232/3
PHYSICS
Paper 3
INSTRUCTIONS TO CANDIDATES
- Write your name and index number in the spaces provided.
- Mathematical tables and non-programmable calculators may be used.
- This paper consists of three questions.
- Attempt all the questions in the spaces provided.
- ALL working MUST be clearly shown.

QUESTIONS
QUESTION ONE
Apparatus
- stopwatch
- 250ml beaker
- Rubber bun
- Thermometer
- Bunsen burner
- Tripod
- Gauze
- Retort stand and clamp
- Hot water
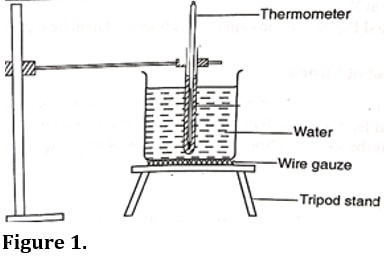
Procedure
-
- Measure and record the ambient temperature, TA =…………………..0C (1 mark)
- Fill an empty beaker with exactly 150ml of hot water (check the side scale of the beaker)
- Set up the apparatus as shown in figure 2. Ensure the thermometer is about 2cm above the bottom of the beaker.
- Record the initial highest temperature of water TH=………………….. 0C (1 mark)
- Start the stopwatch and time for every 2.0 minutes the temperature T of water. Record the temperature in Table below for 20 minutes
(6 mark)Time(t) in minutes 2 4 6 8 10 12 14 16 18 20 Temperature (T) oC (T − TA)oC Log10 (T − TA) 2 d.p - Plot a graph of Log10(T − TA) against time (Hint: Log10(T − TA) should start at 1.0) (5 mark)
- From the graph determine:
- The Slope S (3marks)
- The cooling constant , K of water given S=-0.4343K (2 mark)
- Given that the specific heat capacity of water is 4.2J/g/0C determine the heat lost when the water cools to the temperature of the surrounding ( 2 mark)

QUESTION TWO
PART A
You are provided with the following apparatus :
- One resistor labelled R = 4.0Ω
- A wire labelled W mounted on milliameter scale
- A wire labelled S mounted on a milliameter scale
- One dry cell and a cell holder
- One jockey
- one centre zero galvanometer
- Eight connecting wires, four with crocodile clips at both ends
- A micrometer screw gauge
- A switch
Proceed as follows
- Determine the average diameter D, of the wire labelled W using the micrometer screws gauge provided.
D1 = ............................................................ mm (½ mark)
D2 = ............................................................. mm (½ mark)
D = D1 + D2 (in cm)
2 (1 mark) - Set up the apparatus as shown in the circuit diagram in figure 2
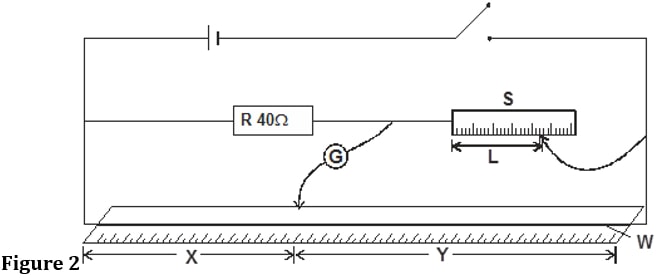
Use the crocodile clips to fix length L, of wire labelled S at 50cm from the end connected to the galvanometer G - Close the switch and use the jockey to touch one end of the wire W, and then the other end. The deflections on the galvanometer should be in opposite directions, if not check the circuit. Adjust the positions of the jockey along the wire W until there is no deflection in the galvanometer. Record the value of x and y.
x = ..................................................................... cm (½ mark)
y = .................................................................... cm (½ mark) - Record for other values of L in table below
(4 marks)L(cm) 45 40 35 30 25 30 X (cm) Y(cm) y/x (3 d.p) -
- Plot a graph of y/x (y-axis) against L. (5 marks)

- Determine the slope, m of the graph. (2 marks)
- Given that K = 100D, determine the value of K. (2 marks)
- Plot a graph of y/x (y-axis) against L. (5 marks)
PART B
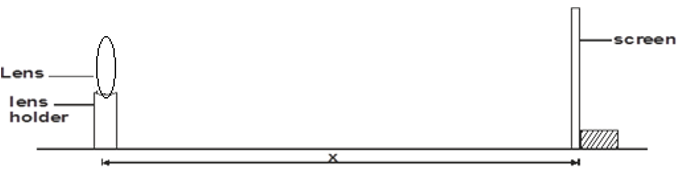
You are provided with a lens P a lens holder a white screen and half metre rule.
Procedure
- Set the apparatus as shown in figure below. Focus a sharp image of a distant object on the screen (e.g window frame). The object should be 10cm away. The object should be at least 10cm away.
Measure the distance x in cm between the lens and the screen at which a sharp image is obtained repeat this two times, using different objects and record your readings in the table below
(2 marks)Object Distance X, (cm) 1 2 - Calculate the average value of x (1 mark)
- What is the physical significance of the result obtained in (iii) above? (1 mark)

