram. Give reasons for your answer. (4mks)
- With reasons, identify E and F. (2mks)
- You are provided with the following:
- Food substance labeled Q
- Iodine solution
- Sodium Hydroxide solution.
- Benedicts solution.
- 4 test tubes
- A dropper
- Source of heat.
- Using the reagents provided, carry out various food tests on substance Q and record your observation in the table below.
(4 ½ mks)Food substance Procedure Observation Conclusion - With reasons, identify the organ of a plant in specimen H photograph. (1mk)
Identity
Reasons: (3mks) - After peeling off the epidermis of lower surface and the upper surface, the number of stomata was determined using a microscope at a high power and recorded in the table below.
Average number of stomata in the field of view. Lower epidermis Upper epidermis 30 10 - Account for the average number of stomata on upper and lower side of specimen H.
- Upper epidermis. (1mk)
- Lower epidermis. (1 mk)
- With reasons, identify the organ of a plant in specimen H photograph. (1mk)
- Using the reagents provided, carry out various food tests on substance Q and record your observation in the table below.
CONFIDENTIAL
- Solution Q (Glucose, egg)
- Iodine solution
- Sodium Hydroxide solution
- Copper sulphate solution.
- Benedicts solutions
- 4 test tubes
- A dropper
- Source of heat.

MARKING SCHEME
- The photographs below show specimens of different types of fruits. Examine them.
- State four differences between specimens P and R. (4mks)
- P has one seed while R has several seeds.
- P has a thick pericarp while R has a thin pericarp.
- P has a distinct epicarp, mesocarp, and endocarp while in R the three layers are distinct.
- P has no suture lines while R has suture lines.
- P has a hollow seed while the seeds of R are not hollow.
- State the types of gynoecium and placentation of specimens P, S and V. (3mks)
Specimen Gynoecium Placentation P monocarpous basal. S syncarpous pariental V syncarpous axile/central - In the table below name the mode of dispersal for each specimen and the features that adapt the specimen its mode of dispersal. (6mks)
Specimen Mode of dispersal Adaptive features P Water Mesocarp has fibres/airspaces for buoyancy Q Wind Has a wing-like membranous structure/membranous extension. R Self dispersal by explosive mechanism Has lines of weakness/sutures on the wall S Animals Is fleshy/succulent T Wind Has hair-like projections/parachute of hairs. V Animals Is fleshy/succulent - Draw and label a plan diagram of specimen V. (2mks)
- State four differences between specimens P and R. (4mks)
- Below are photographs of specimens labeled E and F which were obtained from the same animal. Examine them.
- With reasons, identify E and F. (2mks)
- Specimen E
Identity - molar tooth
Reason - Has two roots/ has cusps - Specimen F
Identity - canine
Reason - Sharp/ has one root
- Specimen E
- On photograph E, label any four parts of the specimen. (4mks)
Ans - Examine the following diagrams labeled L and M.
Ans- Suggest the diet of each of the animals whose skulls are shown in the diagram. Give reasons for your answer. (4mks)
- Skull L
Diet - Vegetation/grass/herbs/plants
Reason - Presence of diastema/ Presence of horny pad/Pronounced cusps/ridges in the molars for grinding vegetation.
(no canines and incisors is incorrect: Reason –negative answer.) - Skull M
Diet - Flesh/meat/bones/feeds on flesh/carnivore
Reason - Pronounced long curved sharp/pointed canines for grasping/gripping/tearing prey.
Carnassials teeth for cutting and crushing bone.
- Skull L
- Label the incisor tooth in diagram L. (1mk)
- Write the dental formula of the animals whose skulls are shown in diagrams L and M. (2mks)
L (2) I 0 C 0 PM 3 M 3 = 32
. 3 1 3 3M (2) I 3 C 1 PM 4 M 2 = 42
. 3 1 3 3
(Demarcating line must be shown in I,C, PM,M.) - Identify the photograph of the skull from which specimens labeled E and F could have been obtained. (1mk)
Specimen E
Specimen F - On the appropriate photograph, label the position where the horny pad would be found in a living animal. (1mk)
- Suggest the diet of each of the animals whose skulls are shown in the diagram. Give reasons for your answer. (4mks)
- With reasons, identify E and F. (2mks)
- You are provided with the following:
- Food substance labeled Q
- Iodine solution
- Sodium Hydroxide solution.
- Benedicts solution.
- 4 test tubes
- A dropper
- Source of heat.
- Using the reagents provided, carry out various food tests on substance Q and record your observation in the table below.
(4 ½ mks)Food substance Procedure Observation Conclusion Starch To 1cm3 of solution M3 on a white tile, add 2 drops of iodine solution. Yellow-brown colour of iodine remains Starch absent Proteins To 2cm3 of solution M3 add 3cm3 dulute NaOH solution, shake and add CuSO4 solution drop wise. Violet – purple colour observed Proteins present Reducing sugars To 2cm3 of solution M3 add an equal amount of Benedict’s solution and boil the mixture Green-yellow-orange-brown-red colour precipitate formed Reducing sugar present. - With reasons, identify the organ of a plant in specimen H photograph. (1mk)
Identity - Leaf
Reasons: (3mks)- Broad leaf blade/lamina
- Presence of leaf petiole
- Mid rib and veins present.
- After peeling off the epidermis of lower surface and the upper surface, the number of stomata was determined using a microscope at a high power and recorded in the table below.
Average number of stomata in the field of view. Lower epidermis Upper epidermis 30 10 - Account for the average number of stomata on upper and lower side of specimen H.
- Upper epidermis. (1mk)
- Fewer/less stomata to reduce water loss/transpiration/evaporation because they are exposed to direct sunlight.
- Lower epidermis. (1 mk)
- More stomata to increase rate of gaseous exchange or more stomata away from direct sunlight reduce rate of transpiration.
- Upper epidermis. (1mk)
- With reasons, identify the organ of a plant in specimen H photograph. (1mk)
- Using the reagents provided, carry out various food tests on substance Q and record your observation in the table below.
Download Biology Paper 3 Questions and Answers - Form 4 End Term 1 Exams 2021.
Tap Here to Download for 50/-
Get on WhatsApp for 50/-
Why download?
- ✔ To read offline at any time.
- ✔ To Print at your convenience
- ✔ Share Easily with Friends / Students