Marking Scheme
QUESTION ONE
Procedure
-
- Measure and record the ambient temperature, TA =…………24………..0C (1 mark)
- Fill an empty beaker with exactly 150ml of hot water (check the side scale of the beaker)
- Set up the apparatus as shown in figure 1. Ensure the thermometer is about 2cm above the bottom of the beaker.
- Record the initial highest temperature of water TH=………83………….. 0C (1 mark)
- Start the stopwatch and time for every 2.0 minutes the temperature T of water. Record the temperature in Table 2 for 20 minutes
(6 mark)Time(t) in minutes 2 4 6 8 10 12 14 16 18 20 Temperature (T) oC 72 71 67 63 60 58 56 54 52 51 (T − TA)oC 48 47 43 39 36 34 32 30 28 27 Log10 (T − TA) 2 d.p 1.68 1.67 1.63 1.59 1.56 1.53 1.51 1.48 1.45 1.43 - Plot a graph of Log10(T-TA) against time (Hint: Log10(T-TA) should start at 1.0) (5 mark)
- From the graph determine:
- The Slope S (3marks)
G =Δy/Δx = (1.65 − 1.45)/(4 − 18)
= − 0.01429/min - The cooling constant , K of water given S=-0.4343K (2 mark)
− 0.01429 = − 0.4343 K
K = 0.03289
- The Slope S (3marks)
- Given that the specific heat capacity of water is 4.2J/g/0C determine the heat lost when the water cools to the temperature of the surrounding ( 2 mark)
H = mcΔθ
m = 150 cm3 × 1 g/cm3
= 150g
H = 0.15 × 4200 × 59
= 37, 170 J

QUESTION TWO
PART A
You are provided with the following apparatus :
- One resistor labelled R = 4.0Ω
- A wire labelled W mounted on milliameter scale
- A wire labelled S mounted on a milliameter scale
- One dry cell and a cell holder
- One jockey
- one centre zero galvanometer
- Eight connecting wires, four with crocodile clips at both ends
- A micrometer screw gauge
- A switch
Proceed as follows
- Determine the average diameter D, of the wire labelled W using the micrometer screws gauge provided.
D1 = ....................0.30................................... mm (½ mark)
D2 = ....................0.30................................... mm (½ mark)D = D1 + D2 (in cm)
2
0.30 + 0.30 = 0.30 mm = 0.03 cm
2 - Set up the apparatus as shown in the circuit diagram in figure below
Use the crocodile clips to fix length L, of wire labelled S at 50cm from the end connected to the galvanometer G - Close the switch and use the jockey to touch one end of the wire W, and then the other end. The deflections on the galvanometer should be in opposite directions, if not check the circuit. Adjust the positions of the jockey along the wire W until there is no deflection in the galvanometer. Record the value of x and y.
x = ............................88.3.............................. cm (½ mark)
y = ............................11.7................................. cm (½ mark) - Record for other values of L in table 3 below
(4 marks)L(cm) 45 40 35 30 25 30 X (cm) 92.6 93.5 94.5 95.0 96.0 96.5 Y(cm) 7.4 6.5 5.5 5.0 4.0 3.5 y/x (3 d.p) 0.080 0.070 0.058 0.053 0.042 0.036 -
- Plot a graph of y/x (y-axis) against L. (5 marks)
- Determine the slope, m of the graph. (2 marks)
G =Δy = (8− 0) × 10−2 = 0.08
Δx (45 − 0) 45
= 1.778 × 10−3 /cm - Given that K = m D2, determine the value of K. (2 marks)
K = 100 × 0.30/10
= 30 mm
PART B
You are provided with a lens P a lens holder a white screen and half metre rule.
Procedure
- Set the apparatus as shown in figure 4 Focus a sharp image of a distant object on the screen (e.g window frame). The object should be 10cm away. The object should be at least 10cm away.
Measure the distance x in cm between the lens and the screen at which a sharp image is obtained repeat this two times, using different objects and record your readings in table 4 below
Table 4
(2 marks)Object Distance X, (cm) 1 10.0 2 10.0 - Calculate the average value of x (1 mark)
10 +10 = 10 cm
2 - What is the physical significance of the result obtained in (iii) above? (1 mark)
Focal length

CONFIDENTIAL
QUESTION ONE
- stopwatch
- 250ml beaker
- Rubber bung
- Thermometer
- 150 ml of boiling water
- Tripod
- Gauze
- Retort stand and clamp
- Hot water
QUESTION 2
PART A
- One resistor labelled R = 40Ω
- A wire labelled W mounted on millimetre scale (32 gauge)
- A wire labelled S mounted on a millimetre scale (28 gauge)
- One dry cell and a cell holder
- One jockey
- One centre zero galvanometer
- Eight connecting wires, four with crocodile clips at both ends
- A micrometer screw gauge
- A switch
PART B
- Lens and a lens holder (f=10cm)
- Half metre rule
- White screen
Download Physics Paper 3 Questions and Answers - Kassu Jet Joint Exams 2020/2021.
Tap Here to Download for 50/-
Get on WhatsApp for 50/-
Why download?
- ✔ To read offline at any time.
- ✔ To Print at your convenience
- ✔ Share Easily with Friends / Students